|
Prospect Bluff Historic Sites
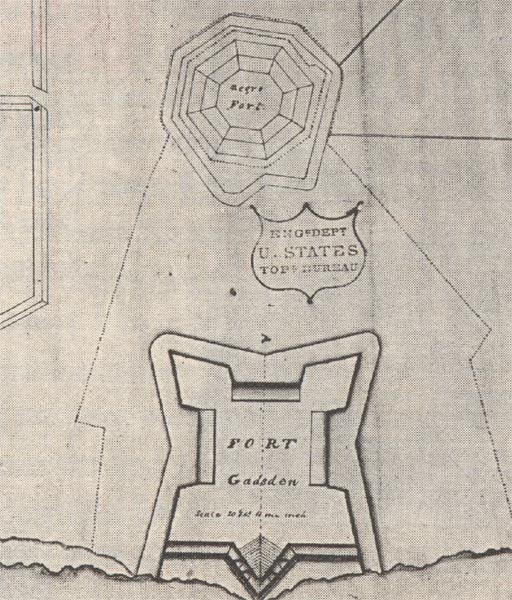
Prospect Bluff Historic Sites (until 2016 known as Fort Gadsden Historic Site, and sometimes written as Fort Gadsden Historic Memorial) is located in Franklin County, Florida, on the Apalachicola River, SW of Sumatra, Florida. The site contains the ruins of two forts. The earlier and larger one was built by the British in 1814, during the War of 1812. They allowed the members of the disbanded Corps of Colonial Marines, made up largely of fugitive slaves, and Creek tribesmen to occupy it after the British evacuated Florida in 1815, deliberately leaving their munitions behind. At that point, since the British had not named it, Americans started referring to it as Negro Fort. It was destroyed in a river attack from U.S. forces in 1816. Fort Gadsden was built in 1818 within the former walls of the former Negro Fort. The site has been known by several other names at various times, including Prospect Bluff, British post, Nicholls' Fort, Blount's Fort, Fort Blount, African Fort, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin County, Florida
Franklin County is a county along the Gulf of Mexico in the panhandle of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 12,451, making it the third-least populous county in Florida. The county seat is Apalachicola. The county includes several large preserved areas and rivers and has been home to commercial timber and fishing industry. More recently it has become popular for tourism and retirement. It includes several rivers, state parks, and islands. History Franklin County was founded in 1832. It was named for Benjamin Franklin. The second largest town in Franklin County is Carrabelle, 25 miles east of Apalachicola on the Carrabelle River. Camp Gordon Johnston During World War II most of Franklin County was used by the U.S. Army for amphibious and jungle training, for which the beaches and islands were ideal. When the war ended and the military left, Lanark Village was established from the remaining officer's quarters. Geography According to the U. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Florida
East Florida ( es, Florida Oriental) was a colony of Great Britain from 1763 to 1783 and a province of Spanish Florida from 1783 to 1821. Great Britain gained control of the long-established Spanish colony of ''La Florida'' in 1763 as part of the treaty ending the French and Indian War (as the Seven Years' War was called in North America). Deciding that the territory was too large to administer as a single unit, Britain divided Florida into two colonies separated by the Apalachicola River: East Florida with its capital in St. Augustine and West Florida with its capital in Pensacola. East Florida was much larger and comprised the bulk of the former Spanish territory of Florida and most of the current state of Florida. It had also been the most populated region of Spanish Florida, but before control was transferred to Britain, most residents – including virtually everyone in St. Augustine – left the territory, with most migrating to Cuba. Britain tried to attract settlers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery In The United States
The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the South. Slavery was established throughout European colonization in the Americas. From 1526, during early colonial days, it was practiced in what became Britain's colonies, including the Thirteen Colonies that formed the United States. Under the law, an enslaved person was treated as property that could be bought, sold, or given away. Slavery lasted in about half of U.S. states until abolition. In the decades after the end of Reconstruction, many of slavery's economic and social functions were continued through segregation, sharecropping, and convict leasing. By the time of the American Revolution (1775–1783), the status of enslaved people had been institutionalized as a racial caste associated with African ancestry. During and immediately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seminoles
The Seminole are a Native American people who developed in Florida in the 18th century. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, and the Miccosukee Tribe of Indians of Florida, as well as independent groups. The Seminole people emerged in a process of ethnogenesis from various Native American groups who settled in Spanish Florida beginning in the early 1700s, most significantly northern Muscogee Creeks from what is now Georgia and Alabama. The word "Seminole" is derived from the Muscogee word ''simanó-li''. This may have been adapted from the Spanish word ''cimarrón'', meaning "runaway" or "wild one". Seminole culture is largely derived from that of the Creek; the most important ceremony is the Green Corn Dance; other notable traditions include use of the black drink and ritual tobacco. As the Seminole adapted to Florida environs, they developed local traditions, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida Panhandle
The Florida Panhandle (also West Florida and Northwest Florida) is the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Florida; it is a Salient (geography), salient roughly long and wide, lying between Alabama on the north and the west, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia on the north, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. Its eastern boundary is arbitrarily defined. In terms of population, major communities include Tallahassee, Florida, Tallahassee, Pensacola, Florida, Pensacola, and Panama City, Florida, Panama City. As is the case with the other eight U.S. states that have Salient (geography)#Panhandles in the United States, panhandles, the geographic meaning of the term is inexact and elastic. References to the Florida Panhandle always include the ten List of counties in Florida, counties west of the Apalachicola River, a natural geographic boundary, which was the historic dividing line between the British colonies of West Florida and East Florida. These western counties also lie in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flint River (Georgia)
The Flint River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 15, 2011 river in the U.S. state of Georgia. The river drains of western Georgia, flowing south from the upper Piedmont region south of Atlanta to the wetlands of the Gulf Coastal Plain in the southwestern corner of the state. Along with the Apalachicola and the Chattahoochee rivers, it forms part of the ACF basin. In its upper course through the red hills of the Piedmont, it is considered especially scenic, flowing unimpeded for over . Historically, it was also called the Thronateeska River. Description The Flint River rises in west central Georgia in the city of East Point in southern Fulton County on the southern outskirts of the Atlanta metropolitan area as ground seepage. The exact start can be traced to the field located between Plant Street, Willingham Drive, Elm Street, and Vesta Avenue. It travels under the runways of the Hartsfi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chattahoochee River
The Chattahoochee River forms the southern half of the Alabama and Georgia border, as well as a portion of the Florida - Georgia border. It is a tributary of the Apalachicola River, a relatively short river formed by the confluence of the Chattahoochee and Flint Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fir ... rivers and emptying from Florida into Apalachicola Bay in the Gulf of Mexico. The Chattahoochee River is about long. The Chattahoochee, Flint, and Apalachicola rivers together make up the Apalachicola–Chattahoochee–Flint River Basin (ACF River Basin). The Chattahoochee makes up the largest part of the ACF's drainage basin. Course The River source, source of the Chattahoochee River is located in Jacks Gap at the southeastern foot of Jacks Knob, in the very southeaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi Territory
The Territory of Mississippi was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 7, 1798, until December 10, 1817, when the western half of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Mississippi. The eastern half was redesignated as the Alabama Territory until it was admitted to the Union as the State of Alabama on December 14, 1819. The Chattahoochee River played a significant role in the definition of the territory's borders. The population rose in the early 1800s from settlement, with cotton being an important cash crop. History The United States and Spain disputed these lands east of the Mississippi River until Spain relinquished its claim with the Treaty of Madrid, initially signed in 1795 by the two countries' representatives. The Mississippi Territory was organized in 1798 from these lands, in an area extending from 31° N latitude to 32°28' North — or approximately the southern half of the present states of Alabama and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arterial Road
An arterial road or arterial thoroughfare is a high-capacity urban road that sits below freeways/motorways on the road hierarchy in terms of traffic flow and speed. The primary function of an arterial road is to deliver traffic from collector roads to freeways or expressways, and between urban centres at the highest level of service possible. As such, many arteries are limited-access roads, or feature restrictions on private access. Because of their relatively high accessibility, many major roads face large amounts of land use and urban development, making them significant urban places. In traffic engineering hierarchy, an arterial road delivers traffic between collector roads and freeways. For new arterial roads, intersections are often reduced to increase traffic flow. In California, arterial roads are usually spaced every half mile, and have intersecting collector(s) and streets. Some arterial roads, characterized by a small fraction of intersections and driveways compared to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (U
Georgia most commonly refers to: * Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia * Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States Georgia may also refer to: Places Historical states and entities * Related to the country in the Caucasus ** Kingdom of Georgia, a medieval kingdom ** Georgia within the Russian Empire ** Democratic Republic of Georgia, established following the Russian Revolution ** Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic, a constituent of the Soviet Union * Related to the US state ** Province of Georgia, one of the thirteen American colonies established by Great Britain in what became the United States ** Georgia in the American Civil War, the State of Georgia within the Confederate States of America. Other places * 359 Georgia, an asteroid * New Georgia, Solomon Islands * South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Canada * Georgia Street, in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada * Strait of Georgia, British Columbia, Canada United K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal city of the Pensacola Metropolitan Area, which had an estimated 502,629 residents . Pensacola is the site of the first Spanish settlement within the borders of the continental United States in 1559, predating the establishment of St. Augustine by 6 years, although the settlement was abandoned due to a hurricane and not re-established until 1698. Pensacola is a seaport on Pensacola Bay, which is protected by the barrier island of Santa Rosa and connects to the Gulf of Mexico. A large United States Naval Air Station, the first in the United States, is located southwest of Pensacola near Warrington; it is the base of the Blue Angels flight demonstration team and the National Naval Aviation Museum. The main campus of the University of West F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |