|
Project MinE
Project MinE is an independent large scale whole genome research project that was initiated by 2 patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and started on World ALS Day, June 21, 2013. The symptoms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are caused by degeneration of motor nerve cells (motor neurons) in the spinal cord, brainstem, and motor cortex. The exact cause of this degeneration is unknown but it is thought that environmental exposures and genetic factors play a role in susceptibility to the disease. In 5-10% of patients the family history is positive for ALS. However, it is not always possible to establish the mode of inheritance in each pedigree and not all familial cases may suffer from a genuine Mendelian or monogenic disorder. Autosomal-dominant mutations in the C9orf72 and the SOD1 gene are found in a substantial number of familial ALS cases. Mutations in other genes (such as VAPB [2], ANG, TARDBP and FUS (gene), FUS) have been reported, but are found at a much lower frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that results in the progressive loss of motor neurons that control voluntary muscles. ALS is the most common type of motor neuron diseases. Early symptoms of ALS include stiff muscles, muscle twitches, and gradual increasing weakness and muscle wasting. ''Limb-onset ALS'' begins with weakness in the arms or legs, while ''bulbar-onset ALS'' begins with difficulty speaking or swallowing. Half of the people with ALS develop at least mild difficulties with thinking and behavior, and about 15% develop frontotemporal dementia. Most people experience pain. The affected muscles are responsible for chewing food, speaking, and walking. Motor neuron loss continues until the ability to eat, speak, move, and finally the ability to breathe is lost. ALS eventually causes paralysis and early death, usually from respiratory failure. Most cases of ALS (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FUS (gene)
RNA-binding protein FUS/TLS (FUused in Sarcoma/Translocated in LipoSarcoma), also known as heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein P2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FUS'' gene. Discovery FUS/TLS was initially identified as a fusion protein (FUS-CHOP) produced as a result of chromosomal translocations in human cancers, especially liposarcomas. In these instances, the promoter and N-terminal part of FUS/TLS is translocated to the C-terminal domain of various DNA-binding transcription factors (e.g. CHOP) conferring a strong transcriptional activation domain onto the fusion proteins. FUS/TLS was independently identified as the hnRNP P2 protein, a subunit of a complex involved in the maturation of pre-mRNA. Structure FUS/TLS is a member of the FET protein family that also includes the EWS protein, the TATA-binding protein TBP-associated factor TAFII68/TAF15, and the Drosophila cabeza/SARF protein. FUS/TLS, EWS and TAF15 have a similar structure, characteris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Genetics
''Nature Genetics'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio. It was established in 1992. It covers research in genetics. The chief editor is Tiago Faial. The journal encompasses genetic and functional genomic studies on human traits and on other model organisms, including mouse, fly, nematode and yeast. Current emphasis is on the genetic basis for common and complex diseases and on the functional mechanism, architecture and evolution of gene networks, studied by experimental perturbation. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 41.379, ranking it 2nd out of 175 journals in the category "Genetics & Heredity". References External links Official websit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurological Disorder
A neurological disorder is any disorder of the nervous system. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms. Examples of symptoms include paralysis, muscle weakness, poor coordination, loss of sensation, seizures, confusion, pain and altered levels of consciousness. There are many recognized neurological disorders, some relatively common, but many rare. They may be assessed by neurological examination, and studied and treated within the specialities of neurology and clinical neuropsychology. Interventions foneurological disordersinclude preventive measures, lifestyle changes, physiotherapy or other therapy, neurorehabilitation, pain management, medication, operations performed by neurosurgeons or a specific diet. The World Health Organization estimated in 2006 that neurological disorders and their sequelae (direct consequences) affect as many as one billion people worldwide, and identified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Next-generation Sequencing
Massive parallel sequencing or massively parallel sequencing is any of several high-throughput approaches to DNA sequencing using the concept of massively parallel processing; it is also called next-generation sequencing (NGS) or second-generation sequencing. Some of these technologies emerged between 1994 and 1998 and have been commercially available since 2005. These technologies use miniaturized and parallelized platforms for sequencing of 1 million to 43 billion short reads (50 to 400 bases each) per instrument run. Many NGS platforms differ in engineering configurations and sequencing chemistry. They share the technical paradigm of massive parallel sequencing via spatially separated, clonally amplified DNA templates or single DNA molecules in a flow cytometry, flow cell. This design is very different from that of Sanger sequencing—also known as capillary sequencing or first-generation sequencing—which is based on electrophoretic separation of chain-termination products produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated with incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imputation (genetics)
Imputation in genetics refers to the statistical inference of unobserved genotypes. It is achieved by using known haplotypes in a population, for instance from the HapMap or the 1000 Genomes Project in humans, thereby allowing to test for association between a trait of interest (e.g. a disease) and experimentally untyped genetic variants, but whose genotypes have been statistically inferred ("imputed"). Genotype imputation is usually performed on SNPs, the most common kind of genetic variation. Genotype imputation hence helps tremendously in narrowing down the location of probably causal variants in genome-wide association studies, because it increases the SNP density (the genome size remains constant, but the number of genetic variants increases) and thus reduces the distance between two adjacent SNPs. Context In genetic epidemiology and quantitative genetics, researchers aim at identifying genomic locations where variation between individuals is associated with variation in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplotype
A haplotype ( haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent. Many organisms contain genetic material ( DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA organized in two sets of pairwise similar chromosomes. The offspring gets one chromosome in each pair from each parent. A set of pairs of chromosomes is called diploid and a set of only one half of each pair is called haploid. The haploid genotype (haplotype) is a genotype that considers the singular chromosomes rather than the pairs of chromosomes. It can be all the chromosomes from one of the parents or a minor part of a chromosome, for example a sequence of 9000 base pairs. However, there are other uses of this term. First, it is used to mean a collection of specific alleles (that is, specific DNA sequences) in a cluster of tightly linked genes on a chromosome that are likely to be inherited together—that is, they are likely to be con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whole Genome Sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast. Whole genome sequencing has largely been used as a research tool, but was being introduced to clinics in 2014. In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data may be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of DNA sequencing, gene sequencing at Single-nucleotide polymorphism, SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
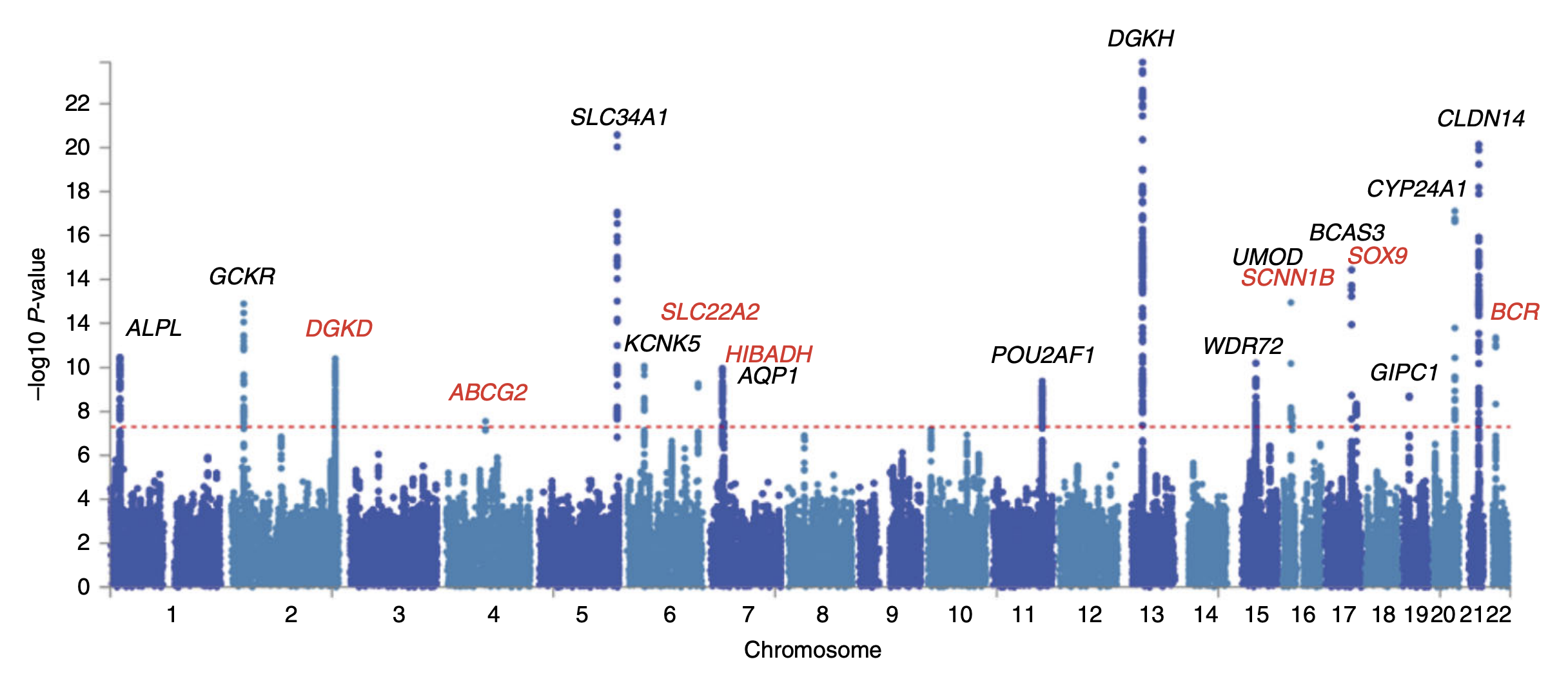
Genome-wide Association Study
In genomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), also known as whole genome association study (WGA study, or WGAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of Single-nucleotide polymorphism, genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and traits like major human diseases, but can equally be applied to any other genetic variants and any other organisms. When applied to human data, GWA studies compare the DNA of participants having varying phenotypes for a particular trait or disease. These participants may be people with a disease (cases) and similar people without the disease (controls), or they may be people with different phenotypes for a particular trait, for example blood pressure. This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as oppose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the nuclear genome and the mitochondrial genome. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA sequences and various types of DNA that does not encode proteins. The latter is a diverse category that includes DNA coding for non-translated RNA, such as that for ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, ribozymes, small nuclear RNAs, and several types of regulatory RNAs. It also includes promoters and their associated gene-regulatory elements, DNA playing structural and replicatory roles, such as scaffolding regions, telomeres, centromeres, and origins of replication, plus large numbers of transposable elements, inserted viral DNA, non-functional pseudogenes and simple, highly-repetitive sequences. Introns make up a large percentage of non-coding DNA. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
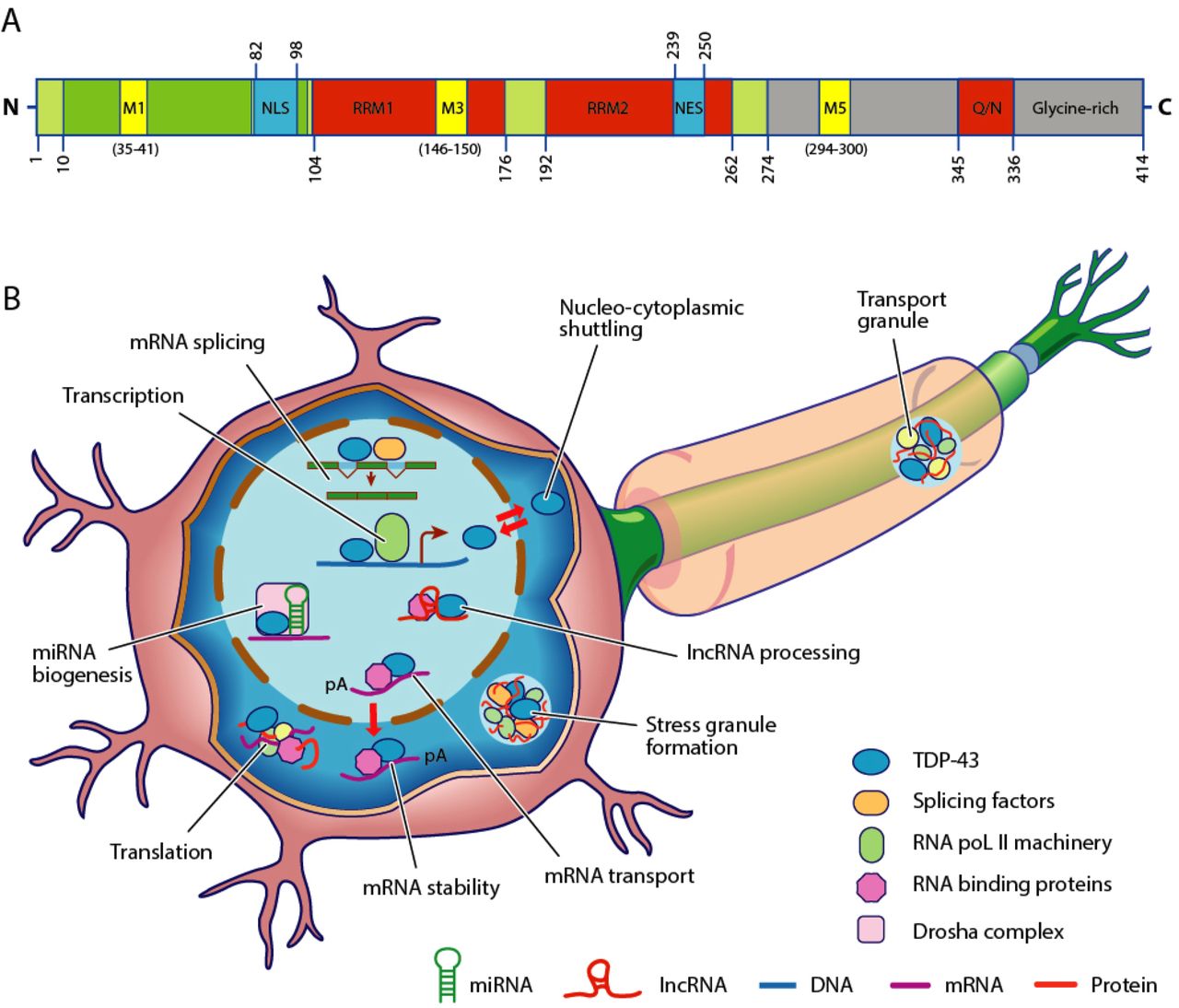
TARDBP
TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43, transactive response DNA binding protein 43 kDa) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TARDBP'' gene. Structure TDP-43 is 414 amino acid residues long. It consists of 4 domains: an N-terminal domain spanning residues 1-76 (NTD) with a well-defined fold that has been shown to form a dimer or oligomer; 2 highly conserved folded RNA recognition motifs spanning residues 106-176 (RRM1) and 191-259 (RRM2), respectively, required to bind target RNA and DNA; an unstructured C-terminal domain encompassing residues 274-414 (CTD), which contains a glycine-rich region, is involved in protein-protein interactions, and harbors most of the mutations associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The entire protein devoid of large solubilising tags has been purified. The full-length protein is a dimer. The dimer is formed due to a self-interaction between two NTD domains, where the dimerisation can be propagated to form higher-order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |