|
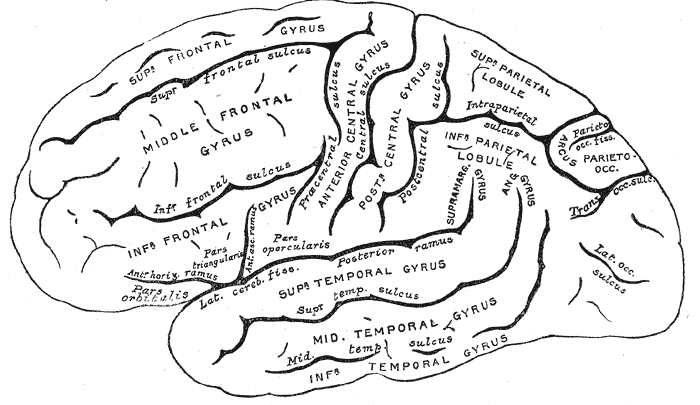
Precentral Sulcus
The precentral sulcus is a part of the human brain that lies parallel to, and in front of, the central sulcus. (A ''sulcus'' is one of the prominent grooves on the surface of the human brain.) The precentral sulcus divides the inferior, middle and superior frontal gyri from the precentral gyrus. In most brains, the precentral sulcus is divided into two parts: the inferior precentral sulcus and the superior precentral sulcus. However, the precentral sulcus may sometimes be divided into three parts or form one continuous sulcus. Additional images File:Precentral sulcus animation small.gif, Position of precentral sulcus (shown in red). File:FrontalCaptsLateral.png, Lateral surface of right frontal lobe The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be .... Precentral sulcus is lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the skull bones of the head. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is conventionally divided into four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Sulcus
In neuroanatomy, the central sulcus (also central fissure, fissure of Rolando, or Rolandic fissure, after Luigi Rolando) is a sulcus, or groove, in the cerebral cortex in the brains of vertebrates. It is sometimes confused with the longitudinal fissure. The central sulcus is a prominent landmark of the brain, separating the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe and the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex. Evolution of the central sulcus The evolution of the central sulcus is theorized to have occurred in mammals when the complete dissociation of the original somatosensory cortex from its mirror duplicate developed in placental mammals such as primates, though the development did not stop there as time progressed the distinction between the two cortices grew. Evolution in primates The central sulcus is more prominent in apes as a result of fine-tuning of the motor system in apes. Hominins (bipedal apes) continued this trend through increased use of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Frontal Gyrus
The inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), (gyrus frontalis inferior), is the lowest positioned gyrus of the frontal gyri, of the frontal lobe, and is part of the prefrontal cortex. Its superior border is the inferior frontal sulcus (which divides it from the middle frontal gyrus), its inferior border is the lateral sulcus (which divides it from the superior temporal gyrus) and its posterior border is the inferior precentral sulcus. Above it is the middle frontal gyrus, behind it is the precentral gyrus. The inferior frontal gyrus contains Broca's area, which is involved in language processing and speech production. Structure The inferior frontal gyrus is highly convoluted and has three cytoarchitecturally diverse regions. The three subdivisions are an opercular part, a triangular part, and an orbital part. These divisions are marked by two rami arising from the lateral sulcus. The ascending ramus separates the opercular and triangular parts. The anterior (horizontal) ramus separates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Frontal Gyrus
The middle frontal gyrus makes up about one-third of the frontal lobe of the human brain. (A ''gyrus'' is one of the prominent "bumps" or "ridges" on the surface of the human brain.) The middle frontal gyrus, like the inferior frontal gyrus and the superior frontal gyrus, is more of a region in the frontal gyrus than a true gyrus. The borders of the middle frontal gyrus are the ''inferior frontal sulcus'' below; the ''superior frontal sulcus'' above; and the precentral sulcus The precentral sulcus is a part of the human brain that lies parallel to, and in front of, the central sulcus. (A ''sulcus'' is one of the prominent grooves on the surface of the human brain.) The precentral sulcus divides the inferior, middl ... behind. Additional images File:Middle frontal gyrus animation small.gif, Position of middle frontal gyrus (shown in red). File:Gray725 middle frontal gyrus.png, Left cerebral hemisphere seen from above. File:Gray726 middle frontal gyrus.png, Lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Frontal Gyrus
In neuroanatomy, the superior frontal gyrus (SFG, also marginal gyrus) is a gyrus – a ridge on the brain's cerebral cortex – which makes up about one third of the frontal lobe. It is bounded laterally by the superior frontal sulcus. The superior frontal gyrus is one of the frontal gyri. Function Self-awareness In fMRI experiments, Goldberg ''et al.'' have found evidence that the superior frontal gyrus is involved in self-awareness, in coordination with the action of the sensory system. Laughter In 1998, neurosurgeon Itzhak Fried described a 16-year-old female patient (referred to as "patient AK") who laughed when her SFG was stimulated with electric current during treatment for epilepsy. Electrical stimulation was applied to the cortical surface of AK's left frontal lobe while an attempt was made to locate the focus of her epileptic seizures (which were never accompanied by laughter). Fried identified a 2 cm by 2 cm area on the left SFG where stimulation produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precentral Gyrus
The precentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus on the surface of the posterior frontal lobe of the brain. It is the site of the primary motor cortex that in humans is cytoarchitecturally defined as Brodmann area 4. Structure The precentral gyrus lies in front of the postcentral gyrus - mostly on the lateral (convex) side of each cerebral hemisphere - from which it is separated by the central sulcus. Its anterior border is represented by the precentral sulcus, while inferiorly it borders to the lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure). Medially, it is contiguous with the paracentral lobule. The internal pyramidal layer (layer V) of the precentral cortex contains giant (70-100 micrometers) pyramidal neurons called Betz cells, which send long axons to the contralateral motor nuclei of the cranial nerves and to the lower motor neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. These axons form the corticospinal tract. The Betz cells along with their long axons are referred to as upper motor n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the skull bones of the head. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is conventionally divided into four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove between tissues called the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe by a deeper groove called the lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure). The most anterior rounded part of the frontal lobe (though not well-defined) is known as the frontal pole, one of the three poles of the cerebrum. The frontal lobe is covered by the frontal cortex. The frontal cortex includes the premotor cortex, and the primary motor cortex – parts of the motor cortex. The front part of the frontal cortex is covered by the prefrontal cortex. There are four principal gyri in the frontal lobe. The precentral gyrus is directly anterior to the central sulcus, running parallel to it and contains the primary motor cortex, which controls voluntary movements of specific body parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum prenatal development, develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the Dorsum (biology), dorsal telencephalon, or Pallium (neuroanatomy), pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or Pallium (neuroanatomy), subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric Lateralization of brain function, left and right cerebral hemispheres. With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the human body. Structure The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal it lies eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulci (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, a sulcus (Latin: "furrow", pl. ''sulci'') is a depression or groove in the cerebral cortex. It surrounds a gyrus (pl. gyri), creating the characteristic folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. The larger sulci are usually called fissures. Structure Sulci, the grooves, and gyri, the folds or ridges, make up the folded surface of the cerebral cortex. Larger or deeper sulci are termed fissures, and in many cases the two terms are interchangeable. The folded cortex creates a larger surface area for the brain in humans and other mammals. When looking at the human brain, two-thirds of the surface are hidden in the grooves. The sulci and fissures are both grooves in the cortex, but they are differentiated by size. A sulcus is a shallower groove that surrounds a gyrus. A fissure is a large furrow that divides the brain into lobes and also into the two hemispheres as the longitudinal fissure. Importance of expanded surface area As the surfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articles Containing Video Clips
Article often refers to: * Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness * Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication Article may also refer to: Government and law * Article (European Union), articles of treaties of the European Union * Articles of association, the regulations governing a company, used in India, the UK and other countries * Articles of clerkship, the contract accepted to become an articled clerk * Articles of Confederation, the predecessor to the current United States Constitution *Articles of Impeachment, Article of Impeachment, a formal document and charge used for impeachment in the United States * Articles of incorporation, for corporations, U.S. equivalent of articles of association * Articles of organization, for limited liability organizations, a U.S. equivalent of articles of association Other uses * Article, an HTML element, delimited by the tags and * Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |