|
Prescaler
A prescaler is an electronic counting circuit used to reduce a high frequency electrical signal to a lower frequency by integer division. The prescaler takes the basic timer clock frequency (which may be the CPU clock frequency or may be some higher or lower frequency) and divides it by some value before feeding it to the timer, according to how the prescaler register(s) are configured. The prescaler values, referred to as prescales, that may be configured might be limited to a few fixed values (powers of 2), or they may be any integer value from 1 to 2^P, where P is the number of prescaler bits. The purpose of the prescaler is to allow the timer to be clocked at the rate a user desires. For shorter (8 and 16-bit) timers, there will often be a tradeoff between resolution (high resolution requires a high clock rate) and range (high clock rates cause the timer to overflow more quickly). For example, one cannot (without some tricks) achieve 1 µs resolution and a 1 sec maxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual-modulus Prescaler
A dual modulus prescaler is an electronic circuit used in high-frequency synthesizer designs to overcome the problem of generating narrowly spaced frequencies that are nevertheless too high to be passed directly through the feedback loop of the system. The modulus of a prescaler is its frequency divisor. A dual-modulus prescaler has two separate frequency divisors, usually M and M+1. The problem A frequency synthesizer produces an output frequency, fo, which divided by the modulus, N, is the reference frequency, fr: \frac = f_r \Rightarrow f_o = Nf_r The modulus is generally restricted to integer values, as the comparator will match when the waveform is in phase. Typically, the possible frequency multiples will be the channels for which the radio equipment is designed, so fr will usually be equal to the channel spacing. For example, on narrow-band radiotelephones, a channel spacing of 12.5 kHz is typical. Suppose that the programmable divider, using N, is only able to ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual-modulus Prescaler
A dual modulus prescaler is an electronic circuit used in high-frequency synthesizer designs to overcome the problem of generating narrowly spaced frequencies that are nevertheless too high to be passed directly through the feedback loop of the system. The modulus of a prescaler is its frequency divisor. A dual-modulus prescaler has two separate frequency divisors, usually M and M+1. The problem A frequency synthesizer produces an output frequency, fo, which divided by the modulus, N, is the reference frequency, fr: \frac = f_r \Rightarrow f_o = Nf_r The modulus is generally restricted to integer values, as the comparator will match when the waveform is in phase. Typically, the possible frequency multiples will be the channels for which the radio equipment is designed, so fr will usually be equal to the channel spacing. For example, on narrow-band radiotelephones, a channel spacing of 12.5 kHz is typical. Suppose that the programmable divider, using N, is only able to ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
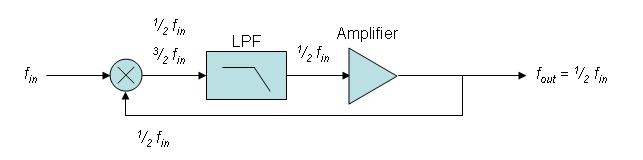
Frequency Divider
A frequency divider, also called a clock divider or scaler or prescaler, is a circuit that takes an input signal of a frequency, f_, and generates an output signal of a frequency: : f_ = \frac where n is an integer. Phase-locked loop frequency synthesizers make use of frequency dividers to generate a frequency that is a multiple of a reference frequency. Frequency dividers can be implemented for both analog and digital applications. Analog Analog frequency dividers are less common and used only at very high frequencies. Digital dividers implemented in modern IC technologies can work up to tens of GHz. Regenerative A regenerative frequency divider, also known as a Miller frequency divider, mixes the input signal with the feedback signal from the mixer. The feedback signal is f_/2. This produces sum and difference frequencies f_/2, 3f_/2 at the output of the mixer. A low pass filter removes the higher frequency and the f_/2 frequency is amplified and fed back into mixer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter (digital)
In digital logic and computing, a counter is a device which stores (and sometimes displays) the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock. The most common type is a sequential digital logic circuit with an input line called the ''clock'' and multiple output lines. The values on the output lines represent a number in the binary or BCD number system. Each pulse applied to the clock input increments or decrements the number in the counter. A counter circuit is usually constructed of several flip-flops connected in a cascade. Counters are a very widely used component in digital circuits, and are manufactured as separate integrated circuits and also incorporated as parts of larger integrated circuits. Electronic counters An electronic counter is a sequential logic circuit that has a clock input signal and a group of output signals that represent an integer "counts" value. Upon each qualified clock edge, the circuit will incremen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is equal to one event per second. The period is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times a minute (2 hertz), the period, —the interval at which the beats repeat—is half a second (60 seconds divided by 120 beats). Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examples of simple harmonic motion, the term ''frequency'' is defined as the number of cycles or vibrations per unit of time. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer Division
Division is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, the ways that numbers are combined to make new numbers. The other operations are addition, subtraction, and multiplication. At an elementary level the division of two natural numbers is, among other possible interpretations, the process of calculating the number of times one number is contained within another. This number of times need not be an integer. For example, if 20 apples are divided evenly between 4 people, everyone receives 5 apples (see picture). The division with remainder or Euclidean division of two natural numbers provides an integer ''quotient'', which is the number of times the second number is completely contained in the first number, and a ''remainder'', which is the part of the first number that remains, when in the course of computing the quotient, no further full chunk of the size of the second number can be allocated. For example, if 21 apples are divided between 4 people, everyone receives 5 ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Counter
A frequency counter is an electronic instrument, or component of one, that is used for measuring frequency. Frequency counters usually measure the number of cycles of oscillation, or pulses per second in a periodic electronic signal. Such an instrument is sometimes referred to as a cymometer, particularly one of Chinese manufacture. Operating principle Most frequency counters work by using a counter which accumulates the number of events occurring within a specific period of time. After a preset period known as the ''gate time'' (1 second, for example), the value in the counter is transferred to a display and the counter is reset to zero. If the event being measured repeats itself with sufficient stability and the frequency is considerably lower than that of the clock oscillator being used, the resolution of the measurement can be greatly improved by measuring the time required for an entire number of cycles, rather than counting the number of entire cycles observed for a pre-set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector in a feedback loop. The oscillator's frequency and phase are controlled proportionally by an applied voltage, hence the term voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The oscillator generates a periodic signal of a specific frequency, and the phase detector compares the phase of that signal with the phase of the input periodic signal, to adjust the oscillator to keep the phases matched. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same. Consequently, in addition to synchronizing signals, a phase-locked loop can track an input frequency, or it can generate a frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Detector
A phase detector or phase comparator is a frequency mixer, analog multiplier or logic circuit that generates a signal which represents the difference in phase between two signal inputs. The phase detector is an essential element of the phase-locked loop (PLL). Detecting phase difference is important in other applications, such as motor control, radar and telecommunication systems, servo mechanisms, and demodulators. Types Phase detectors for phase-locked loop circuits may be classified in two types.Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill, ''The Art of Electronics 2nd Ed. '' Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1989 pg. 644 A Type I detector is designed to be driven by analog signals or square-wave digital signals and produces an output pulse at the difference frequency. The Type I detector always produces an output waveform, which must be filtered to control the phase-locked loop voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). A type II detector is sensitive only to the relative timing of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign (−1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language of mathematics, the set of integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold \mathbb. The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the natural numbers, \mathbb is countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , and are not. The integers form the smallest group and the smallest ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the integers are sometimes qualified as rational integers to distinguish them from the more general algebraic integers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ranges as microwaves; the above broad definition includes both UHF and EHF (millimeter wave) bands. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz (wavelengths between 0.3 m and 3 mm). In all cases, microwaves include the entire SHF band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum. Frequencies in the microwave range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations. The prefix ' in ''microwave'' is not meant to suggest a wavelength in the micrometer range. Rather, it indicates that microwaves are "small" (having shorter wavelengths), compared to the radio waves used prior to microwave te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector in a feedback loop. The oscillator's frequency and phase are controlled proportionally by an applied voltage, hence the term voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The oscillator generates a periodic signal of a specific frequency, and the phase detector compares the phase of that signal with the phase of the input periodic signal, to adjust the oscillator to keep the phases matched. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same. Consequently, in addition to synchronizing signals, a phase-locked loop can track an input frequency, or it can generate a frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |