|
Prairie Creek Site
The Prairie Creek Site is an archaeological site in the southwestern part of the U.S. state of Indiana. Located approximately north of Washington in Daviess County, it lies along the southern bank of the westward-flowing Prairie Creek, a White River tributary. About to the east of the site, the stream leaves the Thousand Acre Woods, a heavily wooded area around a glacial lake; six miles downstream is the creek's confluence with the White River. Excavation In early 1972, a local resident observed the bones of a mastodon along the creekside and reported the finding to the Glenn Black Laboratory of Archaeology at Indiana University Bloomington; before long, university archaeologist Curtis Tomak examined the site, removing portions of the mastodon skeleton and inspecting the stratigraphy of the site. This inspection revealed that the site was heavily stratified, due largely to stream deposits. Tomak led a test excavation at the site on weekends during the final third of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington, Indiana
Washington is a city in Daviess County, Indiana. The population was 11,509 at the time of the 2010 census. The city is the county seat of Daviess County. It is also the principal city of the Washington, Indiana Micropolitan Statistical Area, which comprises all of Daviess County and had an estimated 2017 population of 31,648. History Washington was platted in 1815. It was named from Washington Township. The railroad was built through Washington in 1857. By 1889, it was a major depot and repair yard for the Ohio and Mississippi Railroad. The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad took over the line in 1893. During this time, the railroad employed over 1,000 workers. On November 17, 2013, an EF2 tornado tore through the western edge of the city destroying 20 homes and severely damaging 20 others. The Magnus J. Carnahan House, Daviess County Courthouse, Thomas Faith House, Robert C. Graham House, Dr. John A. Scudder House, Washington Commercial Historic District, and Dr. Nelson Wils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class of soil or soil type; i.e., a soil containing more than 85 percent sand-sized particles by mass. The composition of sand varies, depending on the local rock sources and conditions, but the most common constituent of sand in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal settings is silica (silicon dioxide, or SiO2), usually in the form of quartz. Calcium carbonate is the second most common type of sand, for example, aragonite, which has mostly been created, over the past 500million years, by various forms of life, like coral and shellfish. For example, it is the primary form of sand apparent in areas where reefs have dominated the ecosystem for millions of years like the Caribbean. Somewhat more rarely, sand may be composed of calciu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1972 Archaeological Discoveries
Year 197 ( CXCVII) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Magius and Rufinus (or, less frequently, year 950 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 197 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * February 19 – Battle of Lugdunum: Emperor Septimius Severus defeats the self-proclaimed emperor Clodius Albinus at Lugdunum (modern Lyon). Albinus commits suicide; legionaries sack the town. * Septimius Severus returns to Rome and has about 30 of Albinus's supporters in the Senate executed. After his victory he declares himself the adopted son of the late Marcus Aurelius. * Septimius Severus forms new naval units, manning all the triremes in Italy with heavily armed troops for war in the East. His soldiers embark on an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Archaeological Sites On The National Register Of Historic Places In Indiana
__NOTOC__ This is a list of archaeological sites on the National Register of Historic Places in Indiana. Historic sites in the United States qualify to be listed on the National Register of Historic Places by passing one or more of four different criteria; Criterion D permits the inclusion of proven and potential archaeological sites. More than fifty different sites in Indiana are listed under this criterion, including both Native American and European sites, and two others were once listed but have been removed. This list includes all properties in Indiana that qualify under this criterion. Current listings Former listings See also * National Register of Historic Places listings in Indiana References External linksIndiana Department of Natural Resources which oversees archaeology in the state {{DEFAULTSORT:Native American Archaeological Sites On The National Register Of Historic Places In Indiana Archaeological Sites On NRHP In Indiana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property. The passage of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing resources within historic districts. For most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. Its goals are to help property owners and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Context
This page is a glossary of archaeology, the study of the human past from material remains. A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z See also * Outline of archaeology * Table of years in archaeology * Glossary of history References Bibliography * * * * * * * External links About.com Archaeology Glossary {{Glossaries of science and engineering Archaeology Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishhook
A fish hook or fishhook, formerly also called angle (from Old English ''angol'' and Proto-Germanic ''*angulaz''), is a hook used to catch fish either by piercing and embedding onto the inside of the fish mouth (angling) or, more rarely, by impaling and snagging the external fish body. Fish hooks are normally attached to a line, which tethers the target fish to the angler for retrieval, and are typically dressed with some form of bait or lure that entices the fish to swallow the hook out of its own natural instinct to forage or hunt. Fish hooks have been employed for millennia by fishermen to catch freshwater and saltwater fish. There is an enormous variety of fish hooks in the world of fishing. Sizes, designs, shapes, and materials are all variable depending on the intended purpose of the hook. Fish hooks are manufactured for a range of purposes from general fishing to extremely limited and specialized applications. Fish hooks are designed to hold various types of artificial, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
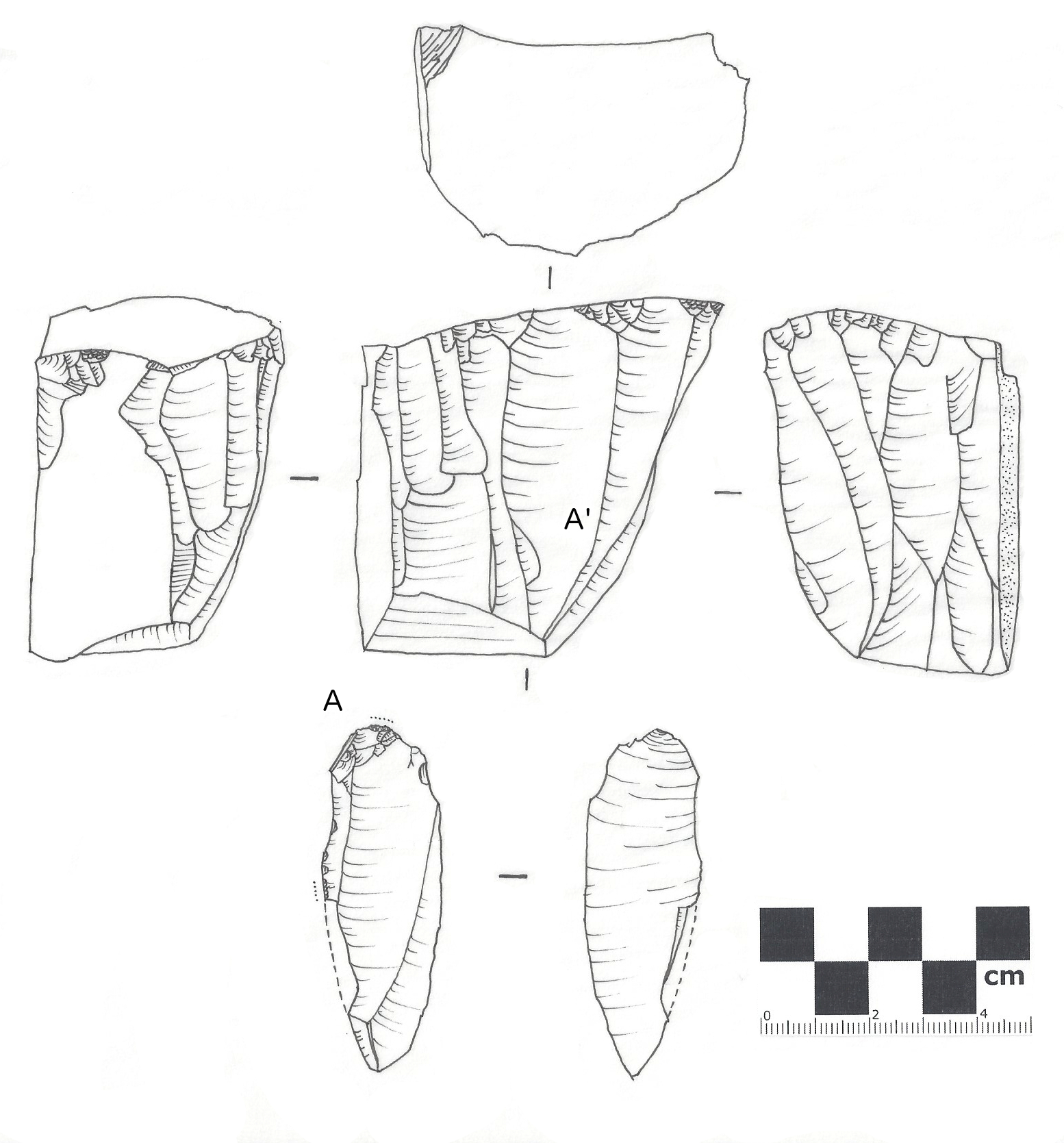
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often ( but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since cores are often struck on an edge with a suitable angle (<90°) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artifact (archaeology)
An artifact, or artefact (see American and British English spelling differences), is a general term for an item made or given shape by humans, such as a tool or a work of art, especially an object of archaeological interest. In archaeology, the word has become a term of particular nuance and is defined as an object recovered by archaeological endeavor, which may be a cultural artifact having cultural interest. Artifact is the general term used in archaeology, while in museums the equivalent general term is normally "object", and in art history perhaps artwork or a more specific term such as "carving". The same item may be called all or any of these in different contexts, and more specific terms will be used when talking about individual objects, or groups of similar ones. Artifacts exist in many different forms and can sometimes be confused with ecofacts and features; all three of these can sometimes be found together at archaeological sites. They can also exist in different t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armadillo
Armadillos (meaning "little armored ones" in Spanish) are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. The Chlamyphoridae and Dasypodidae are the only surviving families in the order, which is part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. Nine extinct genera and 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of different environments. Armadillos are characterized by a leathery armor shell and long, sharp claws for digging. They have short legs, but can move quite quickly. The average length of an armadillo is about , including its tail. The giant armadillo grows up to and weighs up to , while the pink fairy armadillo has a length of only . When threatened by a predator, ''Tolypeutes'' species frequently roll up into a ball; they are the only species of armadillo capable of this. Etymology The wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)