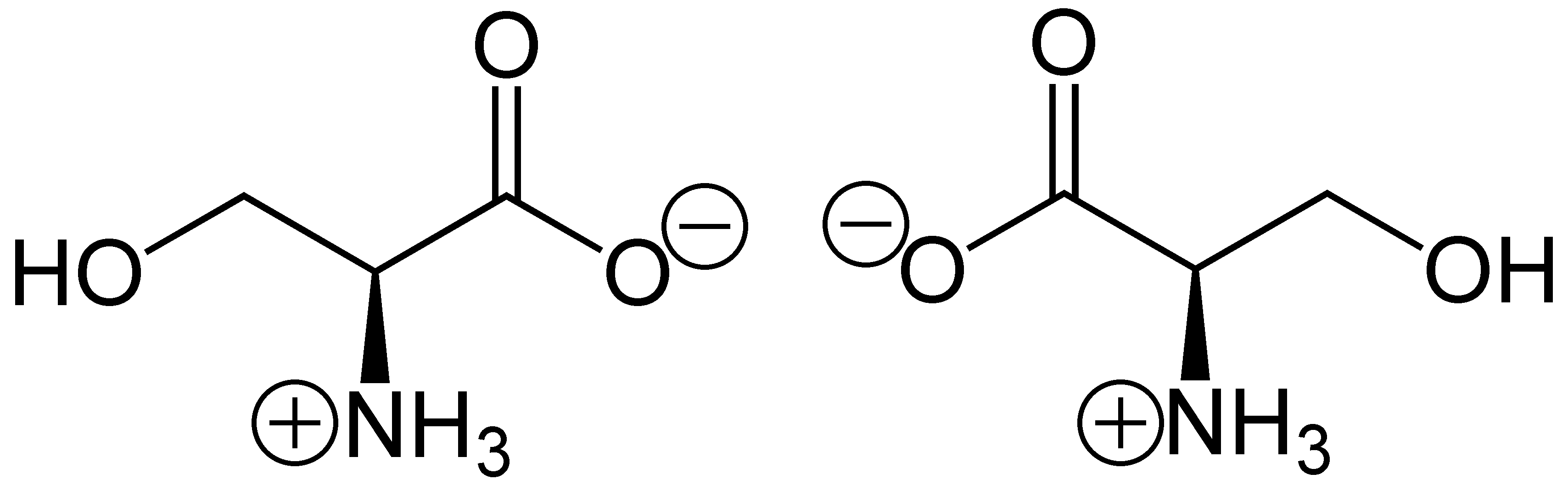|
Properdin Deficiency
Properdin deficiency is a rare X-linked disease in which properdin, an important Complement system, complement factor responsible for the stabilization of the alternative C3 convertase, is deficient. There are three forms of properdin deficiencies: Type I, which is identified by the total absence of the properdin protein in the plasma, Type II, which is a low but detectable amount of the properdin protein in the plasma, and Type III, which is a rare case of normal levels of properdin protein, but a dysfunctional variant. One of the first studied cases of properdin deficiency was in 1980 bDavis and Forrestal These families had members with only partial deficiencies which resulted in a lowered consumption of the Complement component 3, C3 protein. Properdin deficiency was studied again shortly after in 1982 bSjoholmin which all of the subjects were deceased shortly after the study because of their disease. The largest study of properdin deficiency was in 1989 bFijenwhich included nine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-linked
Sex linked describes the sex-specific patterns of inheritance and presentation when a gene mutation (allele) is present on a sex chromosome (allosome) rather than a non-sex chromosome (autosome). In humans, these are termed X-linked recessive, X-linked dominant and Y-linked. The inheritance and presentation of all three differ depending on the sex of both the parent and the child. This makes them characteristically different from autosomal dominance and recessiveness. There are many more X-linked conditions than Y-linked conditions, since humans have several times as many genes on the X chromosome than the Y chromosome. Only females are able to be carriers for X-linked conditions; males will always be affected by any X-linked condition, since they have no second X chromosome with a healthy copy of the gene. As such, X-linked recessive conditions affect males much more commonly than females. In X-linked recessive inheritance, a son born to a carrier mother and an unaffected fath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y Chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers male development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs, making it similar in size to chromosome 19. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest-evolving parts of the human genome. The human Y chromosome carries an estimated 100–200 genes, with between 45 and 73 of these being protein-coding. All single-copy Y-linked genes are hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders
Primary immunodeficiencies are disorders in which part of the body's immune system is missing or does not function normally. To be considered a ''primary'' immunodeficiency (PID), the cause of the immune deficiency must not be secondary in nature (i.e., caused by other disease, drug treatment, or environmental exposure to toxins). Most primary immunodeficiencies are genetic disorders; the majority are diagnosed in children under the age of one, although milder forms may not be recognized until adulthood. While there are over 430 recognized PIDs as of 2019, most are very rare. About 1 in 500 people in the United States are born with a primary immunodeficiency. Immune deficiencies can result in persistent or recurring infections, auto-inflammatory disorders, tumors, and disorders of various organs. There are currently limited treatments available for these conditions; most are specific to a particular type of PID. Research is currently evaluating the use of stem cell transplants (HS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspartic Acid
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the protonated –NH form under physiological conditions, while its α-carboxylic acid group is deprotonated −COO− under physiological conditions. Aspartic acid has an acidic side chain (CH2COOH) which reacts with other amino acids, enzymes and proteins in the body. Under physiological conditions (pH 7.4) in proteins the side chain usually occurs as the negatively charged aspartate form, −COO−. It is a non-essential amino acid in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it as needed. It is encoded by the codons GAU and GAC. D-Aspartate is one of two D-amino acids commonly found in mammals. .html" ;"title="/sup>">/sup> In proteins aspartate sidechains are often hydrogen bonded to form asx turns or asx motifs, which frequently occur at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a Hydrophobe, hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is Genetic code, encoded by the Genetic code#Codons, codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. Functions Aside from being a proteinogenic amino acid, tyrosine has a special role by virtue of the phenol functionality. It occurs in proteins that are part of signal transduction processes and functions as a receiver of phosphate groups that are transferred by way of protein kinases. Phosphorylation of the hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α- carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic beta carbon substituent. It is essential in humans, meaning that the body cannot synthesize it and it must be obtained from the diet. Tryptophan is also a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, the hormone melatonin, and vitamin B3. It is encoded by the codon UGG. Like other amino acids, tryptophan is a zwitterion at physiological pH where the amino group is protonated (–; pKa = 9.39) and the carboxylic acid is deprotonated ( –COO−; pKa = 2.38). Humans and many animals cannot synthesize tryptophan: they need to obtain it through their diet, making it an essential amino acid. Function Amino acids, including tryptophan, are used as building blocks in protein biosynthesis, and proteins are required to sustain life. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the amino and guanidino groups are protonated, resulting in a cation. Only the -arginine (symbol Arg or R) enantiomer is found naturally. Arg residues are common components of proteins. It is encoded by the codons CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG. The guanidine group in arginine is the precursor for the biosynthesis of nitric oxide. Like all amino acids, it is a white, water-soluble solid. History Arginine was first isolated in 1886 from yellow lupin seedlings by the German chemist Ernst Schulze and his assistant Ernst Steiger. He named it from the Greek ''árgyros'' (ἄργυρος) meaning "silver" due to the silver-white appearance of arginine nitrate crystals. In 1897, Schulze and Ernst Winterstein (1865–1949) determined the structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L-stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valine
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isopropyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, beans and legumes. It is encoded by all codons starting with GU (GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG). History and etymology Valine was first isolated from casein in 1901 by Hermann Emil Fischer. The name valine comes from valeric acid, which in turn is named after the plant valerian due to the presence of the acid in the roots of the plant. Nomenclature According to IUPAC, carbon atoms forming valine are numbered sequentially s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a ''Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by the French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transversion
Transversion, in molecular biology, refers to a point mutation in DNA in which a single (two ring) purine ( A or G) is changed for a (one ring) pyrimidine ( T or C), or vice versa. A transversion can be spontaneous, or it can be caused by ionizing radiation or alkylating agents. It can only be reversed by a spontaneous reversion. Ratio of transitions to transversions Although there are two possible transversions but only one possible transition per base, transition mutations are more likely than transversions because substituting a single ring structure for another single ring structure is more likely than substituting a double ring for a single ring. Also, transitions are less likely to result in amino acid substitutions (due to wobble base pair), and are therefore more likely to persist as "silent substitutions" in populations as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). A transversion usually has a more pronounced effect than a transition because the third nucleotide codo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition (genetics)
Transition, in genetics and molecular biology, refers to a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine ( A ↔ G), or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine ( C ↔ T). Approximately two out of three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are transitions. Transitions can be caused by oxidative deamination and tautomerization. Although there are twice as many possible transversions, transitions appear more often in genomes, possibly due to the molecular mechanisms that generate them. 5-Methylcytosine is more prone to transition than unmethylated cytosine, due to spontaneous deamination. This mechanism is important because it dictates the rarity of CpG islands. See also * Transversion Transversion, in molecular biology, refers to a point mutation in DNA in which a single (two ring) purine ( A or G) is changed for a (one ring) pyrimidine ( T or C), or vice versa. A transversion can be spontaneous, or it can be caused by i ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |