|
Prince Bernhard Of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (1792–1862)
Prince Carl Bernhard of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (30 May 1792 – 31 July 1862) was a distinguished soldier, who, in 1815, after the congress of Vienna, became colonel of a regiment in the service of the king of the Netherlands. He fought at the Battle of Quatre Bras and the Battle of Waterloo where he commanded the 2nd Brigade of the 2nd Dutch Division and became a Chief Commander of the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army Early life Prince Bernhard, the seventh child of Charles Augustus, Grand Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, was born on 30 May 1792 in Weimar. He enlisted in the Prussian army and in 1806 he fought in the army of Frederick Louis, Prince of Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen, Hohenlohe-Ingelfingen. By 1809 he had enlisted in the Saxon army and he fought under Charles XIV John of Sweden, Marshal Bernadotte at Battle of Wagram, Wagram. Waterloo campaign Prince Bernhard's 2nd Brigade of the 2nd Dutch Division (Hendrik George de Perponcher Sedlnitsky, Sedlnitsky) was the first of the Arth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Ida Of Saxe-Meiningen
Princess is a regal rank and the feminine equivalent of prince (from Latin ''princeps'', meaning wiktionary:principal, principal citizen). Most often, the term has been used for the consort of a prince, or for the daughter of a king or prince. Princess as a substantive title Some princesses are reigning monarchs of principalities. There have been fewer instances of reigning princesses than reigning princes, as most principalities excluded women from inheriting the throne. Examples of princesses regnant have included Constance of Antioch, princess regnant of Principality of Antioch, Antioch in the 12th century. Since the President of France, an office for which women are eligible, is ''ex-officio'' a Co-Prince of Andorra, then Andorra could theoretically be jointly ruled by a princess. Princess as a courtesy title Descendants of monarchs For many centuries, the title "princess" was not regularly used for a monarch's daughter, who, in English, might simply be called "Lady". Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
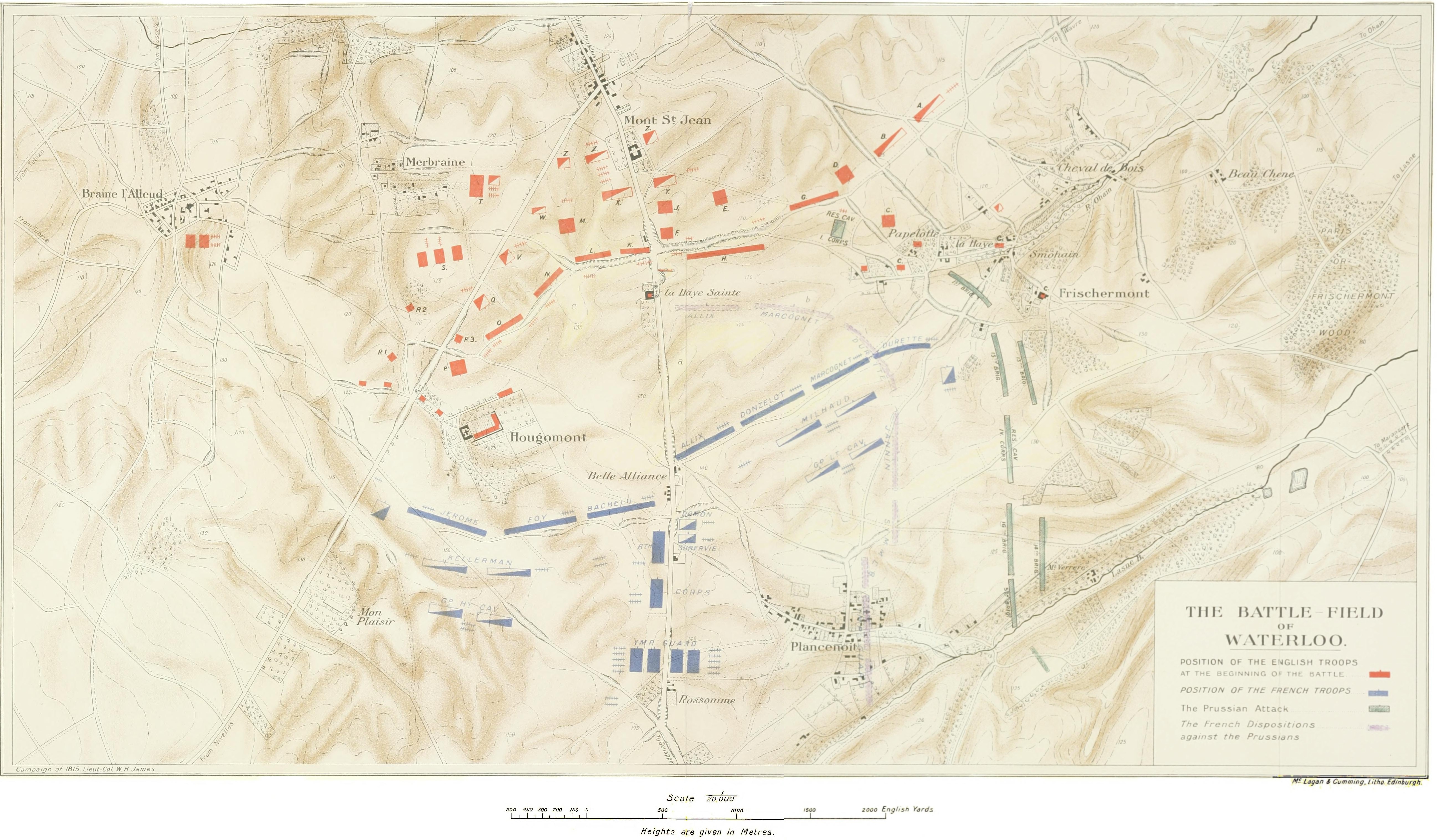
Hendrik George De Perponcher Sedlnitsky
Hendrik George, Count de Perponcher Sedlnitsky (also Sedlnitzky; 19 May 1771 – 29 November 1856) was a Dutch general and diplomat. He commanded the 2nd Netherlands Division at the Battle of Quatre Bras and the Battle of Waterloo. Biography Family life Perponcher was the son of Cornelis, baron de Perponcher Sedlnitsky, (scion of an old Huguenot Dutch family and of old Czech noble family that had fled Bohemia after the 1621 Battle of White Mountain), a justice in the ''Hof van Holland'' (the high court of the province of Holland), and '' Jonkvrouwe'' Johanna Maria van Tuyll van Serooskerke. Though the family was not part of the Dutch nobility under the Dutch Republic it had acquired a number of '' Heerlijkheden'', like many Regents, which gave it a ''de facto'' aristocratic status. When King William I of the Netherlands reorganized, and greatly extended, the Dutch nobility in 1815, the family De Perponcher Sedlnitsky was inducted into the Dutch nobility with the title of baron. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andreas Victor Michiels
Andreas Victor Michiels (Maastricht, Netherlands, 30 May 1797 – Kusamba, Bali 25 May 1849) was a military and administrative officer in the Dutch East Indies. Early life and military career Michiels entered military service at age 17 years, participated in the Battle of Waterloo, and in 1817 went to the island of Java, where he was directly involved in the conflict in Cirebon. On 29 August 1818 he was promoted to captain. He fought in the Java War as a colonel commandant. On 22 November 1828, King William I appointed Michiels a knight and officer in the Military William Order, one year before he was appointed as a major. In the years 1831 and 1832, he participated in the conquest of Narras and Kottiangan, in 1832, he led an expedition against the Jambi Sultanate; the month of May in that year he was appointed lieutenant-colonel and in November he was awarded a knighthood in the Order of the Netherlands Lion. He led the raid on Bonjol and under his leadership he was able to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Intervention In Bali (1849)
The Dutch intervention in Bali in 1849 was a major Dutch military intervention in Northern and Southern Bali, following two failed interventions, the 1846 intervention and the 1848 intervention. The Dutch used as a pretext Balinese salvage claims over shipwrecks, which were customary to the Balinese, but unacceptable under International law. Dutch naval expedition The expedition arrived off Buleleng in 1849. It was a considerable force of the Royal Dutch East Indies Army, composed of 100 ships, 3,000 sailors, and 5,000 well-trained soldiers, including a majority of Dutch troops.''International Dictionary of Historic Places: Asia and Oceania'' by Trudy Ring p.6/ref>''A short history of Bali: Indonesia's Hindu realm'' Robert Pringle p.98''ff'/ref> The Dutch landed in Buleleng and marched on Singaraja, only to discover that the whole town had been abandoned. The Dutch occupied the town, but soon faced a dilemma by the arrival of a Balinese delegation. Dutch General Andreas Victo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East Indies Army
The Royal Netherlands East Indies Army ( nl, Koninklijk Nederlands Indisch Leger; KNIL, ) was the military force maintained by the Kingdom of the Netherlands in its colony of the Dutch East Indies, in areas that are now part of Indonesia. The KNIL's air arm was the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army Air Force. Elements of the Royal Netherlands Navy and Government Navy were also stationed in the Netherlands East Indies. History 1814–1942 The KNIL was formed by royal decree on 14 September 1814. It was not part of the Royal Netherlands Army, but a separate military arm specifically formed for service in the Netherlands East Indies. Its establishment coincided with the Dutch drive to expand colonial rule from the 17th century area of control to the far larger territories constituting the Dutch East Indies seventy years later. The KNIL was involved in many campaigns against indigenous groups in the area including the Padri War (1821–1845), the Java War (1825–1830), crushin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Haye, Lasne
La Haye was a farm, in a hamlet of the same name, in the Belgian municipality of Lasne. It was destroyed by fire in 1910. During the Battle of Waterloo (18 June 1815) the farm was one of the fortified garrisoned points that made up a bulwark on the extreme left (eastern end) of the Duke of Wellington's Anglo-allied line. History Along with La Haye, the eastern bulwark consisted of three other garrisoned and hastily fortified locations: less than to the west was Papelotte farm which like la Hay was on the northern bank of a shallow valley. About to the east was the hamlet of Smohain. At this point the valley had become a defile with a boggy stream at the bottom. The fourth location was the now ruined Châteaux Frischermont (then similar to the better known Châteaux Hougoumont which was located on the Anglo-allies right-hand flank ) which was about to the south-east on a premonitory on other bank of the valley. The bulwark was held during the day by Anglo-allied soldiers unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frischermont
Châteaux Frischermont or Fichermont in the Belgian municipality of Lasne is now a ruin (destroyed by fire in and demolished in 1965).In some sources also Châteaux Frichermont At the start of the Battle of Waterloo in 1815 it was garrisoned by Dutch soldiers on the easternmost flank of Wellington's defensive line. In 1705 the Châteaux was for a time the headquarters of the Duke of Marlborough. While at Frischermont Marlborough wrote that the escarpment of Mont-Saint-Jean would be a good place to defend Brussels if it was attacked from the south. At the start of the Battle of Waterloo on 18 June 1815 it belonged to Monsieur Beaulieu, and it was garrisoned by troops of the 28th Regiment, Orange-Nassau (Regiment Oranje-Nassau No. 28) under the command of Prince Bernhard of Saxe-Weimar. It was here at 10:30 that as a French patrol drove back Dutch pickets the first fighting of the day took place. See also * List of Waterloo Battlefield locations The Waterloo Battlefield is l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papelotte
Papelotte Farm (French: ''Ferme de la Papelotte'') is located at Rue Du Dimont a rural road in the Municipality of Braine-l'Alleud around south of Brussels, Belgium. On June 18th, 1815 during the pivotal Battle of Waterloo it served as one of the advanced defensible positions of the Anglo-allied army under the command of the Duke of Wellington. Along with the walled farm compounds of Hougoumont and La Haye Sainte, it proved to be instrumental to the delay and the disruption of the opposing Napoleonic army's progress on the battlefield. Napoleon diverted disproportionately large numbers of troops in order to capture or eliminate these perimeters, while he failed to achieve a decisive break through in one of several attacks on the lines of the Allies. Papelotte was situated on the center-left flank of Wellington's army. Napoleon would also lose valuable time and resources as he struggled with the Allied strongpoints, whose comparatively rather moderately sized garrisons defended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterloo Campaign
The Waterloo campaign (15 June – 8 July 1815) was fought between the French Army of the North (France), Army of the North and two Seventh Coalition armies, an Anglo-allied army and a Prussian army. Initially the French army was commanded by Napoleon Bonaparte, but he left for Paris after the French defeat at the Battle of Waterloo. Command then rested on Marshals Marshal Soult, Soult and Marshal Grouchy, Grouchy, who were in turn replaced by Marshal Davout, who took command at the request of the French Provisional Government. The Anglo-allied army was commanded by the Duke of Wellington and the Prussian army by Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, Prince Blücher. The war between France and the Seventh Coalition came when the other European Great Powers refused to recognise Napoleon as Emperor of the French upon his return from exile on the Principality of Elba, island of Elba, and declared war on him, rather than France, as they still recognised Louis XVIII as the king of France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'Armée Du Nord
The Army of the North or Armée du Nord is a name given to several historical units of the French Army. The first was one of the French Revolutionary Armies that fought with distinction against the First Coalition from 1792 to 1795. Others existed during the Peninsular War, the Hundred Days and the Franco-Prussian War. Campaigns 1791 to 1797 At the creation of the Army of the North on 14 December 1791, the government of the Kingdom of France appointed Jean-Baptiste Donatien de Vimeur, Comte de Rochambeau, as its commander. Rochambeau was replaced in May 1792, and he retired from service. The suspicious government of the First French Republic later charged him with treason and he barely escaped execution. In 1792-1794, the guillotine awaited military commanders who either failed, belonged to the nobility, or displayed insufficient revolutionary zeal. In the Army of the North these unfortunates included Nicolas Luckner, Adam Custine, and Jean Houchard. Under Charles François D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Battle Of The Waterloo Campaign
This is the complete order of battle for the four major battles of the Waterloo campaign. French Army order of battle Headquarters L'Armée du Nord under the command of Emperor Napoleon I. ''Major Général'' (Chief of Staff): Marshal Soult, Duke of Dalmatia. Commander of artillery: General of Division Charles-Étienne-François Ruty. Field commanders under the direct command of Emperor Napoleon: * Marshal Ney, Prince of the Moskova: ** On 16 June 1815, at the battle of Quatre Bras, in command of the Left Wing: I Corps, II Corps (minus the Girard division, present at the battle of Ligny), III Cavalry Corps (minus the l'Héritier division, present at the battle of Ligny) and Imperial Guard light cavalry division. ** On 18 June 1815, at the battle of Waterloo, effective field commander of all the French forces present, minus those engaged at Plancenoit (VI Corps and elements of the Guard). * Marshal Marquis de Grouchy: ** On 16 June 1815, at the Battle of Ligny, in command ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michel Ney
Michel Ney, 1st Duke of Elchingen, 1st Prince of the Moskva (; 10 January 1769 – 7 December 1815), was a French military commander and Marshal of the Empire who fought in the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He was one of the original 18 Marshals of the Empire created by Napoleon I. He was known as Le Rougeaud by his men; Napoleon characterized him as "le Brave des braves (the Bravest of the Brave), a real paladin in the field, a braggart without judgment and decision in the workroom and after all is said, a Don Quixote." Early life Ney was born in the town of Sarrelouis, in the French province of the Three Bishoprics, along the French–German border. He was the second son of Pierre Ney (1738–1826), a master cooper and veteran of the Seven Years' War, and his wife Marguerite Greiveldinger. He was the paternal grandson of Matthias Ney (1700–1780) and wife Margarethe Becker (d. 1767), and the maternal grandson of Valentin and wife Margaretha Ding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |