|
PowerBook 500 Series
The PowerBook 500 series (codenamed ''Blackbird'', which it shared with the older Macintosh IIfx) is a range of Apple Macintosh PowerBook portable computers first introduced by Apple Computer with the 540c model on May 16, 1994. It was the first to have stereo speakers, a trackpad, and Ethernet networking built-in. It was the first PowerBook series to use a Motorola 68LC040 CPU (simultaneous with Duo 280) and be upgradeable to the PowerPC architecture via a swap-out CPU daughter card (with the PowerPC and 68040 upgrades for sale), use 9.5-inch Dual Scan passive color/B&W displays, 16-bit stereo sound with stereo speakers, have an expansion bay, PC Card capability, two battery bays (and a ten-minute sleep/clock battery, which allowed for main batteries to be swapped out while in sleep mode), full-size keyboard with F1–F12 function keys, be able to sleep while connected to an external monitor and have a battery contact cover included on the actual batteries. It included a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
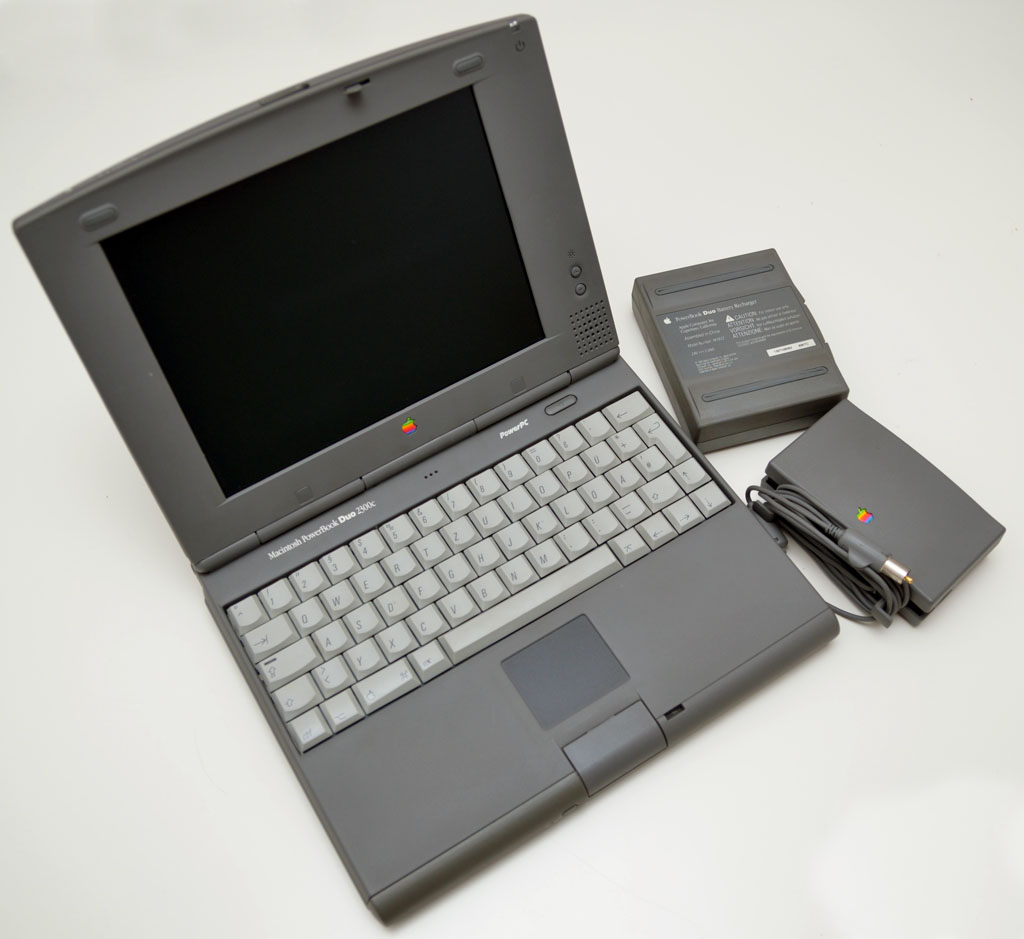
PowerBook Duo
The PowerBook Duo is a line of subnotebooks manufactured and sold by Apple Computer from 1992 until 1997 as a more compact companion to the PowerBook line. Improving upon the PowerBook 100's portability (its immediate predecessor and Apple's third-smallest laptop), the Duo came in seven different models. They were the Duo 210, 230, 250, 270c, 280, 280c, and 2300c, with the 210 and 230 being the earliest, and the 2300c being the final incarnation before the entire line was dropped in early 1997. Weighing and slightly smaller than a sheet of paper at , and only thick, it was the lightest and smallest of all of Apple's PowerBooks at the time, and remains one of Apple's smallest notebooks ever produced. Only the MacBook Air, the Retina MacBook Pro and the Retina MacBook weigh less, though they are wider and deeper (but considerably thinner). The Duo had the most in common with the original MacBook Air which only included one USB 2.0 port, one video port (requiring an adapter) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Village Communication
Global Village Communication Inc. was a leading manufacturer of easy-to-use fax modems and other telecommunications products for Apple's Macintosh platform. It was one of the few manufacturers to support the Mac's RS-422 serial ports without requiring an adapter. Major product lines included the TelePort series of high-speed desktop dial-up modems, and the PowerPort series of internal PowerBook modems, as well as a series of modems that connected to the Mac's ADB port. Many of its products were bundled with the Macintosh Performa series of computers, and it was the manufacturer for the internal modem in the PowerBook 500 series. The company also produced the OneWorld fax server and the GlobalFax fax Fax (short for facsimile), sometimes called telecopying or telefax (the latter short for telefacsimile), is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material (both text and images), normally to a telephone number connected to a printer o ... software for Macintosh comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Display Resolution
The graphics display resolution is the width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized (e.g. by VESA) and typically given a name and an initialism that is descriptive of its dimensions. A graphics display resolution can be used in tandem with the size of the graphics display to calculate pixel density. An increase in the pixel density often correlates with a decrease in the size of individual pixels on a display. Overview by vertical resolution and aspect ratio Aspect ratio The favored aspect ratio of mass-market display industry products has changed gradually from 4:3, then to 16:10, then to 16:9, and is now changing to 18:9 for smartphones. The 4:3 aspect ratio generally reflects older products, especially the era of the cathode ray tube (CRT). The 16:10 aspect ratio had its largest use in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
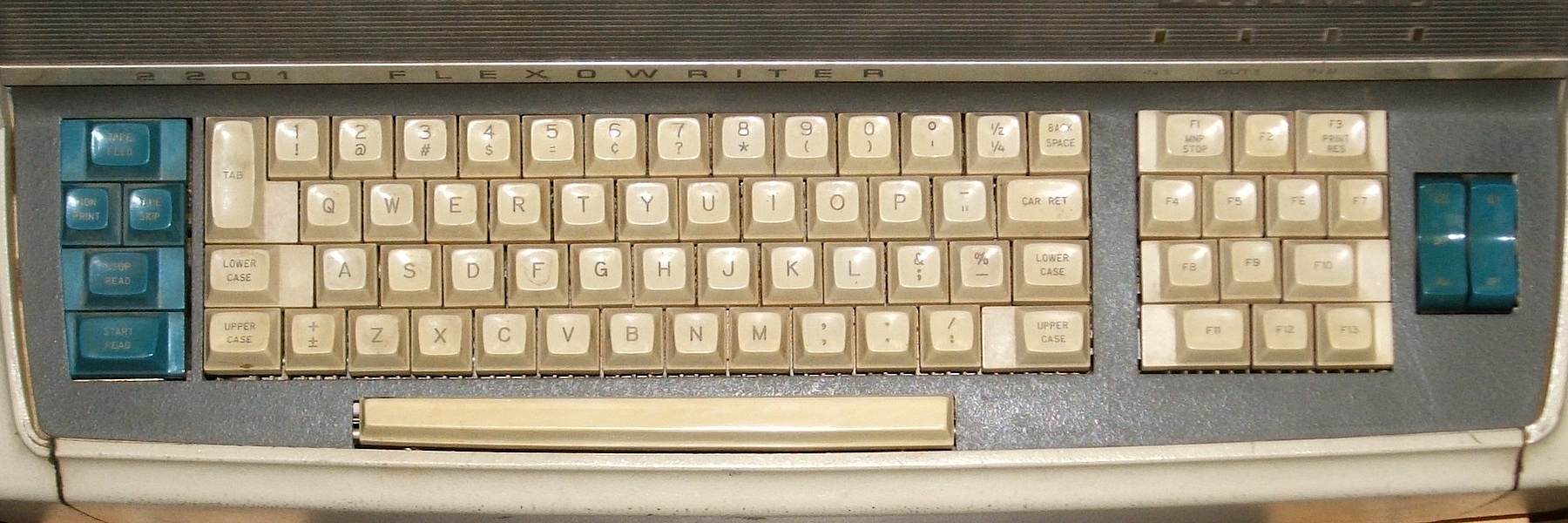
Function Key
A function key is a key on a computer or terminal keyboard that can be programmed so as to cause an operating system command interpreter or application program to perform certain actions, a form of soft key. On some keyboards/computers, function keys may have default actions, accessible on power-on. Function keys on a terminal may either generate short fixed sequences of characters, often beginning with the escape character (ASCII 27), or the characters they generate may be configured by sending special character sequences to the terminal. On a standard computer keyboard, the function keys may generate a fixed, single byte code, outside the normal ASCII range, which is translated into some other configurable sequence by the keyboard device driver or interpreted directly by the application program. Function keys may have abbreviations or pictographic representations of default actions printed on/besides them, or they may have the more common "F-number" designations. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Math Co-processor
A coprocessor is a computer processor used to supplement the functions of the primary processor (the CPU). Operations performed by the coprocessor may be floating-point arithmetic, graphics, signal processing, string processing, cryptography or I/O interfacing with peripheral devices. By offloading processor-intensive tasks from the main processor, coprocessors can accelerate system performance. Coprocessors allow a line of computers to be customized, so that customers who do not need the extra performance do not need to pay for it. Functionality Coprocessors vary in their degree of autonomy. Some (such as FPUs) rely on direct control via coprocessor instructions, embedded in the CPU's instruction stream. Others are independent processors in their own right, capable of working asynchronously; they are still not optimized for general-purpose code, or they are incapable of it due to a limited instruction set focused on accelerating specific tasks. It is common for these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
68LC040
The Motorola 68040 ("''sixty-eight-oh-forty''") is a 32-bit microprocessor in the Motorola 68000 series, released in 1990. It is the successor to the 68030 and is followed by the 68060, skipping the 68050. In keeping with general Motorola naming, the 68040 is often referred to as simply the '040 (pronounced ''oh-four-oh'' or ''oh-forty''). The 68040 was the first 680x0 family member with an on-chip Floating-Point Unit (FPU). It thus included all of the functionality that previously required external chips, namely the FPU and Memory Management Unit (MMU), which was added in the 68030. It also had split instruction and data caches of 4 kilobytes each. It was fully pipelined, with six stages. Versions of the 68040 were created for specific market segments, including the 68LC040, which removed the FPU, and the 68EC040, which removed both the FPU and MMU. Motorola had intended the EC variant for embedded use, but embedded processors during the 68040's time did not need the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Processor Direct Slot
A processor direct slot (PDS) is a slot incorporated into many older Macintosh models that allowed direct access to the signal pins of a CPU, similar to the functionality of a local bus in PCs. This would result in much higher speeds than having to go through a bus layer, such as NuBus, which typically ran at a slower 10 MHz speed. Overview Typically, a machine would feature multiple bus expansions slots, if any. However, there was never more than one PDS slot. Rather than providing a sophisticated communication protocol with ''arbitration'' between different bits of hardware that might be trying to use the communication channel at the same time, the PDS slot, for the most part, just gave direct access to signal pins on the CPU, making it closer in nature to a local bus. Thus, PDS slots tended to be CPU-specific, and therefore a card designed for the PDS slot in the Motorola 68030-based Macintosh SE/30, for example, would not work in the Motorola 68040-based Quadra 700. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerBook 1400
The PowerBook 1400 is a notebook computer that was designed and sold by Apple Computer, Inc. (now Apple Inc.) from 1996 to 1998 as part of their PowerBook series of Macintosh computers. Introduced in October 1996 at a starting price of $2,499, it was the first new PowerBook after the controversial PowerBook 5300. After the introduction of the more powerful PowerBook 3400c in February 1997, the 1400 took on the role of Apple's entry level notebook and remained there until its discontinuation in May 1998. Its successor, the PowerBook G3 Series (i.e. - "Wallstreet"/"Mainstreet"), would ultimately go on to replace and consolidate not only the 1400, but the 2400c and 3400c as well. Throughout its 18 months on the market, the PowerBook 1400 was available in a number of different configurations. It was originally released with a 117 MHz PowerPC 603e processor; a 133 MHz processor was added in July 1997, and the line topped out with a 166 MHz processor the following Dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newer Technology
Newer Technology is an American technology company headquartered in Woodstock, Illinois, that designs and manufactures accessories primarily for Apple, Inc. products. History Founded in 1988 Newer Technology initially focused on manufacturing computer upgrades and accessories such as processor cards, CPU caches, memory, and PowerBook batteries. At its peak in the mid-1990s the company was known in Apple Macintosh communities for its end-of-life extending upgrades. This included user-installable MAXpowr CPU cards that could upgrade an obsolete Macintosh computer across architectures, such as from Motorola 68000 to PowerPC thereby extending the usable life of the computer by years. NewerTech filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in June 1996 due to a rapidly declining Apple Macintosh market and sharp decrease in memory prices. An effort to diversify revenue by developing Windows products was announced, but by the end of 2000 and the company was dissolved. The name and remaining int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
68040
The Motorola 68040 ("''sixty-eight-oh-forty''") is a 32-bit microprocessor in the Motorola 68000 series, released in 1990. It is the successor to the 68030 and is followed by the 68060, skipping the 68050. In keeping with general Motorola naming, the 68040 is often referred to as simply the '040 (pronounced ''oh-four-oh'' or ''oh-forty''). The 68040 was the first 680x0 family member with an on-chip Floating-Point Unit (FPU). It thus included all of the functionality that previously required external chips, namely the FPU and Memory Management Unit (MMU), which was added in the 68030. It also had split instruction and data caches of 4 kilobytes each. It was fully pipelined, with six stages. Versions of the 68040 were created for specific market segments, including the 68LC040, which removed the FPU, and the 68EC040, which removed both the FPU and MMU. Motorola had intended the EC variant for embedded use, but embedded processors during the 68040's time did not need the pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Francisco Examiner
The ''San Francisco Examiner'' is a newspaper distributed in and around San Francisco, California, and published since 1863. Once self-dubbed the "Monarch of the Dailies" by then-owner William Randolph Hearst, and flagship of the Hearst Corporation chain, the ''Examiner'' converted to free distribution early in the 21st century and is owned by Clint Reilly Communications, which bought the newspaper at the end of 2020 along with the ''SF Weekly''. History Founding The ''Examiner'' was founded in 1863 as the ''Democratic Press'', a pro- Confederacy, pro-slavery, pro-Democratic Party paper opposed to Abraham Lincoln, but after his assassination in 1865, the paper's offices were destroyed by a mob, and starting on June 12, 1865, it was called ''The Daily Examiner''. Hearst acquisition In 1880, mining engineer and entrepreneur George Hearst bought the ''Examiner''. Seven years later, after being elected to the U.S. Senate, he gave it to his son, William Randolph Hearst, who was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |