|
Prokaryotic Initiation Factor-1
Bacterial initiation factor 1 is a bacterial initiation factor. IF1 associates with the 30S ribosomal subunit in the A site and prevents an aminoacyl-tRNA from entering. It modulates IF2 binding to the ribosome by increasing its affinity. It may also prevent the 50S The 50s decade ran from January 1, 50, to December 31, 59. It was the sixth decade in the Anno Domini/Common Era, if the nine-year period from 1 AD to 9 AD is considered as a "decade". Significant people * Claudius, Roman Emperor (AD 41� ... subunit from binding, stopping the formation of the 70S subunit. It also contains a β-domain fold common for nucleic acid binding proteins. IF1– IF3 may also perform ribosome recycling. References {{GeneticTranslation Molecular biology Protein biosynthesis Gene expression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Initiation Factor
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationships wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
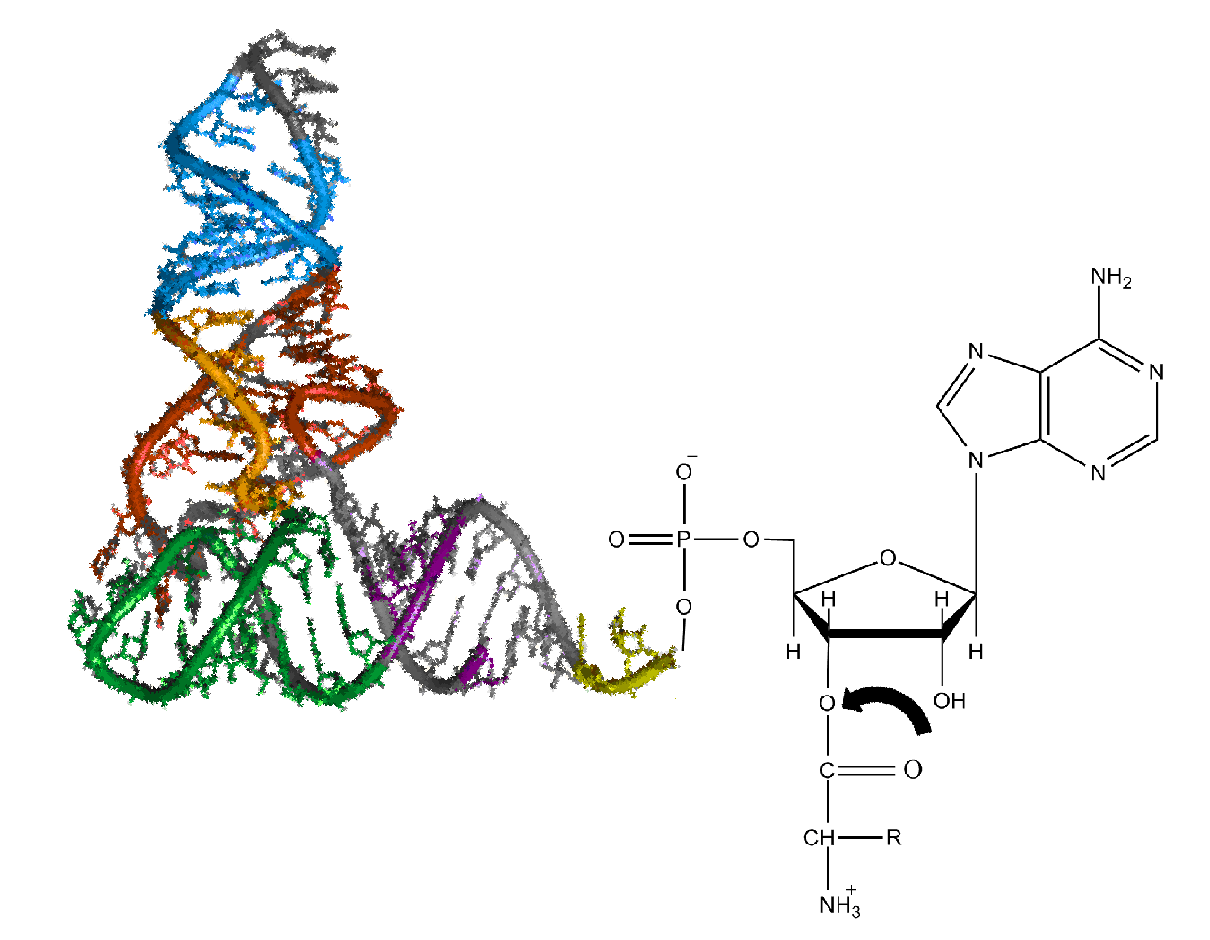
A Site
Ribosomes ( ) are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA, ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and many ribosomal proteins (RPs or r-proteins). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA chain. Ribosomes bind to messenger RNAs and use their sequences for determining the correct sequence of amino acids to generate a given protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA, transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoacyl-tRNA
Aminoacyl-tRNA (also aa-tRNA or charged tRNA) is tRNA to which its cognate amino acid is chemically bonded (charged). The aa-tRNA, along with particular elongation factors, deliver the amino acid to the ribosome for incorporation into the polypeptide chain that is being produced during translation. Alone, an amino acid is not the substrate necessary to allow for the formation of peptide bonds within a growing polypeptide chain. Instead, amino acids must be "charged" or aminoacylated with a tRNA to form their respective aa-tRNA. Every amino acid has its own specific aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, which is utilized to chemically bind to the tRNA that it is specific to, or in other words, "cognate" to. The pairing of a tRNA with its cognate amino acid is crucial, as it ensures that only the particular amino acid matching the anticodon of the tRNA, and in turn matching the codon of the mRNA, is used during protein synthesis. In order to prevent translational errors, in which the wrong am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryotic Initiation Factor-3
In molecular biology, translation initiation factor IF-3 (gene infC) is one of the three factors required for the initiation of protein biosynthesis in bacteria. IF-3 is thought to function as a fidelity factor during the assembly of the ternary initiation complex which consists of the 30S ribosomal subunit, the initiator tRNA and the messenger RNA. IF-3 is a basic protein that binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit. The chloroplast homolog enhances the poly( A, U, G)-dependent binding of the initiator tRNA to its ribosomal 30s subunits. IF1–IF3 may also perform ribosome recycling. IF3 is not universally found in all bacterial species. However, in ''E. coli'', it is required for the 30S subunit to bind to the initiation site in mRNA. In addition, it has several other jobs including the stabilization of free 30S subunits, enables 30S subunits to bind to mRNA and checks for accuracy against the first aminoacyl-tRNA. It also allows for rapid codon-anticodon pairing for the initiato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physical structure of biological macromolecules is known as molecular biology. Molecular biology was first described as an approach focused on the underpinnings of biological phenomena - uncovering the structures of biological molecules as well as their interactions, and how these interactions explain observations of classical biology. In 1945 the term molecular biology was used by physicist William Astbury. In 1953 Francis Crick, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and colleagues, working at Medical Research Council unit, Cavendish laboratory, Cambridge (now the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology), made a double helix model of DNA which changed the entire research scenario. They proposed the DNA structure based on previous research done by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Biosynthesis
Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation or export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences. Protein synthesis can be divided broadly into two phases - transcription and translation. During transcription, a section of DNA encoding a protein, known as a gene, is converted into a template molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This conversion is carried out by enzymes, known as RNA polymerases, in the nucleus of the cell. In eukaryotes, this mRNA is initially produced in a premature form ( pre-mRNA) which undergoes post-transcriptional modifications to produce mature mRNA. The mature mRNA is exported from the cell nucleus via nuclear pores to the cytoplasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |