|
Problem Of Future Contingents
Future contingent propositions (or simply, future contingents) are statements about states of affairs in the future that are ''contingent:'' neither necessarily true nor necessarily false. The problem of future contingents seems to have been first discussed by Aristotle in chapter 9 of his ''On Interpretation'' (''De Interpretatione''), using the famous sea-battle example. Roughly a generation later, Diodorus Cronus from the Megarian school of philosophy stated a version of the problem in his notorious ''master argument''. The problem was later discussed by Leibniz. The problem can be expressed as follows. Suppose that a sea-battle will not be fought tomorrow. Then it was also true yesterday (and the week before, and last year) that it will not be fought, since any true statement about what will be the case in the future was also true in the past. But all past truths are now necessary truths; therefore it is now necessarily true in the past, prior and up to the original statement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miracle
A miracle is an event that is inexplicable by natural or scientific lawsOne dictionary define"Miracle"as: "A surprising and welcome event that is not explicable by natural or scientific laws and is therefore considered to be the work of a divine agency." and accordingly gets attributed to some supernatural or praeternatural cause. Various religions often attribute a phenomenon characterized as miraculous to the actions of a supernatural being, (especially) a deity, a magician, a miracle worker, a saint, or a religious leader. Informally, English-speakers often use the word ''miracle'' to characterise any beneficial event that is statistically unlikely but not contrary to the laws of nature, such as surviving a natural disaster, or simply a "wonderful" occurrence, regardless of likelihood (e.g. "the miracle of childbirth"). Some coincidences may be seen as miracles. A true miracle would, by definition, be a non-natural phenomenon, leading many writers to dismiss miracles as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Łukasiewicz
Jan Łukasiewicz (; 21 December 1878 – 13 February 1956) was a Polish logician and philosopher who is best known for Polish notation and Łukasiewicz logic His work centred on philosophical logic, mathematical logic and history of logic. He thought innovatively about traditional propositional logic, the principle of non-contradiction and the law of excluded middle, offering one of the earliest systems of many-valued logic. Contemporary research on Aristotelian logic also builds on innovative works by Łukasiewicz, which applied methods from modern logic to the formalization of Aristotle's syllogistic. The Łukasiewicz approach was reinvigorated in the early 1970s in a series of papers by John Corcoran and Timothy Smiley that inform modern translations of ''Prior Analytics'' by Robin Smith in 1989 and Gisela Striker in 2009. Łukasiewicz is regarded as one of the most important historians of logic. Life He was born in Lemberg in Austria-Hungary (now Lviv, Ukraine; pl, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Many-valued Logic
Many-valued logic (also multi- or multiple-valued logic) refers to a propositional calculus in which there are more than two truth values. Traditionally, in Aristotle's logical calculus, there were only two possible values (i.e., "true" and "false") for any proposition. Classical two-valued logic may be extended to ''n''-valued logic for ''n'' greater than 2. Those most popular in the literature are three-valued (e.g., Łukasiewicz's and Kleene's, which accept the values "true", "false", and "unknown"), four-valued, nine-valued, the finite-valued (finitely-many valued) with more than three values, and the infinite-valued (infinitely-many-valued), such as fuzzy logic and probability logic. History It is wrong that the first known classical logician who did not fully accept the law of excluded middle was Aristotle (who, ironically, is also generally considered to be the first classical logician and the "father of wo-valuedlogic"). In fact, Aristotle did not contest the univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Individual
An individual is that which exists as a distinct entity. Individuality (or self-hood) is the state or quality of being an individual; particularly (in the case of humans) of being a person unique from other people and possessing one's own Maslow's hierarchy of needs, needs or goals, rights and moral responsibility, responsibilities. The concept of an individual features in diverse fields, including biology, law, and philosophy. Etymology From the 15th century and earlier (and also today within the fields of statistics and metaphysics) ''individual'' meant "divisible, indivisible", typically describing any numerically singular thing, but sometimes meaning "a person". From the 17th century on, ''individual'' has indicated separateness, as in individualism. Law Although individuality and individualism are commonly considered to mature with age/time and experience/wealth, a sanity, sane adult human, human being is usually considered by the State (polity), state as an "individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concept
Concepts are defined as abstract ideas. They are understood to be the fundamental building blocks of the concept behind principles, thoughts and beliefs. They play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied by several disciplines, such as linguistics, psychology, and philosophy, and these disciplines are interested in the logical and psychological structure of concepts, and how they are put together to form thoughts and sentences. The study of concepts has served as an important flagship of an emerging interdisciplinary approach called cognitive science. In contemporary philosophy, there are at least three prevailing ways to understand what a concept is: * Concepts as mental representations, where concepts are entities that exist in the mind (mental objects) * Concepts as abilities, where concepts are abilities peculiar to cognitive agents (mental states) * Concepts as Fregean senses, where concepts are abstract objects, as opposed to mental ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monad (philosophy)
The term ''monad'' () is used in some cosmic philosophy and cosmogony to refer to a most basic or original substance. As originally conceived by the Pythagoreans, the Monad is the Supreme Being, divinity or the totality of all things. In the philosophy of Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, there are infinite monads, which are the basic and immaterial elementary particles, or simplest units, that make up the universe. Historical background According to Hippolytus, the worldview was inspired by the Pythagoreans, who called the first thing that came into existence the "monad", which begat (bore) the dyad (from the Greek word for two), which begat the numbers, which begat the point, begetting lines or finiteness, etc. It meant divinity, the first being, or the totality of all beings, referring in cosmogony (creation theories) variously to source acting alone and/or an indivisible origin and equivalent comparators. Pythagorean and Platonic philosophers like Plotinus and Porphyry cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance Theory
Substance theory, or substance–attribute theory, is an ontological theory positing that objects are constituted each by a ''substance'' and properties borne by the substance but distinct from it. In this role, a substance can be referred to as a ''substratum'' or a ''thing-in-itself''. ''Substances'' are particulars that are ontologically independent: they are able to exist all by themselves. Another defining feature often attributed to substances is their ability to ''undergo changes''. Changes involve something existing ''before'', ''during'' and ''after'' the change. They can be described in terms of a persisting substance gaining or losing properties. ''Attributes'' or ''properties'', on the other hand, are entities that can be exemplified by substances. Properties characterize their bearers, they express what their bearer is like. ''Substance'' is a key concept in ontology and metaphysics, which may be classified into monist, dualist, or pluralist varieties according to how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject (philosophy)
A subject is a being who has a unique consciousness and/or unique personal experiences, or an entity that has a relationship with another entity that exists outside itself (called an "object"). A ''subject'' is an observer and an ''object'' is a thing observed. This concept is especially important in Continental philosophy, where 'the subject' is a central term in debates over the nature of the self. The nature of the subject is also central in debates over the nature of subjective experience within the Anglo-American tradition of analytical philosophy. The sharp distinction between subject and object corresponds to the distinction, in the philosophy of René Descartes, between thought and extension. Descartes believed that thought (subjectivity) was the essence of the mind, and that extension (the occupation of space) was the essence of matter. German idealism ''Subject'' as a key-term in thinking about human consciousness began its career with the German idealists, in respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Sufficient Reason
The principle of sufficient reason states that everything must have a reason or a cause. The principle was articulated and made prominent by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, with many antecedents, and was further used and developed by Arthur Schopenhauer and Sir William Hamilton, 9th Baronet. History The modern formulation of the principle is usually ascribed to early Enlightenment philosopher Gottfried Leibniz. Leibniz formulated it, but was not an originator.See chapter on Leibniz and Spinoza in A. O. Lovejoy, ''The Great Chain of Being''. The idea was conceived of and utilized by various philosophers who preceded him, including Anaximander, Parmenides, Archimedes, Plato and Aristotle,Hamilton 1860:66 Cicero, Avicenna, Thomas Aquinas, and Spinoza. One often pointed to is in Anselm of Canterbury: his phras''quia Deus nihil sine ratione facit''and the formulation of the ontological argument for the existence of God. A clearer connection is with the cosmological argument for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compossible
Compossibility is a philosophical concept from Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz. According to Leibniz, a complete individual thing (for example a person) is characterized by all its properties, and these determine its relations with other individuals. The existence of one individual may negate the possibility of the existence of another. A possible world is made up of individuals that are compossible—that is, individuals that can exist together. Composability and possible worlds Leibniz indicates that a world is a set of compossible things, however, that a world is a kind of collection of things that God could bring into existence. For not even God can bring into existence a world in which there is some contradiction among its members or their properties. When Leibniz speaks of a possible world, he means a set of compossible, finite things that God could have brought into existence if he were not constrained by the goodness that is part of his nature. The actual world, on the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
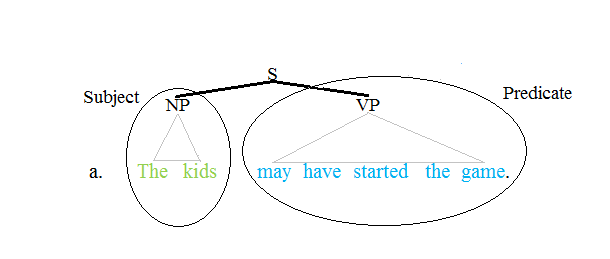
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in one of two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject, and the other views it as just the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake''. By the second definition, the predicate of the same sentence is just the content verb ''likes'', whereby ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the arguments of this predicate. Differences between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of predicates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |