|
Prodilidine
Prodilidine is an opioid analgesic which is a ring-contracted analogue of prodine. It has around the same analgesic efficacy as codeine, but is only around 1/3 the potency (100mg prodilidine is equivalent to 3mg oral morphine). It has little abuse potential. See also * Profadol Profadol (CI-572) is an opioid analgesic which was developed in the 1960s by Parke-Davis. It acts as a mixed agonist-antagonist of the μ-opioid receptor. The analgetic potency is about the same as of pethidine (meperidine), the antagonistic eff ... References Opioids Propionate esters Pyrrolidines Mu-opioid receptor agonists {{analgesic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioids
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, reversing opioid overdose, and suppressing cough. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for veterinary use. Opioids are also frequently used non-medically for their euphoric effects or to prevent withdrawal. Opioids can cause death and have been used for executions in the United States. Side effects of opioids may include itchiness, sedation, nausea, respiratory depression, constipation, and euphoria. Long-term use can cause tolerance, meaning that increased doses are required to achieve the same effect, and physical dependence, meaning that abruptly discontinuing the drug leads to unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. The euphoria attracts recreational use, and frequent, escalating recreational use of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, reversing opioid overdose, and suppressing cough. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for veterinary use. Opioids are also frequently used non-medically for their euphoric effects or to prevent withdrawal. Opioids can cause death and have been used for executions in the United States. Side effects of opioids may include itchiness, sedation, nausea, respiratory depression, constipation, and euphoria. Long-term use can cause tolerance, meaning that increased doses are required to achieve the same effect, and physical dependence, meaning that abruptly discontinuing the drug leads to unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. The euphoria attracts recreational use, and frequent, escalating recreational use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
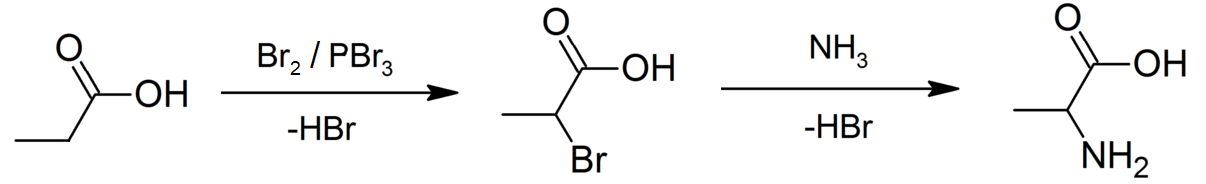
Profadol
Profadol (CI-572) is an opioid analgesic which was developed in the 1960s by Parke-Davis. It acts as a mixed agonist-antagonist of the μ-opioid receptor. The analgetic potency is about the same as of pethidine (meperidine), the antagonistic effect is 1/50 of nalorphine. Synthesis The Knoevenagel condensation between 3'-Methoxybutyrophenone 1550-06-1and Ethyl cyanoacetate gives (1). Conjugate addition of cyanide gives (2). Hydrolysis of both nitrile groups, saponification of the ester and decarboxylation gives the diacidCID:164137621(3). Imide formation occurs upon treatment with methylamine giving 3-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-1-methyl-3-propylpyrrolidine-2,5-dioneCID:163444474(4). Reduction of the imide by lithium aluminium hydride gave 505-32-429369-01-5] (5). Demethylation completed the synthesis of Profadol (6). See also * BDPC, Bromadol * C-8813 * Ciramadol * Faxeladol * Prodilidine * Tapentadol * Tramadol Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It is typically used to induce cooperation with a medical procedure. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in some instances eliminate, sensation, although analgesia and anesthesia are neurophysiologically overlapping and thus various drugs have both analgesic and anesthetic effects. Analgesic choice is also determined by the type of pain: For neuropathic pain, traditional analgesics are less effective, and there is often benefit from classes of drugs that are not normally considered analgesics, such as tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants. Various analgesics, such as many NSAIDs, are available over the counter in most countries, whereas various others are prescription drugs owing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodine
Prodine (trade names Prisilidine and Nisentil) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of pethidine (meperidine). It was developed in Germany in the late 1940s. There are two isomers of the trans form of prodine, alphaprodine and betaprodine. Both exhibit optical isomerism and alphaprodine and betaprodine are racemates. Alphaprodine is closely related to desomorphine in steric configuration. The cis form also has active isomers but none are used in medicine. Betaprodine is around five times more potent than alphaprodine but is metabolized more rapidly, and only alphaprodine was developed for medicinal use. It has similar activity to pethidine, but with a more rapid onset and shorter duration of effects. Betaprodine produces more euphoria and side effects than alphaprodine at all dose levels, and it was found that 5 to 10 mg of betaprodine is equivalent to 25 to 40 mg of alphaprodine. Testing in rats showed alphaprodine to be 97% the strength of morphine via the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically used to treat mild to moderate degrees of pain. Greater benefit may occur when combined with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Evidence does not support its use for acute cough suppression in children or adults. In Europe, it is not recommended as a cough medicine in those under 12 years of age. It is generally taken by mouth. It typically starts working after half an hour, with maximum effect at two hours. Its effects last for about four to six hours. Codeine exhibits abuse potential similar to other opioid medications. Common side effects include vomiting, constipation, itchiness, lightheadedness, and drowsiness. Serious side effects may include breathing difficult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abuse Potential
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, medical and criminal justice contexts. In some cases, criminal or anti-social behaviour occurs when the person is under the influence of a drug, and long-term personality changes in individuals may also occur. In addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, the use of some drugs may also lead to criminal penalties, although these vary widely depending on the local jurisdiction.. Drugs most often associated with this term include: Ethanol, alcohol, Substituted amphetamine, amphetamines, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, cannabis (drug), cannabis, cocaine, hallucinogens (although there is no known Psychedelic drug, ''psychedelic'', one of the three categories of Hallucinogen, hallucinogens, that has been found to have any add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionate Esters
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2CO2H. It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion CH3CH2CO2− as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas established all the acids to be the same compound, which he called propionic acid, from the Greek words πρῶτος (prōtos), meaning ''first'', and πίων (piōn), meaning ''fat'', because it is the smallest H(CH2)''n''COOH acid that exhibits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrolidines
Pyrrolidine, also known as tetrahydropyrrole, is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)4NH. It is a cyclic secondary amine, also classified as a saturated heterocycle. It is a colourless liquid that is miscible with water and most organic solvents. It has a characteristic odor that has been described as "ammoniacal, fishy, shellfish-like". In addition to pyrrolidine itself, many substituted pyrrolidines are known. Production and synthesis Industrial production Pyrrolidine is prepared industrially by the reaction of 1,4-butanediol and ammonia at a temperature of 165–200 °C and a pressure of 17–21 MPa in the presence of a cobalt- and nickel oxide catalyst, which is supported on alumina. : The reaction is carried out in the liquid phase in a continuous tube- or tube bundle reactor, which is operated in the cycle gas method. The catalyst is arranged as a fixed-bed and the conversion is carried out in the downflow mode. The product is obtained after mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |