|
Prince Kan'in Kotohito
was the sixth head of a cadet branch of the Japanese imperial family, and a career army officer who served as Chief of the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff from 1931 to 1940. During his tenure as the Chief of the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff, the Imperial Japanese Army committed numerous war crimes against Chinese civilians including the Nanking massacre and the systemic use of chemical and bacteriological weapons. Prince Kan'in Kotohito died several months before the end of the Second World War and was not tried for war crimes. Early years Prince Kotohito was born in Kyoto on November 10, 1865 as the sixteenth son of Prince Fushimi Kuniye (1802–1875). His father was the twentieth head of the Fushimi-no-miya, one of the four shinnōke, branches of the Imperial Family which were eligible to succeed to the throne if the main line should die out. Since the infant mortality rate in the main imperial household was quite high, Emperor Kōmei, the father of Emperor Meiji, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, literally "the one who takes the first lace/position), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the '' princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the formal position of monarch on the basis of principate, not dominion. He also tasked his grandsons as summer rulers of the city when most of the government were on holiday in the country or attending religious rituals, and, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gensui (Imperial Japanese Army)
, formal rank designations: was the highest title in the pre-war Imperial Japanese military. The title originated from the Chinese title ''yuanshuai'' (元帥). The term ''gensui'', which was used for both the Imperial Japanese Army and the Imperial Japanese Navy, was at first a rank held by Saigō Takamori as the Commander of the Armies (陸軍元帥 Rikugun-gensui) in 1872. However, in May 1873 Saigō was "demoted" to general, with ''gensui'' thereafter no longer a rank as such, but a largely honorific title awarded for extremely meritorious service to the Emperor - thus similar in concept to the French title of Marshal of France. Equivalent to a five-star rank (OF-10), it is similar to Field Marshal in the British Army and General of the Army in the United States Army. While ''gensui'' would retain their actual ranks of general or admiral, they were entitled to wear an additional enamelled breast badge, depicting paulownia leaves between crossed army colors and a naval en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Army General Staff
The , also called the Army General Staff, was one of the two principal agencies charged with overseeing the Imperial Japanese Army. Role The was created in April 1872, along with the Navy Ministry, to replace the Ministry of Military Affairs (''Hyōbushō'') of the early Meiji government. Initially, the Army Ministry was in charge of both administration and operational command of the Imperial Japanese Army however, from December 1878, the Imperial Army General Staff Office took over all operational control of the Army, leaving the Army Ministry only with administrative functions. The Imperial Army General Staff was thus responsible for the preparation of war plans; the military training and employment of combined arms military intelligence; the direction of troop maneuvers; troop deployments; and the compilation of field service military regulations, military histories, and cartography. The Chief of the Army General Staff was the senior ranking uniformed officer in the Imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Household Of Japan
The , also referred to as the Imperial Family or the House of Yamato, comprises those members of the extended family of the reigning Emperor of Japan who undertake official and public duties. Under the present Constitution of Japan, the Emperor is "the symbol of the State and of the unity of the people". Other members of the Imperial Family perform ceremonial and social duties, but have no role in the affairs of government. The duties as an Emperor are passed down the line to their male children. This Japanese monarchy is the oldest continuous hereditary monarchy in the world. The Imperial House recognizes 126 monarchs, beginning with Emperor Jimmu (traditionally dated to 11 February 660 BC), and continuing up to the current emperor, Naruhito. However, scholars have agreed that there is no evidence of Jimmu's existence, that the traditional narrative of Japan’s founding is mythical, and that Jimmu is a mythical figure. Historical evidence for the first 25 emperors is mythical, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinnōke
was the collective name for the four cadet branches of the Imperial family of Japan, which were until 1947 entitled to provide a successor to the Chrysanthemum throne if the main line failed to produce an heir. The heads of these royal houses held the title of , regardless of their genealogical distance from the reigning Emperor, as the term ''seshū'' in their designation meant that they were eligible for succession. History The Imperial family of Japan considers itself a single dynasty in unbroken succession; however, the succession has often not been directly from father to son, but has been in the male line within a closely related group of people. In the Muromachi period, Prince Yoshihito, the son of the Northern Emperor Sukō was permitted to establish a parallel lineage to the main imperial line, and took the name Fushimi-no-miya from the location of his palace. Without this permission, the line would be considered commoners, and therefore excluded from the succession. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Kan'in Haruhito
was a career officer in the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II and the 7th (and final) head of the Kan'in-no-miya line of ''shinnōke'' cadet branches of the Imperial Family of Japan. Biography Prince Kan'in Haruhito was the only surviving son of Field Marshal Prince Kan'in Kotohito (1864–1945) and his consort, the former Sanjō Chieko (1872–1947). He married Ichijō Naoko (1908–1991), daughter of Prince (peer) Saneteru Ichijō on July 14, 1926. Prince Kan'in attended the Gakushuin Peers' School and graduated from the 44th class of the Imperial Japanese Army Academy in 1924. He was a lieutenant in the infantry and served in the Imperial Guard Division. Following a course in the Military Staff College in 1927, he was promoted to captain and joined the faculty of the Cavalry School. He graduated from the 44th class of the Army Staff College in 1932 and rose to the rank of major in 1936. Prince Kan'in saw a brief tour of combat duty during the Second Sino-Japanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Chrysanthemum
is Japan's highest order. The Grand Cordon of the Order was established in 1876 by Emperor Meiji of Japan; the Collar of the Order was added on 4 January 1888. Unlike its European counterparts, the order may be conferred posthumously. Apart from the Imperial Family, only seven Japanese citizens have ever been decorated with the collar in their lifetimes; the last such award was to former Prime Minister Saionji Kinmochi in 1928. Eight others have been posthumously decorated with the collar; the last such award was to former Prime Minister Shinzo Abe in 2022. Today, only the reigning Emperor holds this dignity as sovereign of the order; however, exceptions are made for foreign heads of state, who can be awarded the collar in friendship. The grand cordon is the highest possible honour a Japanese citizen can be awarded during his or her lifetime. Aside from members of the Imperial Family, 53 Japanese citizens have been decorated with the grand cordon; of these, only 23 were living ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Golden Kite
The was an order of the Empire of Japan, established on 12 February 1890 by Emperor Meiji "in commemoration of Jimmu Tennō, the Romulus of Japan". It was officially abolished 1947 by the Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers (SCAP) during the occupation of Japan, after World War II. Background The Order of the Golden Kite was an exclusively military award, conferred for bravery, leadership or command in battle. It ranked just below the Order of the Chrysanthemum in precedence and was the military equivalent of the Order of the Paulownia Flowers; therefore, it could be considered analogous to the military division of the Order of the Bath in the United Kingdom. The first three classes were roughly equivalent to the three divisions of the Order of the Bath, the fourth, fifth, sixth and seventh classes were analogous to the DSO, MC/DSC, DCM/CGM and DSM/MM, respectively . The order consisted of seven classes. Enlisted rank soldiers were eligible for the 7th–5th classes, non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Wuhan
The Battle of Wuhan (武漢之戰), popularly known to the Chinese as the Defense of Wuhan, and to the Japanese as the Capture of Wuhan, was a large-scale battle of the Second Sino-Japanese War. Engagements took place across vast areas of Anhui, Henan, Jiangxi, Zhejiang, and Hubei provinces over a period of four and a half months. It was the longest, the largest, and arguably the most significant battle in the early stages of the Second Sino-Japanese War. More than one million National Revolutionary Army troops from the Fifth and Ninth War Zone were put under the direct command of Chiang Kai-shek, defending Wuhan from the Central China Area Army of the Imperial Japanese Army led by Shunroku Hata. Chinese forces were also supported by the Soviet Volunteer Group, a group of volunteer pilots from Soviet Air Forces. Although the battle ended with the eventual capture of Wuhan by the Japanese forces, it resulted in heavy casualties on both sides, as high as 1.2 million combined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Theater of the Second World War. The beginning of the war is conventionally dated to the Marco Polo Bridge Incident on 7 July 1937, when a dispute between Japanese and Chinese troops in Peking escalated into a full-scale invasion. Some Chinese historians believe that the Japanese invasion of Manchuria on 18 September 1931 marks the start of the war. This full-scale war between the Chinese and the Empire of Japan is often regarded as the beginning of World War II in Asia. China fought Japan with aid from Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union, United Kingdom and the United States. After the Japanese attacks on Malaya and Pearl Harbor in 1941, the war merged with other conflicts which are generally categorized under those conflicts of World War II a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
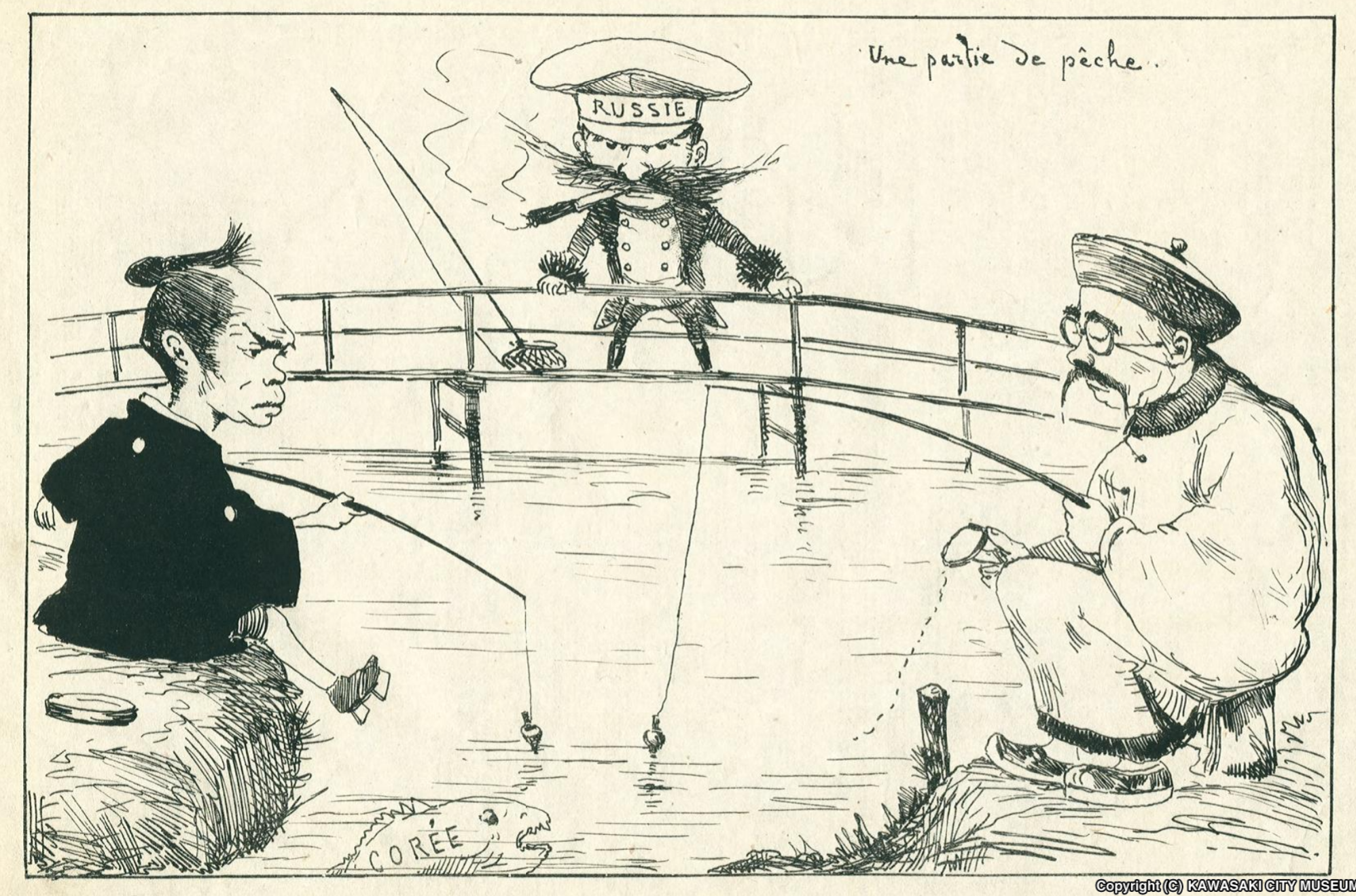
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1905 over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major theatres of military operations were located in Liaodong Peninsula and Mukden in Southern Manchuria, and the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Russia sought a warm-water port on the Pacific Ocean both for its navy and for maritime trade. Vladivostok remained ice-free and operational only during the summer; Port Arthur, a naval base in Liaodong Province leased to Russia by the Qing dynasty of China from 1897, was operational year round. Russia had pursued an expansionist policy east of the Urals, in Siberia and the Far East, since the reign of Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century. Since the end of the First Sino-Japanese War in 1895, Japan had feared Russian en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the port of Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895. The war demonstrated the failure of the Qing dynasty's attempts to modernize its military and fend off threats to its sovereignty, especially when compared with Japan's successful Meiji Restoration. For the first time, regional dominance in East Asia shifted from China to Japan; the prestige of the Qing dynasty, along with the classical tradition in China, suffered a major blow. The humiliating loss of Korea as a tributary state sparked an unprecedented public outcry. Within China, the defeat was a catalyst for a series of political upheavals led by Sun Yat-sen and Kang Youwei, culminating in the 1911 Xinhai Revolution. The war is commonly known in China as the War of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |