|
Prince Takechi
was a member of the royal family in Japan during the Asuka period. He was the eldest son of Emperor Tenmu. He fought on the side of his father in the Jinshin War (672), a battle of succession, which resulted in his father becoming Emperor. At the age of 19, he was dispatched by his father to the battle front in what is now Fuwa District, Mino Province (now the southern part of Gifu Prefecture) as vanguard and general commander. In 679, while in Yoshino with his father, he swore to an oath of cooperation with his siblings. When Empress Jitō ascended to the throne in 686 he became the ''Daijō-daijin'' and handled government affairs. He died suddenly in 696, thought by some to be an assassination. He loved Princess Tōchi (his elder half-sister, Prince Ōtomo's wife). He left only three ''waka'' poems during his whole life, but they were all poetry offered to her. Family Parents *Father: Emperor Tenmu (天武天皇, c. 631 – 1 October 686) *Mother: Munakata no Amako-no-irats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
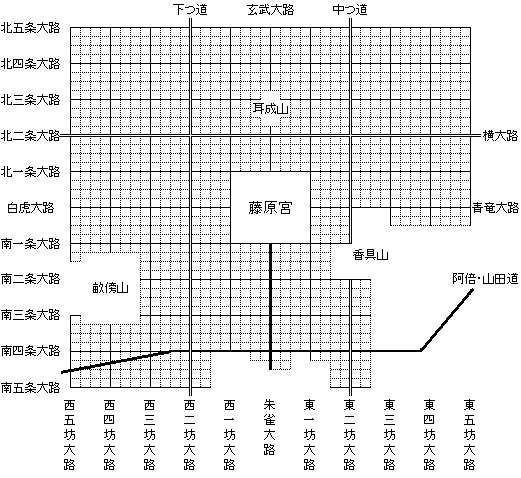
Fujiwara-kyō
was the Imperial capital of Japan for sixteen years, between 694 and 710. It was located in Yamato Province (present-day Kashihara, Nara, Kashihara in Nara Prefecture), having been moved from nearby Asuka, Yamato, Asuka. However, the name Fujiwara-kyō was never used in the ''Nihon Shoki''. During those times it was recorded as Aramashi-kyō (新益京). As of 2006, ongoing excavations have revealed construction on the site of Fujiwara-kyō as early as 682, near the end of the reign of Emperor Tenmu. With a brief halt upon Emperor Tenmu's death, construction resumed under Empress Jitō, who officially moved the capital in 694. Fujiwara-kyō remained the capital for the reigns of Emperor Monmu and Empress Genmei, but in 710 the Imperial court moved to the Heijō Palace in Nara, Nara, Nara, beginning the Nara period. History Fujiwara was Japan's first capital built in a grid pattern on the Chinese model (条坊制 ''jōbō-sei''); recent investigation has revealed that the city c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoshino, Nara
is a town located in Yoshino District, Nara Prefecture, Japan. As of September 1, 2007, the town had an estimated population of 6,337 and a density of . The total area was . Geography The town of Yoshino is located in the northern portion of Yoshino District. Most of the area is mountainous, but the section along the Yoshino River is somewhat flatter and contains most of the town's roads, train tracks and houses. * Mountains: Yoshino Mountain * Rivers: Yoshino River * Lakes: Lake Tsuburo The most well-known area within the town is Yoshino Mountain, famous for its many thousands of sakura trees; much poetry has been written on the subject by several famous authors, including Chiyo and Uejima Onitsura. These flowering cherry trees were planted in four groves at different altitudes, in part so that the trees would be visible coming into bloom at different times in the spring. An account of Yoshino written in about 1714 explained that, on their climb to the top, travelers would be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
650s Births , Gobi 65, or Paneer 65
{{Numberdis ...
65 may refer to: * 65 (number) * ''65'' (film), an upcoming American science fiction thriller film * One of the years 65 BC, AD 65, 1965, 2065 * A type of dish in Indian cuisine, such as Chicken 65 Chicken 65 is a spicy, deep-fried chicken dish originating from Hotel Buhari, Chennai, India, as an entrée, or quick snack. The flavour of the dish can be attributed to red chillies, but the exact set of ingredients for the recipe can vary. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Princes
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Genmei
, also known as Empress Genmyō, was the 43rd monarch of Japan, Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 元明天皇 (43) retrieved August 22, 2013. according to the traditional order of succession. Genmei's reign spanned the years 707 through 715 CE. In the history of Japan, Genmei was the fourth of eight women to take on the role of empress regnant. The three female monarchs before Genmei were Suiko, Kōgyoku/Saimei, and Jitō. The four women sovereigns reigning after Genmei were Genshō, Kōken/Shōtoku, Meishō, and Go-Sakuramachi. Traditional narrative Before her ascension to the Chrysanthemum Throne, her personal name (''imina'') was Abe''-hime''.Brown, p. 271. Empress Genmei was the fourth daughter of Emperor Tenji; and she was a younger sister of Empress Jitō by a different mother. Her mother, Mei-no-Iratsume (also known as Soga''-hime''), was a daughter of ''Udaijin'' Soga-no-Kura-no-Yamada-no-Ishikawa-no-Maro (also known as Soga Yamada-no Ō-omi). Events o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Tenji
, also known as Emperor Tenchi, was the 38th emperor of Japan, Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'')天智天皇 (38)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession.Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1959). ''The Imperial House of Japan'', p. 52. Tenji's reign spanned the years from 661 through 672.Titsingh, Isaac. (1834). Traditional narrative He was the son of Emperor Jomei, but was preceded as ruler by his mother Empress Saimei. Prior to his accession, he was known as . Events of Tenji's life As prince, Naka no Ōe played a crucial role in ending the near-total control the Soga clan had over the imperial family. In 644, seeing the Soga continue to gain power, he conspired with Nakatomi no Kamatari and Soga no Kurayamada no Ishikawa no Maro to assassinate Soga no Iruka in what has come to be known as the Isshi Incident. Although the assassination did not go exactly as planned, Iruka was killed, and his father and predecessor, Soga no Emishi, committed suicide soon afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kōkyū
is the section of a Japanese Imperial Palace called the where the Imperial Family and court ladies lived. Many cultured women gathered as wives of Emperors, and court ladies, as well as the maids for these women; court officials often visited these women for influence, literary charm, or romances. Significant contributions to the literature of Japan were created in the Kōkyū during this period: works such as '' The Tale of Genji'' by Murasaki Shikibu, ''The Pillow Book'' by Sei Shōnagon, and many anthologies of ''waka'' poems. Conflated definitions The term ''"Dairi"'' refers not only to the buildings in which the Japanese Imperial family resided; it also refers indirectly to the women of the Imperial family (the Kōkyū), to the Imperial court of Japan, or as an indirect (now archaic) way of referring to the Emperor himself. The names of the several gates in the walls surrounding the Imperial grounds refer not only to the specific wall-openings themselves; these names were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waka (poetry)
is a type of poetry in classical Japanese literature. Although ''waka'' in modern Japanese is written as , in the past it was also written as (see Wa, an old name for Japan), and a variant name is . Etymology The word ''waka'' has two different but related meanings: the original meaning was "poetry in Japanese" and encompassed several genres such as ''chōka'' and ''sedōka'' (discussed below); the later, more common definition refers to poetry in a 5-7-5-7-7 metre. Up to and during the compilation of the ''Man'yōshū'' in the eighth century, the word ''waka'' was a general term for poetry composed in Japanese, and included several genres such as , , and . However, by the time of the '' Kokinshūs compilation at the beginning of the tenth century, all of these forms except for the ''tanka'' and ''chōka'' had effectively gone extinct, and ''chōka'' had significantly diminished in prominence. As a result, the word ''waka'' became effectively synonymous with ''tanka'', and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Kōbun
was the 39th emperor of Japan, Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 弘文天皇 (39)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession.Ponsonby-Fane, Richard. (1959). ''The Imperial House of Japan'', p. 53. Kōbun's reign lasted only a few months in 672. Traditional narrative Emperor Kōbun was named the 39th emperor by the Meiji government in 1870; and since the late 19th century, he is known by the posthumous name accorded to him by Meiji scholars. In his lifetime, he was known as Prince Ōtomo (大友皇子, ''Ōtomo no ōji''). He was the favorite son of Emperor Tenji; and he was also the first to have been accorded the title of ''Daijō-daijin.'' Contemporary historians now place the reign of Emperor Kōbun between the reigns of Emperor Tenji and Emperor Tenmu; but the ''Nihongi'', the ''Gukanshō'', and the ''Jinnō Shōtōki'' do not recognize this reign. Prince Ōtomo was only given his posthumous title and name in 1870. :Post-Meiji chronology :* ''In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Tōchi
was a Japanese Imperial House of Japan, Imperial princess during the Asuka period of Japanese history and the empress consort to her cousin Emperor Kōbun. Her name Tōchi is derived from the Tōchi district, a neighbourhood located a few miles north of Asuka. Princess Tōchi was daughter of Emperor Tenmu and Princess Nukata. She married Prince Ōtomo, who became Emperor Kōbun. They lived in the capital of Ōtsu in the Ōmi Province (currently Ōtsu, Shiga, Ōtsu, Shiga). He succeeded after his father, Emperor Tenji, died. She subsequently was Empress-consort until Emperor Kōbun was killed by her father in the Jinshin War. After the war, she returned to Asuka and lived with her mother and her son in the Asuka Kiyomihara palace. In 675 she visited the Ise Grand Shrine with Empress Genmei, Princess Abe. In 678, she was appointed a Saiō by Onmyōdō, divination and was supposed to leave her residence to stay in Saikū (斎宮) in the 7th day of the 4th month, when she suddenly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daijō-daijin
The was the head of the ''Daijō-kan'' (Great Council of State) during and after the Nara period and briefly under the Meiji Constitution. Equivalent to the Chinese (Grand Preceptor). History Emperor Tenji's favorite son, Prince Ōtomo, was the first to have been accorded the title of ''Daijō-daijin'' during the reign of his father. The Asuka Kiyomihara Code of 689 marks the initial appearance of the ''Daijō Daijin'' in the context of a central administrative body composed of the three ministers: the ''Daijō-daijin'' (Chancellor), the ''Sadaijin'' (Minister of the Left), and the ''Udaijin'' (Minister of the Right). These positions were consolidated under the Code of Taihō in 702.Hall, John Whitney ''et al.''. (1993)''The Cambridge History of Japan'', p. 232 As the Fujiwara clan—which dominated the regency—gained influence, the official government offices diminished in power. By the 10th century, chancellors had no power to speak of unless they were simultaneously r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Jitō
was the 41st monarch of Japan, Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 持統天皇 (41)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession. Jitō's reign spanned the years from 686 through 697.Titsingh, Isaac. (1834). In the history of Japan, Jitō was the third of eight women to take on the role of empress regnant. The two female monarchs before Jitō were Suiko and Kōgyoku/ Saimei. The five women sovereigns reigning after Jitō were Genmei, Genshō, Kōken/ Shōtoku, Meishō, and Go-Sakuramachi. Traditional narrative Empress Jitō was the daughter of Emperor Tenji. Her mother was Ochi-no-Iratsume, the daughter of Minister Ō-omi Soga no Yamada-no Ishikawa Maro. She was the wife of Tenji's full brother Emperor Tenmu, whom she succeeded on the throne.Varley, H. Paul. ''Jinnō Shōtōki,'' p. 137. Empress Jitō's given name was , or alternately Uno.Brown, D. (1979). ''Gukanshō'', p. 270. Events of Jitō's reign Jitō took responsibility for court administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


-by-Utagawa-Kuniyoshi.png)


