|
Prostatic Stent
A prostatic stent is a stent used to keep open the male urethra and allow the passing of urine in cases of prostatic obstruction and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). Prostatic obstruction is a common condition with a variety of causes. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is the most common cause, but obstruction may also occur acutely after treatment for BPH such as transurethral needle ablation of the prostate (TUNA), transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT), prostate cancer or after radiation therapy. Classification There are two types of prostatic stent: temporary and permanent. Although a permanent prostatic stent is not a medical treatment, it falls under the classification of a surgical procedure. Placement of a permanent prostatic stent is carried out as an outpatient treatment under local, topical or spinal anesthesia and usually takes about 15–30 minutes. A temporary prostatic stent can be inserted in a similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urology
Urology (from Greek οὖρον ''ouron'' "urine" and '' -logia'' "study of"), also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the urinary-tract system and the reproductive organs. Organs under the domain of urology include the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and the male reproductive organs (testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, and penis). The urinary and reproductive tracts are closely linked, and disorders of one often affect the other. Thus a major spectrum of the conditions managed in urology exists under the domain of genitourinary disorders. Urology combines the management of medical (i.e., non-surgical) conditions, such as urinary-tract infections and benign prostatic hyperplasia, with the management of surgical conditions such as bladder or prostate cancer, kidney stones, congenital abnormalities, traumatic injury, and stress incontinence. Urologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foley Catheter
In urology, a Foley catheter (named for Frederic Foley, who produced the original design in 1929) is a flexible tube that a clinician passes through the urethra and into the bladder to drain urine. It is the most common type of indwelling urinary catheter. The tube has two separated channels, or ''lumens'', running down its length. One lumen, open at both ends, drains urine into a collection bag. The other has a valve on the outside end and connects to a balloon at the inside tip. The balloon is inflated with sterile water when it lies inside the bladder to stop it from slipping out. Manufacturers usually produce Foley catheters using silicone or coated natural latex. Coatings include polytetrafluoroethylene, hydrogel, or a silicon elastomer – the different properties of these surface coatings determine whether the catheter is suitable for 28-day or 3-month indwelling duration. Foley catheters should be used only when indicated, as use increases the risk of catheter-ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) refer to a group of clinical symptoms involving the bladder, urinary sphincter, urethra and, in men, the prostate. The term is more commonly applied to men—over 40% of older men are afected—but lower urinary tract symptoms also affect women. The condition is also termed prostatism in men, but LUTS is preferred. Symptoms and signs Symptoms can be categorised into: Filling (storage) or irritative symptoms * Increased frequency of urination * Increased urgency of urination * Urge incontinence * Excessive passage of urine at night Voiding or obstructive symptoms * Poor stream (unimproved by straining) * Hesitancy * Terminal dribbling * Incomplete voiding * Urinary retention * Overflow incontinence (occurs in chronic retention) * Episodes of near retention As the symptoms are common and non-specific, LUTS is not necessarily a reason to suspect prostate cancer. Large studies of patients have also failed to show any correlation between low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include loss of bladder control, mild lower abdominal pain, and a weak urine stream. Those with long-term problems are at risk of urinary tract infections. Causes include blockage of the urethra, nerve problems, certain medications, and weak bladder muscles. Blockage can be caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), urethral strictures, bladder stones, a cystocele, constipation, or tumors. Nerve problems can occur from diabetes, trauma, spinal cord problems, stroke, or heavy metal poisoning. Medications that can cause problems include anticholinergics, antihistamines, tricyclic antidepressants, cyclobenzaprine, diazepam, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID), amphetamines, and opioids. Diagnosis is typically based on measuring the amount of urine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that surrounds the urethra just below the bladder. It is located in the hypogastric region of the abdomen. To give an idea of where it is located, the bladder is superior to the prostate gland as shown in the image The rectum is posterior in perspective to the prostate gland and the ischial tuberosity of the pelvic bone is inferior. Only those who have male reproductive organs are able to get prostate cancer. Most prostate cancers are slow growing. Cancerous cells may spread to other areas of the body, particularly the bones and lymph nodes. It may initially cause no symptoms. In later stages, symptoms include pain or difficulty urinating, blood in the urine, or pain in the pelvis or back. Benign prostatic hyperplasia may produce similar symptoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
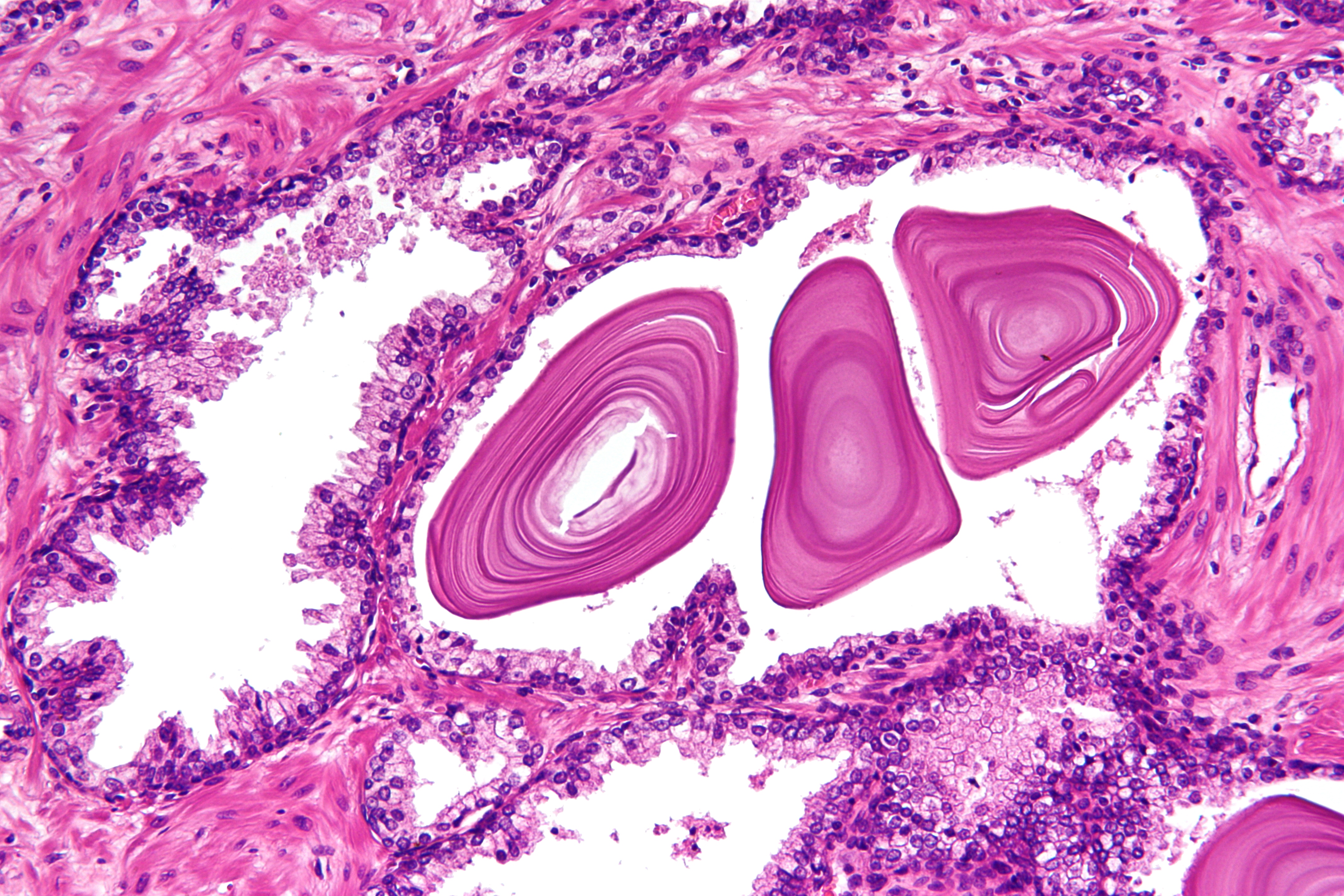
Prostate
The prostate is both an Male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the Urinary bladder, bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue as well as connective tissue. The prostate glands produce and contain fluid that forms part of semen, the substance emitted during ejaculation as part of the male Human sexual response cycle, sexual response. This prostatic fluid is slightly alkaline, milky or white in appearance. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vagina, vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include loss of bladder control, mild lower abdominal pain, and a weak urine stream. Those with long-term problems are at risk of urinary tract infections. Causes include blockage of the urethra, nerve problems, certain medications, and weak bladder muscles. Blockage can be caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), urethral strictures, bladder stones, a cystocele, constipation, or tumors. Nerve problems can occur from diabetes, trauma, spinal cord problems, stroke, or heavy metal poisoning. Medications that can cause problems include anticholinergics, antihistamines, tricyclic antidepressants, cyclobenzaprine, diazepam, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID), amphetamines, and opioids. Diagnosis is typically based on measuring the amount of urine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
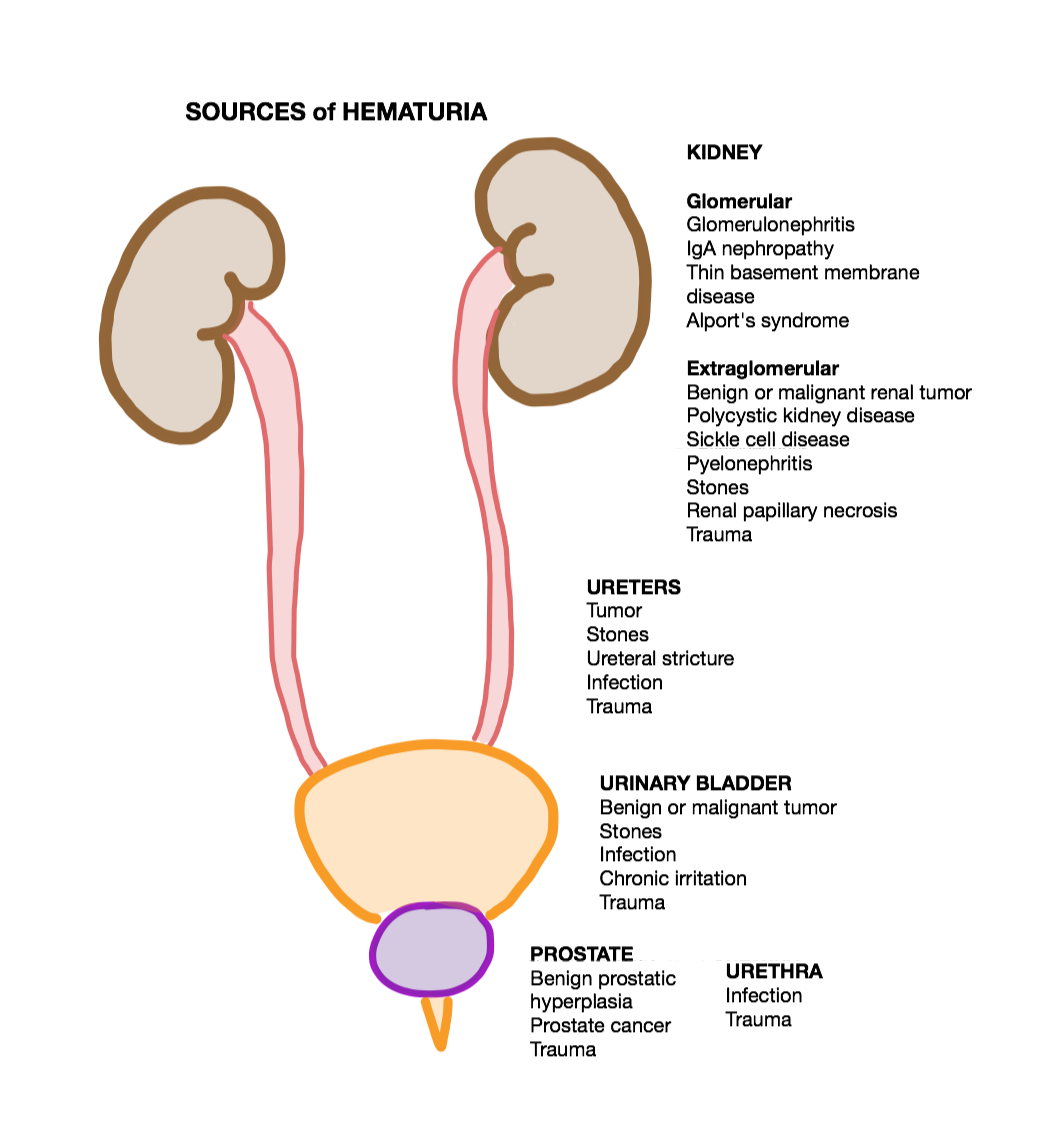
Hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. “Gross hematuria” occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and foods (e.g. blackberries, beets, food dyes) can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dipstick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detrusor Muscle
The detrusor muscle, also detrusor urinae muscle, muscularis propria of the urinary bladder and (less precise) muscularis propria, is smooth muscle found in the wall of the bladder. The detrusor muscle remains relaxed to allow the bladder to store urine, and contracts during urination to release urine. Related are the urethral sphincter muscles which envelop the urethra to control the flow of urine when they contract. Structure The fibers of the detrusor muscle arise from the posterior surface of the body of the pubis in both sexes (musculi pubovesicales), and in the male from the adjacent part of the prostate. These fibers pass, in a more or less longitudinal manner, up the inferior surface of the bladder, over its apex, and then descend along its fundus to become attached to the prostate in the male, and to the front of the vagina in the female. At the sides of the bladder the fibers are arranged obliquely and intersect one another. The 3 layers of muscles are arranged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
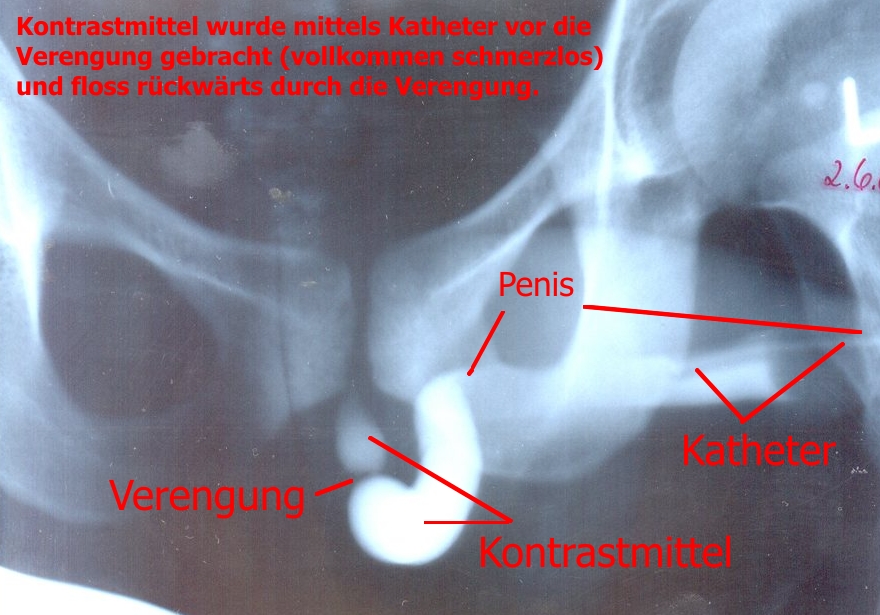
Urethral Stricture
A urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra, the tube connected to the bladder that allows the passing of urine. The narrowing reduces the flow of urine and makes it more difficult or even painful to empty the bladder. Urethral stricture is caused by injury, instrumentation, infection, and certain non-infectious forms of urethritis The condition is more common in men due to their longer urethra. Signs and symptoms The hallmark sign of urethral stricture is a weak urinary stream. Other symptoms include: * Splaying of the urinary stream * Urinary frequency * Urinary urgency * Straining to urinate * Pain during urination * Urinary tract infection * Prostatitis * Inability to completely empty the bladder. Some people with severe urethral strictures are completely unable to urinate. This is referred to as acute urinary retention, and is a medical emergency. Hydronephrosis and kidney failure may also occur. Complications * Urinary retention * Prostatitis * Bladder dysfunc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the prostate gland. Symptoms may include frequent urination, trouble starting to urinate, weak stream, inability to urinate, or loss of bladder control. Complications can include urinary tract infections, bladder stones, and chronic kidney problems. The cause is unclear. Risk factors include a family history, obesity, type 2 diabetes, not enough exercise, and erectile dysfunction. Medications like pseudoephedrine, anticholinergics, and calcium channel blockers may worsen symptoms. The underlying mechanism involves the prostate pressing on the urethra and thereby making it difficult to pass urine out of the bladder. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and examination after ruling out other possible causes. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, a number of procedures, and surgery. In those with mild symptoms, weight loss, exercise, and decre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of The United States
The law of the United States comprises many levels of Codification (law), codified and uncodified forms of law, of which the most important is the nation's Constitution of the United States, Constitution, which prescribes the foundation of the federal government of the United States, federal government of the United States, as well as various civil liberties. The Constitution sets out the boundaries of federal law, which consists of Act of Congress, Acts of Congress, treaty, treaties ratified by the United States Senate, Senate, regulations promulgated by the executive branch, and case law originating from the United States federal courts, federal judiciary. The United States Code is the official compilation and Codification (law), codification of general and permanent federal statutory law. Federal law and treaties, so long as they are in accordance with the Constitution, preempt conflicting state and territorial laws in the 50 U.S. states and in the territories. However, the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
