|
Process-based Management
Process-based management is a management approach that views a business as a collection of processes, managed to achieve a desired result."''Process-based Management''" Barron's Business Guides: Dictionary of Accounting Terms, Jae K. Shim et al., Barron's Educational Series, 2014. Credo Reference, Accessed 09 Oct 2016. The processes are managed and improved by the organisation in purpose of achieving their vision, mission and core value. A clear correlation between processes and the vision supports the company to plan strategies, build a business structure and use sufficient resources that are required to achieve success in the long run. From a process perspective, an organisation regards its business as a system of vision-achieving vertical processes rather than specific activities and tasks of individual functions. (19:25) The system is not a method or tool for a particular process, but a holistic approach to manage all the processes in one organisation. Therefore, to manage proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goal
A goal is an idea of the future or desired result that a person or a group of people envision, plan and commit to achieve. People endeavour to reach goals within a finite time by setting deadlines. A goal is roughly similar to a purpose or aim, the anticipated result which guides reaction, or an end, which is an object, either a physical object or an abstract object, that has intrinsic value. Goal setting Goal-setting theory was formulated based on empirical research and has been called one of the most important theories in organizational psychology. Edwin A. Locke and Gary P. Latham, the fathers of goal-setting theory, provided a comprehensive review of the core findings of the theory in 2002. In summary, Locke and Latham found that specific, difficult goals lead to higher performance than either easy goals or instructions to "do your best", as long as feedback about progress is provided, the person is committed to the goal, and the person has the ability and knowledge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowchart
A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents a workflow or process. A flowchart can also be defined as a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step approach to solving a task. The flowchart shows the steps as boxes of various kinds, and their order by connecting the boxes with arrows. This diagrammatic representation illustrates a solution model to a given problem. Flowcharts are used in analyzing, designing, documenting or managing a process or program in various fields. * ''Document flowcharts'', showing controls over a document-flow through a system * ''Data flowcharts'', showing controls over a data-flow in a system * ''System flowcharts'', showing controls at a physical or resource level * ''Program flowchart'', showing the controls in a program within a system Notice that every type of flowchart focuses on some kind of control, rather than on the particular flow itself. However, there are some different classifications. For example, Andrew Veronis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Process Modeling
Business process modeling (BPM) in business process management and systems engineering is the activity of process modeling, representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current business processes may be analyzed, improved, and automated. BPM is typically performed by business analysts, who provide expertise in the modeling discipline; by subject matter experts, who have specialized knowledge of the processes being modeled; or more commonly by a team comprising both. Alternatively, the process model can be derived directly from events' logs using process mining tools. The business objective is often to increase process speed or reduce cycle time; to increase quality; or to reduce costs, such as labor, materials, scrap, or capital costs. In practice, a management decision to invest in business process modeling is often motivated by the need to document requirements for an information technology project. Change management programs are typically involved to put any improved b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to attain strategic goals. It may also extend to control mechanisms for guiding the implementation of the strategy. Strategic planning became prominent in corporations during the 1960s and remains an important aspect of strategic management. It is executed by strategic planners or strategists, who involve many parties and research sources in their analysis of the organization and its relationship to the environment in which it competes. ''Strategy'' has many definitions, but it generally involves setting strategic goals, determining actions to achieve the goals, setting a timeline, and mobilizing resources to execute the actions. A strategy describes how the ends (goals) will be achieved by the means (resources) in a given span of time. Often, Strategic Planning is long term and organizational action steps are established from two to five year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Management
Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time, and budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet pre-defined objectives. The objective of project management is to produce a complete project which complies with the client's objectives. In many cases, the objective of project management is also to shape or reform the client's brief to feasibly address the client's objectives. Once the client's objectives are clearly established, they should influence all decisions made by other people involved in the project – for example, project managers, designers, contractors, and subcontractors. Ill-defined or too tightly prescribed project management objectives are detrimental to decision-maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gap Analysis
In management literature, gap analysis involves the comparison of actual performance with potential or desired performance. If an organization does not make the best use of current resources, or forgoes investment in capital or technology, it may produce or perform below an idealized potential. This concept is similar to an economy's production being below the production possibilities frontier. Gap analysis identifies gaps between the optimized allocation and integration of the inputs (resources), and the current allocation-level. This reveals areas that can be improved. Gap analysis involves determining, documenting and improving the difference between business requirements and current capabilities. Gap analysis naturally flows from benchmarking and from other assessments. Once the general expectation of performance in an industry is understood, it is possible to compare that expectation with the company's current level of performance. This comparison becomes the gap analysis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
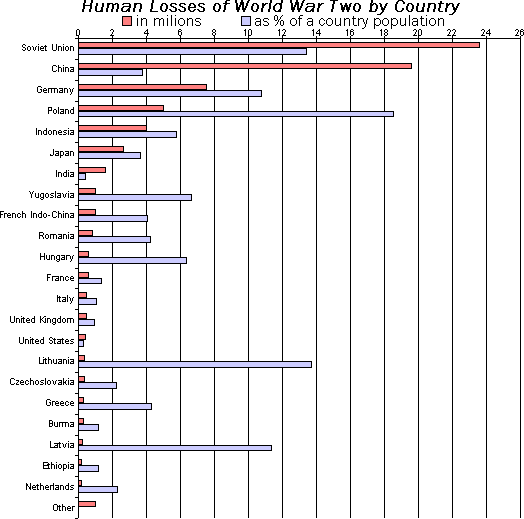
Bar Chart
A bar chart or bar graph is a chart or graph that presents categorical data with rectangular bars with heights or lengths proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. A vertical bar chart is sometimes called a column chart. A bar graph shows comparisons among discrete categories. One axis of the chart shows the specific categories being compared, and the other axis represents a measured value. Some bar graphs present bars clustered in groups of more than one, showing the values of more than one measured variable. History Many sources consider William Playfair (1759-1824) to have invented the bar chart and the ''Exports and Imports of Scotland to and from different parts for one Year from Christmas 1780 to Christmas 1781'' graph from his ''The Commercial and Political Atlas'' to be the first bar chart in history. Diagrams of the velocity of a constantly accelerating object against time published in ''The Latitude of Forms'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pie Chart
A pie chart (or a circle chart) is a circular Statistical graphics, statistical graphic, which is divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportion. In a pie chart, the arc length of each slice (and consequently its central angle and area) is Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the quantity it represents. While it is named for its resemblance to a pie which has been sliced, there are variations on the way it can be presented. The earliest known pie chart is generally credited to William Playfair's ''Statistical Breviary'' of 1801.Spence (2005)Tufte, p. 44 Pie charts are very widely used in the business world and the mass media.Cleveland, p. 262 However, they have been criticized,Wilkinson, p. 23. and many experts recommend avoiding them,Tufte, p. 178.van Belle, p. 160–162.Stephen Few"Save the Pies for Dessert" August 2007, Retrieved 2010-02-02Steve Fento"Pie Charts Are Bad"/ref> as research has shown it is difficult to compare different sections of a given pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service-level Agreement
A service-level agreement (SLA) is a commitment between a service provider and a customer. Particular aspects of the service – quality, availability, responsibilities – are agreed between the service provider and the service user. The most common component of an SLA is that the services should be provided to the customer as agreed upon in the contract. As an example, Internet service providers and telcos will commonly include service level agreements within the terms of their contracts with customers to define the level(s) of service being sold in plain language terms. In this case, the SLA will typically have a technical definition of ''mean time between failures'' (MTBF), ''mean time to repair'' or ''mean time to recovery'' (MTTR); identifying which party is responsible for reporting faults or paying fees; responsibility for various data rates; throughput; jitter; or similar measurable details. Overview A service-level agreement is an agreement between two or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a short statement of why an organization exists, what its overall goal is, the goal of its operations: what kind of product or service it provides, its primary customers or market, and its geographical region of operation. It may include a short statement of such fundamental matters as the organization's values or philosophies, a business's main competitive advantages, or a desired future state—the "vision". Historically it is associated with Christian religious groups; indeed, for many years, a missionary was assumed to be a person on a specifically religious mission. The word "mission" dates from 1598, originally of Jesuits sending ("missio", Latin for "act of sending") members abroad. A mission is not simply a description of an organization by an external party, but an expression, made by an organization's leaders, of their desires and intent for the organization. A mission statement aims to communicate the organisation's purpose and direction to it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customer Service
Customer service is the assistance and advice provided by a company to those people who buy or use its products or services. Each industry requires different levels of customer service, but in the end, the idea of a well-performed service is that of increasing revenues. The perception of success of the customer service interactions is dependent on employees "who can adjust themselves to the personality of the customer". Customer service is often practiced in a way that reflects the strategies and values of a firm. Good quality customer service is usually measured through customer retention. Customer service for some firms is part of the firm’s intangible assets and can differentiate it from others in the industry. One good customer service experience can change the entire perception a customer holds towards the organization. Customer service does not only focus on the external aspect of the organization, but also the internal relations that facilitate the business activity. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intellectual Capital
Intellectual capital is the result of mental processes that form a set of intangible objects that can be used in economic activity and bring income to its owner (organization), covering the competencies of its people ( human capital), the value relating to its relationships (relational capital), and everything that is left when the employees go home (structural capital), of which intellectual property (IP) is but one component. It is the sum of everything everybody in a company knows that gives it a competitive edge. The term is used in academia in an attempt to account for the value of intangible assets not listed explicitly on a company's balance sheets. On a national level, intellectual capital refers to national intangible capital (NIC). A second meaning that is used in academia and was adopted in large corporations is focused on the recycling of knowledge via knowledge management and intellectual capital management (ICM). Creating, shaping and updating the stock of intellectua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)