|
Protoprioniodus
''Protoprioniodus'' is an extinct genus of conodonts. Use in stratigraphy The Whiterock Stage refers mainly to the early Middle Ordovician in North America. It is often used in the older literature in a global sense. The Whiterock Stage is given a range from 471.8 (ca. 472) to 462 m.y.a., spanning close to 10 million years. Officially its start is defined by the potentially lowest occurrence of the conodonts ''Protoprioniodus aranda'' or '' Baltoniodus triangularis''. References External links * * Prioniodontida genera Ordovician conodonts {{conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracordylodontidae
Paracordylodontidae is an extinct family of conodonts in the clade Prioniodontida Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts", is a large clade of conodonts that includes two major evolutionary grades; the Prioniodinina and the Ozarkodinina. It includes many of the more famous conodonts, such as the giant ordovician ..., also known as the "complex conodonts". Genera Genera are: * †'' Cooperignathus'' * †'' Fahraeusodus'' * †'' Oelandodus'' * †'' Paracordylodus'' * †'' Protoprioniodus'' References External links Prioniodontida Conodont families {{conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1973 In Paleontology
Pinophyta Arthropods Insects Conodonts Archosauromorphs Newly named crurotarsins Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Newly named birds Newly named pterosaurs References {{portal, Paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ... Paleontology 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whiterock Stage
The Whiterockian, often referred to simply as the Whiterock, is an earliest or lowermost stage of the Middle Ordovician. Although the Whiterockian or Whiterock Stage refers mainly to the early Middle Ordovician in North America, it is often used in the older literature in a global sense. The Whitetrock Stage was introduced by Cooper and Cooper (in Cooper, 1956, p. 6–7) "as a post-Canadian – pre-Chazyan chrono-stratographic unit" based on strata "in the Monitor and Antelope Ranges, flanking Antelope Valley, and in the Toquima Range of central Nevada", referred to as the Antelope Valley Limestone. The strato-type section in Whiterock Canyon in the northern Monitor Range and reference section at Meiklejohn Peak, Bare Mountain Quad. Nev. both show the boundary between the middle Ordovician Whiterock and underlying (mostly Canadian) Ibex series lies between the conodont ''Oepikodus evae'', below, and ''Tripodus laevis'', above, at the start of the ''Isograptus victoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltoniodus Triangularis
''Baltoniodus'' is an extinct genus of conodonts. Use in stratigraphy The base of the Dapingian, the third stage of the Middle Ordovician, is defined as the first appearance of ''Baltoniodus triangularis''. The Whiterock Stage refers mainly to the early Middle Ordovician in North America, it is often used in the older literature in a global sense. The Whiterock Stage is given a range from 471.8 (ca. 472) to 462 m.y.a., spanning close to 10 million years. Officially its start is defined by the potentially lowest occurrence of the conodont '' Protoprioniodus aranda'' or ''Baltoniodus triangularis''. ''B. gerdae'' has been found in the early Sandbian Bromide Formation The Bromide Formation is a geological formation in Oklahoma, USA. It is well known for its diverse echinoderm and trilobite fossil fauna. Location The Bromide Formation crops out in the Arbuckle and Wichita Mountains and in the Criner Hills ..., in Oklahoma, USA. References External links * P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordata
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These five synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name “chordate” comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also Bilateral symmetry, bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit Metameric, metameric segmentation. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and mitochondrial inner membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
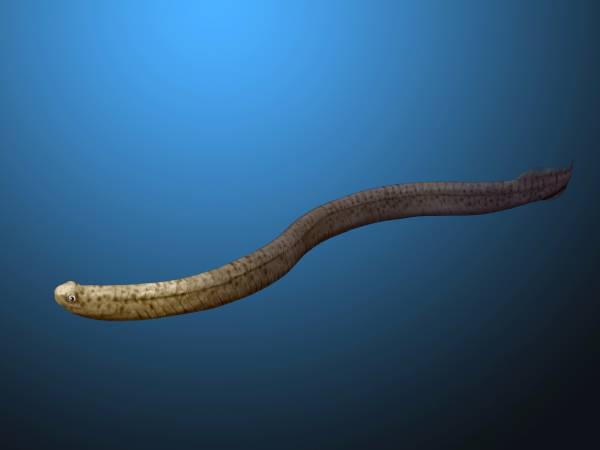
Conodont
Conodonts (Greek ''kōnos'', "cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evidence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prioniodontida
Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts", is a large clade of conodonts that includes two major evolutionary grades; the Prioniodinina and the Ozarkodinina. It includes many of the more famous conodonts, such as the giant ordovician ''Promissum'' (Prioniodinina) from the Soom Shale and the Carboniferous specimens from the Granton Shrimp bed (Ozarkodinina). They are euconodonts, in that their elements are composed of two layers; the crown and the basal body, and are assumed to be a clade A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, .... Phylogeny This is a recent cladogram of the Prioniodontida, simplified from Donoghue ''et al.'', (2008). Notes References {{Taxonbar, from=Q6581502 Vertebrate unranked clades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RA McTavish
Ra (; egy, rꜥ; also transliterated ; cuneiform: ''ri-a'' or ''ri-ia''; Phoenician: 𐤓𐤏,CIS I 3778 romanized: rʿ) or Re (; cop, ⲣⲏ, translit=Rē) was the ancient Egyptian deity of the sun. By the Fifth Dynasty, in the 25th and 24th centuries BC, he had become one of the most important gods in ancient Egyptian religion, identified primarily with the noon-day sun. Ra ruled in all parts of the created world: the sky, the earth, and the underworld. He was the god of the sun, order, kings and the sky. Ra was portrayed as a falcon and shared characteristics with the sky-god Horus. At times the two deities were merged as Ra-Horakhty, "''Ra, who is Horus of the Two Horizons''". In the New Kingdom, when the god Amun rose to prominence he was fused with Ra as Amun-Ra. The cult of the Mnevis bull, an embodiment of Ra, had its center in Heliopolis and there was a formal burial ground for the sacrificed bulls north of the city. All forms of life were belie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conodont
Conodonts (Greek ''kōnos'', "cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evidence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prioniodontida Genera
Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts", is a large clade of conodonts that includes two major evolutionary grades; the Prioniodinina and the Ozarkodinina. It includes many of the more famous conodonts, such as the giant ordovician ''Promissum ''Promissum'' is an extinct genus of conodonts, primitive chordates, that lived during the Upper Ordovician period. A conodont, ''Promissum'' had a primitive mouth under its eyes with mineralized teeth, which are both typical for conodonts. It h ...'' (Prioniodinina) from the Soom Shale and the Carboniferous specimens from the Granton Shrimp bed (Ozarkodinina). They are euconodonts, in that their elements are composed of two layers; the crown and the basal body, and are assumed to be a clade. Phylogeny This is a recent cladogram of the Prioniodontida, simplified from Donoghue ''et al.'', (2008). Notes References {{Taxonbar, from=Q6581502 Vertebrate unranked clades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |