|
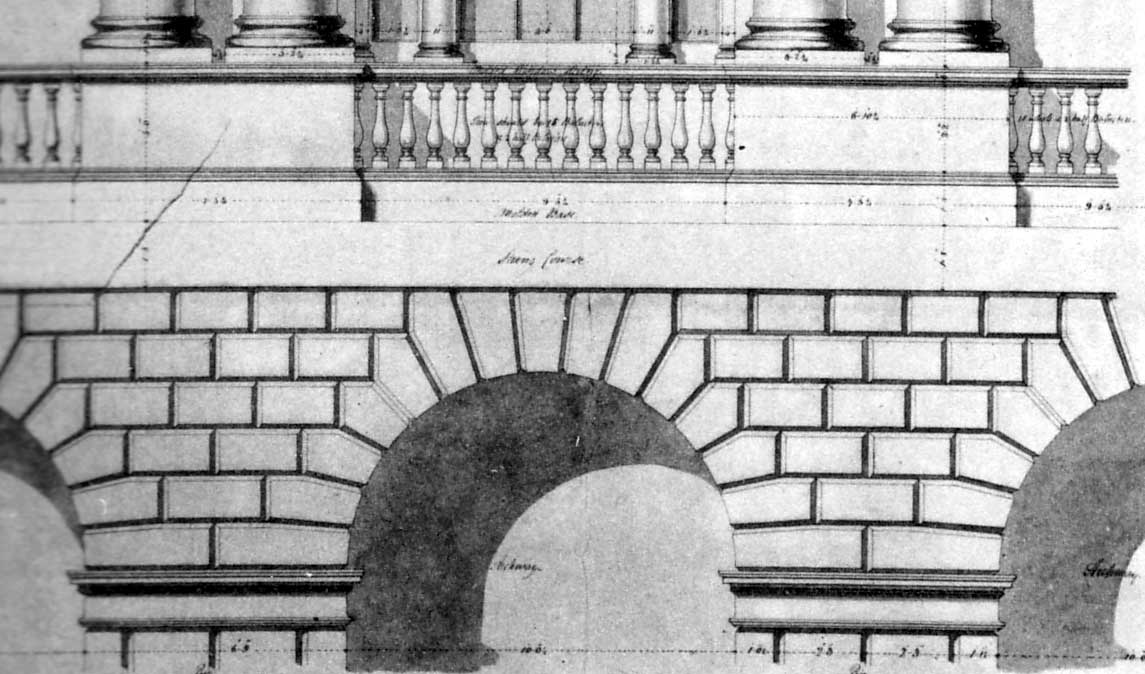
Primrose Hill Tunnel
Primrose Hill Tunnel is a railway tunnel on the West Coast Main Line, approximately from . It is located in South Hampstead in the London Borough of Camden, just north of Primrose Hill park and consists of two bores: the slow line to the northern side, driven through the London clay by the engineer Robert Stephenson for the London and Birmingham Railway in 1838, and the fast line to its south, added by the London and North Western Railway in 1879. The original tunnel's Italianate portals were designed by William Budden and later replicated for the fast line. The western portals have been listed at Grade II and the eastern at Grade II* since 1974. As the first railway tunnel in London, Historic England considers it to be of special historic interest, as well as because "it was the first nationally to negotiate the issue of competing claims for the use of land in an urban context; and the first tunnel to treat one of its portals architecturally". Description Primrose Hill Tunnel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Coast Main Line
The West Coast Main Line (WCML) is one of the most important railway corridors in the United Kingdom, connecting the major cities of London and Glasgow with branches to Birmingham, Liverpool, Manchester and Edinburgh. It is one of the busiest mixed-traffic railway routes in Europe, carrying a mixture of intercity rail, regional rail, commuter rail and rail freight traffic. The core route of the WCML runs from London to Glasgow for and was opened from 1837 to 1869. With additional lines deviating to Northampton, Birmingham, Manchester, Liverpool and Edinburgh, this totals a route mileage of . The Glasgow–Edinburgh via Carstairs line connects the WCML to Edinburgh, however the main London–Edinburgh route is the East Coast Main Line. Several sections of the WCML form part of the suburban railway systems in London, Coventry, Birmingham, Liverpool, Manchester and Glasgow, with many more smaller commuter stations, as well as providing links to more rural towns. It is one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primrose Hill Tunnels, Western Portals At South Hampstead, June 2020
Primrose may refer to: Botany * Primulaceae, a family of flowering plants * ''Primula vulgaris'', commonly known as the primrose (also called the common primrose or English primrose) * ''Oenothera'', commonly known as evening primrose, a plant genus * Onagraceae, commonly known as the willowherb family or evening primrose family Places ;Britain * Primrose Hill in London ;Canada * Primrose Lake on the Alberta/Saskatchewan border ;South Africa * Primrose, Gauteng ;United States * Primrose, Alaska * Primrose, Georgia * Primrose, Kentucky * Primrose, Nebraska * Primrose, Ohio * Primrose, Pennsylvania * Primrose, Rhode Island * Primrose, Wisconsin, a town ** Primrose (community), Wisconsin, an unincorporated community People Families * Clan Primrose, a Scottish clan headed by the Earl of Rosebery **Earl of Rosebery, a title linked with the Clan Primrose **Laird of Burnbrae, a title linked with the Clan Primrose Surname * Archibald Primrose (other), various people * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Central Railway
The Great Central Railway in England was formed when the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway changed its name in 1897, anticipating the opening in 1899 of its London Extension. On 1 January 1923, the company was grouped into the London and North Eastern Railway. History New name On assuming its new title, the Great Central Railway had a main line from Manchester London Road Station via , Sheffield Victoria, and Grimsby to . A second line left the line at Penistone and served , and Scunthorpe, before rejoining the Grimsby line at . Other lines linked Sheffield to Barnsley (via ) and Doncaster (via Rotherham) and also and Wrawby Junction. Branch lines in north Lincolnshire ran to Barton-upon-Humber and New Holland and served ironstone quarries in the Scunthorpe area. In the Manchester area, lines ran to Stalybridge and Glossop. In the 1890s, the MS&LR began constructing its Derbyshire lines, the first part of its push southwards. Leaving its east–west mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiltern Main Line
The Chiltern Main Line is a railway line which links London () and Birmingham ( Moor Street and Snow Hill), the United Kingdom's two largest cities, by a route via High Wycombe, Bicester, Banbury, Leamington Spa and Solihull. It is one of two main line railway routes between London and Birmingham; the other is the West Coast Main Line between London Euston and , which is the principal InterCity route between the two cities. The name ''Chiltern Line'' was invented as a marketing name for the line by Network SouthEast in 1985, in reference to the Chiltern Hills which the route passes through near its southern end. The route was originally part of the Great Western Railway's main line from London Paddington to Birmingham Snow Hill, and . Most main line services between London and Birmingham on this route were discontinued in 1967 after the West Coast Main Line was electrified, and Snow Hill station was closed. Services were resumed between London and the reopened Snow Hill in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italianate Architecture
The Italianate style was a distinct 19th-century phase in the history of Classical architecture. Like Palladianism and Neoclassicism, the Italianate style drew its inspiration from the models and architectural vocabulary of 16th-century Italian Renaissance architecture, synthesising these with picturesque aesthetics. The style of architecture that was thus created, though also characterised as "Neo-Renaissance", was essentially of its own time. "The backward look transforms its object," Siegfried Giedion wrote of historicist architectural styles; "every spectator at every period—at every moment, indeed—inevitably transforms the past according to his own nature." The Italianate style was first developed in Britain in about 1802 by John Nash, with the construction of Cronkhill in Shropshire. This small country house is generally accepted to be the first Italianate villa in England, from which is derived the Italianate architecture of the late Regency and early Victorian eras. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediment
Pediments are gables, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the lintel, or entablature, if supported by columns. Pediments can contain an overdoor and are usually topped by hood moulds. A pediment is sometimes the top element of a portico. For symmetric designs, it provides a center point and is often used to add grandness to entrances. The tympanum, the triangular area within the pediment, is often decorated with a pedimental sculpture which may be freestanding or a relief sculpture. The tympanum may hold an inscription, or in modern times, a clock face. Pediments are found in ancient Greek architecture as early as 600 BC (e.g. the archaic Temple of Artemis). Variations of the pediment occur in later architectural styles such as Classical, Neoclassical and Baroque. Gable roofs were common in ancient Greek temples with a low pitch (angle of 12.5° to 16°). History The pediment is found in classical Greek temples, Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital (architecture)
In architecture the capital (from the Latin ''caput'', or "head") or chapiter forms the topmost member of a column (or a pilaster). It mediates between the column and the load thrusting down upon it, broadening the area of the column's supporting surface. The capital, projecting on each side as it rises to support the abacus, joins the usually square abacus and the usually circular shaft of the column. The capital may be convex, as in the Doric order; concave, as in the inverted bell of the Corinthian order; or scrolling out, as in the Ionic order. These form the three principal types on which all capitals in the classical tradition are based. The Composite order established in the 16th century on a hint from the Arch of Titus, adds Ionic volutes to Corinthian acanthus leaves. From the highly visible position it occupies in all colonnaded monumental buildings, the capital is often selected for ornamentation; and is often the clearest indicator of the architectural orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hip Roof
A hip roof, hip-roof or hipped roof, is a type of roof where all sides slope downwards to the walls, usually with a fairly gentle slope (although a tented roof by definition is a hipped roof with steeply pitched slopes rising to a peak). Thus, a hipped roof has no gables or other vertical sides to the roof. A square hip roof is shaped like a pyramid. Hip roofs on houses may have two triangular sides and two trapezoidal ones. A hip roof on a rectangular plan has four faces. They are almost always at the same pitch or slope, which makes them symmetrical about the centerlines. Hip roofs often have a consistent level fascia, meaning that a gutter can be fitted all around. Hip roofs often have dormer slanted sides. Construction Hip roofs are more difficult to construct than a gabled roof, requiring more complex systems of rafters or trusses. Hip roofs can be constructed on a wide variety of plan shapes. Each ridge is central over the rectangle of the building below it. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bracket (architecture)
A bracket is an architectural element: a structural or decorative member. It can be made of wood, stone, plaster, metal, or other media. It projects from a wall, usually to carry weight and sometimes to "...strengthen an angle". A corbel or console are types of brackets. In mechanical engineering a bracket is any intermediate component for fixing one part to another, usually larger, part. What makes a bracket a bracket is that it is intermediate between the two and fixes the one to the other. Brackets vary widely in shape, but a prototypical bracket is the L-shaped metal piece that attaches a shelf (the smaller component) to a wall (the larger component): its vertical arm is fixed to one (usually large) element, and its horizontal arm protrudes outwards and holds another (usually small) element. This shelf bracket is effectively the same as the architectural bracket: a vertical arm mounted on the wall, and a horizontal arm projecting outwards for another element to be attached o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a pedestal, or along the top of an interior wall. A simple cornice may be formed just with a crown, as in crown moulding atop an interior wall or above kitchen cabinets or a bookcase. A projecting cornice on a building has the function of throwing rainwater free of its walls. In residential building practice, this function is handled by projecting gable ends, roof eaves and gutters. However, house eaves may also be called "cornices" if they are finished with decorative moulding. In this sense, while most cornices are also eaves (overhanging the sides of the building), not all eaves are usually considered cornices. Eaves are primarily functional and not necessarily decorative, while cornices have a decorative aspect. A building's projecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voussoir
A voussoir () is a wedge-shaped element, typically a stone, which is used in building an arch or vault. Although each unit in an arch or vault is a voussoir, two units are of distinct functional importance: the keystone and the springer. The keystone is the centre stone or masonry unit at the apex of an arch. The springer is the lowest voussoir on each side, located where the curve of the arch springs from the vertical support or abutment of the wall or pier. The keystone is often decorated or enlarged. An enlarged and sometimes slightly dropped keystone is often found in Mannerist arches of the 16th century, beginning with the works of Giulio Romano, who also began the fashion for using voussoirs above rectangular openings, rather than a lintel (Palazzo Stati Maccarani, Rome, circa 1522). The word is a stonemason's term borrowed in Middle English from French verbs connoting a "turn" (''OED''). Each wedge-shaped voussoir ''turns aside'' the thrust of the mass above, transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rustication (architecture)
Two different styles of rustication in the Palazzo Medici-Riccardi in Florence; smooth-faced above and rough-faced below.">Florence.html" ;"title="Palazzo Medici-Riccardi in Florence">Palazzo Medici-Riccardi in Florence; smooth-faced above and rough-faced below. Rustication is a range of masonry techniques used in classical architecture giving visible surfaces a finish texture that contrasts with smooth, squared-block masonry called ashlar. The visible face of each individual block is cut back around the edges to make its size and placing very clear. In addition the central part of the face of each block may be given a deliberately rough or patterned surface. Rusticated masonry is usually "dressed", or squared off neatly, on all sides of the stones except the face that will be visible when the stone is put in place. This is given wide joints that emphasize the edges of each block, by angling the edges ("channel-jointed"), or dropping them back a little. The main part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |