|
Provinces Of Scotland
The Provinces of Scotland were the primary subdivisions of the early Kingdom of Alba, first recorded in the 10th century and probably developing from earlier Pictish territories. Provinces were led by a '' mormaer'', the leader of the most powerful provincial kin-group, and had military, fiscal and judicial functions. Their high degree of local autonomy made them important regional powerbases for competing claimants to the throne of Alba. Provinces declined in importance during the late 12th and early 13th centuries as expanding royal power saw feudal landholding rather than local kinship established as the dominant basis of secular authority. The power of ''mormaers'' became increasingly focused on their earldom, the territory that they controlled directly, rather than their leadership of the broader provincial community, and large provincial lordships were established that often rivalled earldoms in size and were granted to loyal supporters of the king. Local justice and admin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
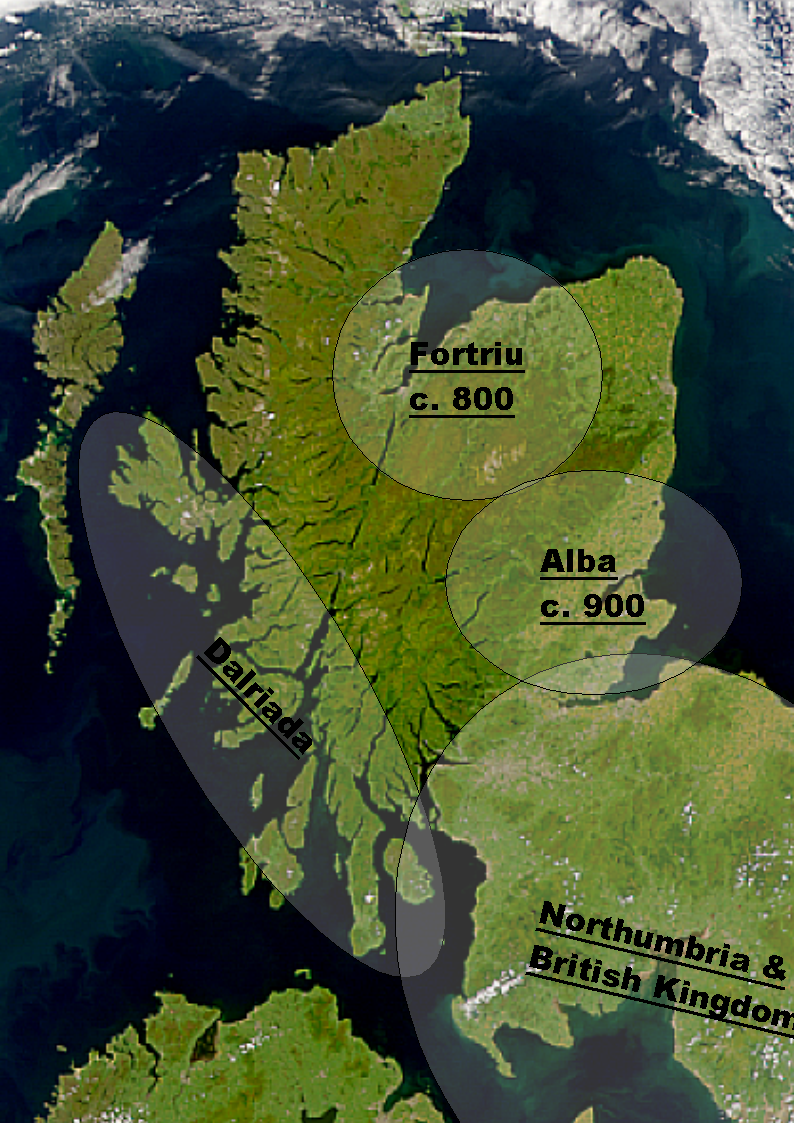
Kingdom Of Alba
The Kingdom of Alba ( la, Scotia; sga, Alba) was the Kingdom of Scotland between the deaths of Donald II in 900 and of Alexander III in 1286. The latter's death led indirectly to an invasion of Scotland by Edward I of England in 1296 and the First War of Scottish Independence. Alba included Dalriada, but not large parts of the present day Scottish Lowlands, which were then divided between Strathclyde and Northumbria as far north as the Firth of Forth. Fortriu, a Pictish kingdom in the north, was added to Alba in the tenth century. Until the early 13th century, Moray was not considered part of Alba, which was seen as extending only between the Firth of Forth and the River Spey. The name of Alba is one of convenience, as throughout this period both the ruling and lower classes of the Kingdom were predominantly Pictish-Gaels, later Pictish-Gaels and Scoto-Normans. This differs markedly from the period of the House of Stuart, beginning in 1371, in which the ruling classe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Moray
Moray ( mga, Muréb; la-x-medieval, Moravia; non, Mýræfi) was a province within the area of modern-day Scotland, that may at times up to the 12th century have operated as an independent kingdom or as a power base for competing claimants to the Kingdom of Alba. It covered a much larger territory than the modern council area of Moray, extending approximately from the River Spey in the east to the River Beauly in the north, and encompassing Badenoch, Lochaber and Glenelg in the south and west. Moray emerged in the 10th century as a successor to the dominant Pictish kingdom of Fortriu. The status of its rulers was ambiguous: being described in some sources as ''mormaers'', in others as Kings of Moray, and in others as Kings of Alba. The ruling kin-group of Moray, sometimes called the House of Moray, attained the throne of Alba between 1040 and 1058 in the person of Mac Bethad mac Findláich (Shakespeare's Macbeth) and his stepson Lulach. After Lulach was killed and succeed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrick, Scotland
Carrick (Irish Gaelic) is a former ''comital'' district of Scotland which today forms part of South Ayrshire. History The district of Carrick originally formed part of the 11th- to 12th-century Kingdom of Galloway, whose lords ruled it until 1186, when it was granted to Duncan, son of Gilbert of Galloway. He became the first to hold the Earldom of Carrick. His son Neil became the second Earl, but he had no male heir - accordingly, his daughter, Margaret (also known as Marjorie of Carrick) inherited and became Countess of Carrick. Upon her death in 1292 the earldom passed to her son Robert de Bruce, later to become King Robert I of Scotland (). Carrick saw some involvement in the Scottish wars of independence under the said Robert the Bruce, which culminated in his victory over the English at Bannockburn (1314). It witnessed much inter-family feuding during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, with various branches of the powerful Kennedys contending for land and hon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lennox
The Lennox ( gd, Leamhnachd, ) is a region of Scotland centred on The Vale of Leven, including its great loch: Loch Lomond. The Gaelic name of the river is ''Leamhn'', meaning ''the smooth stream'', which anglicises to ''Leven'' (as Gaelic ''mh'' is spirantised). The surrounding area is ''the field of the smooth stream'' - ''Leamhnachd'' in Gaelic; this was originally anglicised as ''Levenauchen'' / ''Levenachs'', then softened into Levenax / Lennax, and eventually the area was known simply as ''Lennox''. Lennox was not one of the so-called seven ancient Provinces of Scotland, but formed as a province in the Middle Ages. The district embraced the whole of the ancient sheriffdom of Dumbarton: the parishes of Rosneath, Arrochar, Row, Luss, Cardross, Bonhill, Dumbarton, Kilmaronock, New Kilpatrick, Old Kilpatrick, Baldernock, Buchanan, Drymen, Killearn, Balfron, Fintry, and Strathblane, with Campsie and Kilsyth, being all within the bounds ruled over by the Earls of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Dunbar
The title Earl of Dunbar, also called Earl of Lothian or Earl of March, was the head of a comital lordship in south-eastern Scotland between the early 12th century and the early 15th century. The first man to use the title of Earl in this earldom was Gospatric II, Earl of Lothian, son of Gospatric, Earl of Northumbria. It descended to George de Dunbar, 11th Earl of March, who was forfeited by parliament of his titles & estates in 1435, and retired into obscurity in England. His son Patrick retained a barony at Kilconquhar in Fife. The title of Earl of Dunbar was resurrected in 1605 for George Home, 1st Lord Hume of Berwick, Chancellor of the Exchequer, and ''his heirs male''. This title became dormant only six years after its creation, upon Home's death in 1611. Some of his kinsmen were said to be acknowledged as ''de jure'' holders of the title, but none of them ever appears to have assumed the title. There have been no subsequent creations; however, two other peerages with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point they diverged into the Welsh, Cornish and Bretons (among others). They spoke the Common Brittonic language, the ancestor of the modern Brittonic languages. The earliest written evidence for the Britons is from Greco-Roman writers and dates to the Iron Age.Koch, pp. 291–292. Celtic Britain was made up of many tribes and kingdoms, associated with various hillforts. The Britons followed an Ancient Celtic religion overseen by druids. Some of the southern tribes had strong links with mainland Europe, especially Gaul and Belgica, and minted their own coins. The Roman Empire conquered most of Britain in the 1st century, creating the province of Britannia. The Romans invaded northern Britain, but the Britons and Caledonians in the north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum , conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria , common_name = Northumbria , status = State , status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (after 876)South: Danish kingdom (876–914)South: Norwegian kingdom (after 914) , life_span = 654–954 , flag_type = Oswald's Stripes, the provincial flag of Northumbria and red was previously purple , image_coat = , image_map = Map_of_the_Kingdom_of_Northumbria_around_700_AD.svg , image_map_size = 250 , image_map_caption = Northumbria around 700 AD , image_map2 = , image_map2_size = , image_map2_caption = , government_type = Monarchy , year_start = 653 , year_end = 954 , event_end = South is annexed by Kingdom of England , event1 = South is annexed by the Danelaw , date_even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Norway
The Norwegian monarch is the head of state of Norway, which is a constitutional and hereditary monarchy with a parliamentary system. The Norwegian monarchy can trace its line back to the reign of Harald Fairhair and the previous petty kingdoms which were united to form Norway; it has been in unions with both Sweden and Denmark for long periods. The present monarch is King Harald V, who has reigned since 17 January 1991, succeeding his father, Olav V. The heir apparent is his only son, Crown Prince Haakon. The crown prince undertakes various public ceremonial functions, as does the king's wife, Queen Sonja. The crown prince also acts as regent in the king's absence. There are several other members of the royal family, including the king's daughter, grandchildren and sister. Since the dissolution of the union between Norway and Sweden and the subsequent election of a Danish prince as King Haakon VII in 1905, the reigning royal house of Norway has been a branch of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earls Of Orkney
Earl of Orkney, historically Jarl of Orkney, is a title of nobility encompassing the archipelagoes of Orkney and Shetland, which comprise the Northern Isles of Scotland. Originally founded by Norse invaders, the status of the rulers of the Northern Isles as Norwegian vassals was formalised in 1195. Although the Old Norse term ''jarl'' is etymologically related to "earl", and the jarls were succeeded by earls in the late 15th century, a Norwegian ''jarl'' is not the same thing. In the Norse context the distinction between jarls and kings did not become significant until the late 11th century and the early jarls would therefore have had considerable independence of action until that time. The position of Jarl of Orkney was eventually the most senior rank in medieval Norway except for the king himself. The jarls were periodically subject to the kings of Alba for those parts of their territory in what is now mainland Scotland (i.e. Caithness and Sutherland). In 1232, a Scotti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caithness
Caithness ( gd, Gallaibh ; sco, Caitnes; non, Katanes) is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. Caithness has a land boundary with the historic county of Sutherland to the west and is otherwise bounded by sea. The land boundary follows a watershed and is crossed by two roads (the A9 and the A836) and by one railway (the Far North Line). Across the Pentland Firth, ferries link Caithness with Orkney, and Caithness also has an airport at Wick. The Pentland Firth island of Stroma is within Caithness. The name was also used for the earldom of Caithness ( 1334 onwards) and for the Caithness constituency of the Parliament of the United Kingdom (1708 to 1918). Boundaries are not identical in all contexts, but the Caithness area lies entirely within the Highland council area. Toponymy The ''Caith'' element of the name ''Caithness'' comes from the name of a Pictish tribe known as the ''Cat'' or ''Catt'' people, or ''Catti'' (see Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm III
Malcolm III ( mga, Máel Coluim mac Donnchada, label=Medieval Gaelic; gd, Maol Chaluim mac Dhonnchaidh; died 13 November 1093) was King of Scotland from 1058 to 1093. He was later nicknamed "Canmore" ("ceann mòr", Gaelic, literally "big head"; Gaelic meaning and understood as "great chief"). Malcolm's long reign of 35 years preceded the beginning of the Scoto-Norman age. Henry I of England and Eustace III of Boulogne were his sons-in-law, making him the maternal grandfather of Empress Matilda, William Adelin and Matilda of Boulogne. All three of them were prominent in English politics during the 12th century. Malcolm's kingdom did not extend over the full territory of modern Scotland: many of the islands and the land north of the River Oykel were Scandinavian, and south of the Firth of Forth there were numerous independent or semi-independent realms, including the kingdom of Strathclyde and Bamburgh, and it is not certain what if any power the Scots exerted there on Malco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Ross
The Earl or Mormaer of Ross was the ruler of the province of Ross in northern Scotland. Origins and transfers In the early Middle Ages, Ross was part of the vast earldom of Moray. It seems to have been made a separate earldom in the mid 12th century, when Malcolm MacHeth is found designated Earl of Ross. Malcolm had earlier been imprisoned at Roxburgh for rebelling against David I, but when Malcolm's brother-in-law Somerled invaded Scotland, David was forced to relent and grant the earldom unto Malcolm. The title was later granted by William the Lion to Floris III of Holland in 1161 upon Floris's marriage to William's sister Ada of Huntingdon. However, Floris held the title only in a nominal sense, as he took no active part in the governance of Ross. The title seems not to have been passed on, for in 1291 Floris's descendant is found complaining that the earldom had been deprived from him. The true founder was the famous Ferquhard, from the Irish Ó Beólláin (O'Beolai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)