|
Propyläen (Munich)
The Propylaea (german: Propyläen) is a city gate in Munich at the west side of Königsplatz. History The building, constructed in Doric order, was completed by Leo von Klenze in 1862 and evokes the monumental entrance of the Propylaea for the Athenian Acropolis. The gate was created as a memorial for the accession to the throne of Otto of Greece, a son of King Ludwig I of Bavaria. As early as 1816, the Propylaea was in the early planning stages, but 30 years passed before the order was issued for its construction. Klenze painted a picture of the planned Propylaea, to promote the project. After King Ludwig I abdicated in 1848, the project was called into question, as, by that time, Munich no longer needed a city gate. Finally, Ludwig I financed the building from his private resources as a symbol of the friendship between Greece and Bavaria, as well as a monument to the Greek War of Independence. The Propylaea was opened shortly before King Otto was forced to resign as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Gate
A city gate is a gate which is, or was, set within a city wall. It is a type of fortified gateway. Uses City gates were traditionally built to provide a point of controlled access to and departure from a walled city for people, vehicles, goods and animals. Depending on their historical context they filled functions relating to defense, security, health, trade, taxation, and representation, and were correspondingly staffed by military or municipal authorities. The city gate was also commonly used to display diverse kinds of public information such as announcements, tax and toll schedules, standards of local measures, and legal texts. It could be heavily fortified, ornamented with heraldic shields, sculpture or inscriptions, or used as a location for warning or intimidation, for example by displaying the heads of beheaded criminals or public enemies. Notably in Denmark, many market towns used to have at least one city gate mostly as part of the city's fortifications, but during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, became an ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Completed In 1862
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortified Gateway
A fortified gateway is an element of a variety of fortified structures, such as a castle or walled town. Fortified gates or gateways appear in the Bronze Age and reach into the modern times. City gate Gatehouse {{main, Gatehouse ''Torburg'' In German, a "Torburg", lit. "gate castle", is a relatively autonomous and heavily fortified gateway of a castle or town. Medieval castle gateways of this type usually have additional fortifications in front of them. A common form is the tower gateway (German: ''Turmtorburg''); a variant is the bastion gateway (German: ''Halbrundturmtorburg''). They are common in Europe. Examples in Europe France Château du Sou in Lacenas Germany * Deutsches Tor in Metz * Ehrentor, Eigelsteintorburg, Hahnentorburg, Kuniberts Tower, Schaafentor and Severin Gate in Cologne *Town fortifications of Erkelenz * Friedländer Tor in Neubrandenburg *Marching Gate and Bridge Gate in Aachen as well as Aachen's city walls * Upper Gate in Neuss *Fortified ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porta Nigra
The Porta Nigra (Latin for ''black gate'') is a large Roman city gate in Trier, Germany. It is today the largest Roman city gate north of the Alps. It was designated as part of the Roman Monuments, Cathedral of St Peter and Church of Our Lady in Trier UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1986, because of its testimony to the influence of Trier in the Roman Empire and its unique architecture as both a city gate and a double church. The name ''Porta Nigra'' originated in the Middle Ages due to the darkened colour of its stone; the original Roman name has not been preserved. Locals commonly refer to the Porta Nigra simply as ''Porta''. History Roman The Porta Nigra was built in grey sandstone after 170 AD. The original gate consisted of two four-storeyed towers, projecting as near semicircles on the outer side. A narrow courtyard separated the two gate openings on either side. For unknown reasons, however, the construction of the gate remained unfinished. For example, the stones at the nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordertor
The Nordertor ( da, Nørreport) is an old town gate in Flensburg, Germany, which was built around 1595. Today the landmark is used as a symbol for Flensburg. History The town wall of Flensburg was built step by step from 1345 onwards. A town gate, named ''Norder Porte'', was built in the northern section of the wall. At the end of the 16th century it was replaced by the Nordertor, a building with stepped gables and archway. At this time the Nordertor marked the northern boundary of the town. It was a checkpoint that was closed at night. On the north face of the gate are two plaques. The left one bears the royal coat of arms of King Christian IV, 1577-1648 and the Latin words: ''Regna Firmat Pietas'' — Piety strengthens the Realm. The right one bears the coat of arms of Flensburg with the German words: ''Friede ernährt, Unfrieden verzehrt'' — Peace nurtures, strife devours. Also to be seen is the date of renovation, inscribed as "Renov. 1767". The town gate was restor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Michael Schwanthaler
Ludwig Michael Schwanthaler, later ennobled as Ritter von Schwanthaler (26 August 1802 – 14 November 1848), was a German sculptor who taught at the Academy of Fine Arts, Munich. Biography Schwanthaler was born in Munich. His family had been sculptors in Tyrol and Innviertel for three centuries; young Ludwig received his earliest lessons from his father, Franz Schwanthaler (1762–1820), and the father had been instructed by the grandfather. The last to bear the name was Xaver, who worked in his cousin Ludwig's studio and survived till 1854. For successive generations the family lived by the carving of busts and sepulchral monuments, and from the condition of craftsmen rose to that of artists. From the Munich '' Gymnasium'' Schwanthaler passed as a student to the Munich Academy; at first he purposed to be a painter, but afterwards reverted to the sculptural arts of his ancestors. His talents received timely encouragement by a commission for an elaborate silver service for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sculptural processes originally used carving (the removal of material) and modelling (the addition of material, as clay), in stone, metal, ceramic art, ceramics, wood and other materials but, since Modernism, there has been an almost complete freedom of materials and process. A wide variety of materials may be worked by removal such as carving, assembled by welding or modelling, or Molding (process), moulded or Casting, cast. Sculpture in stone survives far better than works of art in perishable materials, and often represents the majority of the surviving works (other than pottery) from ancient cultures, though conversely traditions of sculpture in wood may have vanished almost entirely. However, most ancient sculpture was brightly painted, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane. When a relief is carved into a flat surface of stone (relief sculpture) or wood (relief carving), the field is actually lowered, leaving the unsculpted areas seeming higher. The approach requires a lot of chiselling away of the background, which takes a long time. On the other hand, a relief saves forming the rear of a subject, and is less fragile and more securely fixed than a sculpture in the round, especially one of a standing figure where the ankles are a potential weak point, particularly in stone. In other materials such as metal, clay, plaster stucco, ceramics or papier-mâché the form can be simply added to or raised up from the background. Monumental bronze reliefs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floor Plan
In architecture and building engineering, a floor plan is a technical drawing to scale, showing a view from above, of the relationships between rooms, spaces, traffic patterns, and other physical features at one level of a structure. Dimensions are usually drawn between the walls to specify room sizes and wall lengths. Floor plans may also include details of fixtures like sinks, water heaters, furnaces, etc. Floor plans may include notes for construction to specify finishes, construction methods, or symbols for electrical items. It is also called a ''plan'' which is a measured plane typically projected at the floor height of , as opposed to an ''elevation'' which is a measured plane projected from the side of a building, along its height, or a section or ''cross section'' where a building is cut along an axis to reveal the interior structure. Overview Similar to a map, the orientation of the view is downward from above, but unlike a conventional map, a plan is drawn at a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
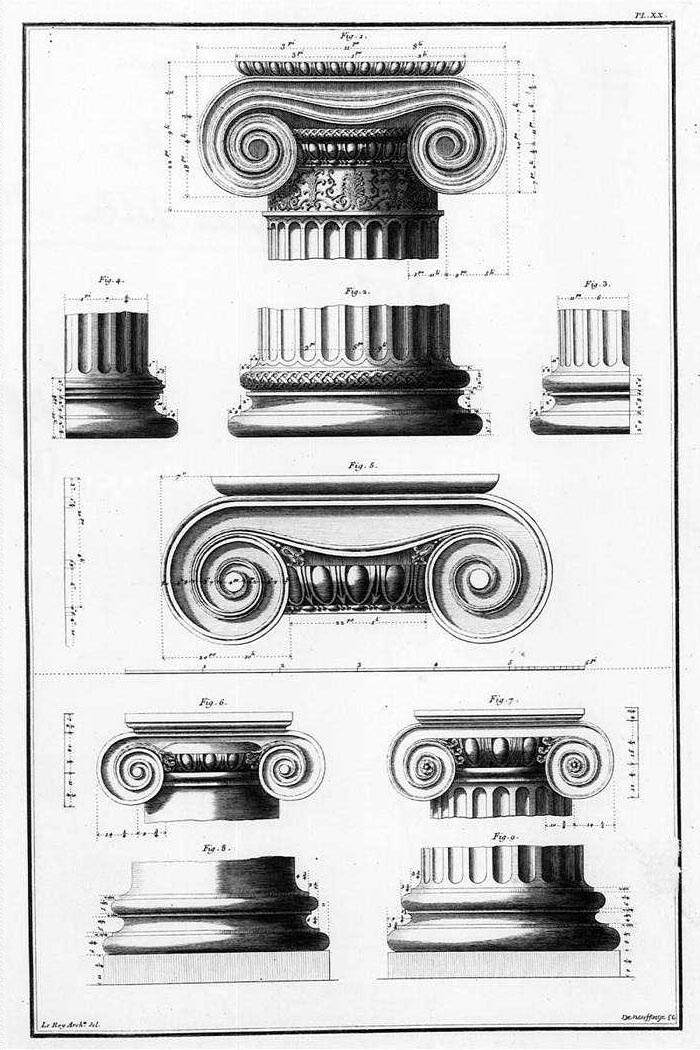
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffer
A coffer (or coffering) in architecture is a series of sunken panels in the shape of a square, rectangle, or octagon in a ceiling, soffit or vault. A series of these sunken panels was often used as decoration for a ceiling or a vault, also called ''caissons'' ("boxes"), or ''lacunaria'' ("spaces, openings"), so that a coffered ceiling can be called a ''lacunar'' ceiling: the strength of the structure is in the framework of the coffers. History The stone coffers of the ancient Greeks and Romans are the earliest surviving examples, but a seventh-century BC Etruscan chamber tomb in the necropolis of San Giuliano, which is cut in soft tufa-like stone reproduces a ceiling with beams and cross-beams lying on them, with flat panels filling the ''lacunae''. For centuries, it was thought that wooden coffers were first made by crossing the wooden beams of a ceiling in the Loire Valley châteaux of the early Renaissance. In 2012, however, archaeologists working under the Packard Humani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


.jpg)