|
Porta Querquetulana
The Porta Querquetulana or Querquetularia was a gateway in the Servian Wall, named after the sacred grove of the Querquetulanae adjacent to and just within it. The grove appears not to have still existed in the latter 1st century BC. The location of the gate is problematic. Lawrence Richardson located it at the edge of Regio V Esquiliae, with the Clivus Scauri passing through it. Platner located the gate and the wood on or near the Caelian Hill, but between the Porta Capena and the Porta Caelimontana. The Caelian Hill was supposed to have been named ''Querquetulanus'' before it was settled by Caelius Vibenna and named for him, and the location of the gate on the Caelian is based in part on the earlier name. In the early 21st century, photogrammetric data and 3D visualization have suggested that the grove of the Querquetulanae may have been incorporated into the Gardens of Maecenas. A nymphaeum from the time of Hadrian would have replaced the natural spring within it. In this view ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Student's Manual Of Ancient Geography, Based Upon The Dictionary Of Greek And Roman Geography (1861) (14768984432)
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is the science and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment through the process of recording, measuring and interpreting photographic images and patterns of electromagnetic radiant imagery and other phenomena. The term photogrammetry was coined by the Prussian architect Albrecht Meydenbauer, which appeared in his 1867 article "Die Photometrographie." There are many variants of photogrammetry. One example is the extraction of three-dimensional measurements from two-dimensional data (i.e. images); for example, the distance between two points that lie on a plane parallel to the photographic image plane can be determined by measuring their distance on the image, if the scale (map), scale of the image is known. Another is the extraction of accurate color ranges and values representing such quantities as albedo, specular reflection, Metallicity#Photometric colors, metallicity, or ambient occlusion from photographs of mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter Fagutalis
The Esquiline Hill (; la, Collis Esquilinus; it, Esquilino ) is one of the Seven Hills of Rome. Its southernmost cusp is the ''Oppius'' (Oppian Hill). Etymology The origin of the name ''Esquiline'' is still under much debate. One view is that the hill was named after the abundance of ( Italian oaks) growing there. Another view is that, during Rome's infancy, the Capitolium, the Palatinum, and the northern fringes of the Caelian were the most-populated areas of the city, whose inhabitants were considered ("in-towners"); those who inhabited the external regions – Aurelian, Oppius, Cispius, Fagutal – were considered ("suburbanites"). History The Esquiline Hill includes three prominent spurs, which are sometimes called "hills" as well: *Cispian (''Cispius'') – northern spur *Oppian (''Oppius'') – southern spur *Fagutal (''Fagutalis'') – western spur Rising above the valley in which was later built the Colosseum, the Esquiline was a fashionable residential dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Natural History''), which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. His nephew, Pliny the Younger, wrote of him in a letter to the historian Tacitus: Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume work ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus and Suetonius. Tacitus—who many scholars agree had never travelled in Germania—used ''Bella Germani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esquiline Hill
The Esquiline Hill (; la, Collis Esquilinus; it, Esquilino ) is one of the Seven Hills of Rome. Its southernmost cusp is the ''Oppius'' ( Oppian Hill). Etymology The origin of the name ''Esquiline'' is still under much debate. One view is that the hill was named after the abundance of ( Italian oaks) growing there. Another view is that, during Rome's infancy, the Capitolium, the Palatinum, and the northern fringes of the Caelian were the most-populated areas of the city, whose inhabitants were considered ("in-towners"); those who inhabited the external regions – Aurelian, Oppius, Cispius, Fagutal – were considered ("suburbanites"). History The Esquiline Hill includes three prominent spurs, which are sometimes called "hills" as well: *Cispian (''Cispius'') – northern spur * Oppian (''Oppius'') – southern spur *Fagutal (''Fagutalis'') – western spur Rising above the valley in which was later built the Colosseum, the Esquiline was a fashionable residential d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
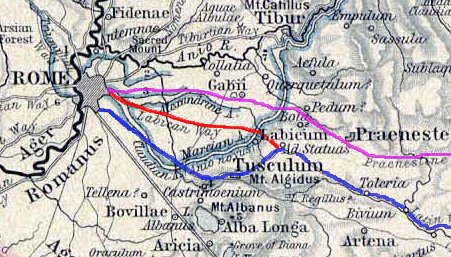
Via Labicana
The Via Labicana was an ancient road of Italy, leading east-southeast from Rome. It seems possible that the road at first led to Tusculum, that it was then extended to Labici, and later still became a road for through traffic; it may even have superseded the Via Latina as a route to the southeast, for, while the distance from Rome to their main junction at Ad Bivium (or to another junction at Compitum Anagninum) is practically identical, the summit level of the former is lower than that of the latter, a little to the west of the pass of Mount Algidus. After their junction it is probable that the road bore the name Via Latina rather than Via Labicana. The course of the road after the first six miles from Rome is not identical with that of any modern road, but can be clearly traced by remains of pavement and buildings along its course. Ashby cites his own contribution to ''Papers of the British School at Rome'', i .215 sqq. Via Labicana entered Rome through the Aurelian walls via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
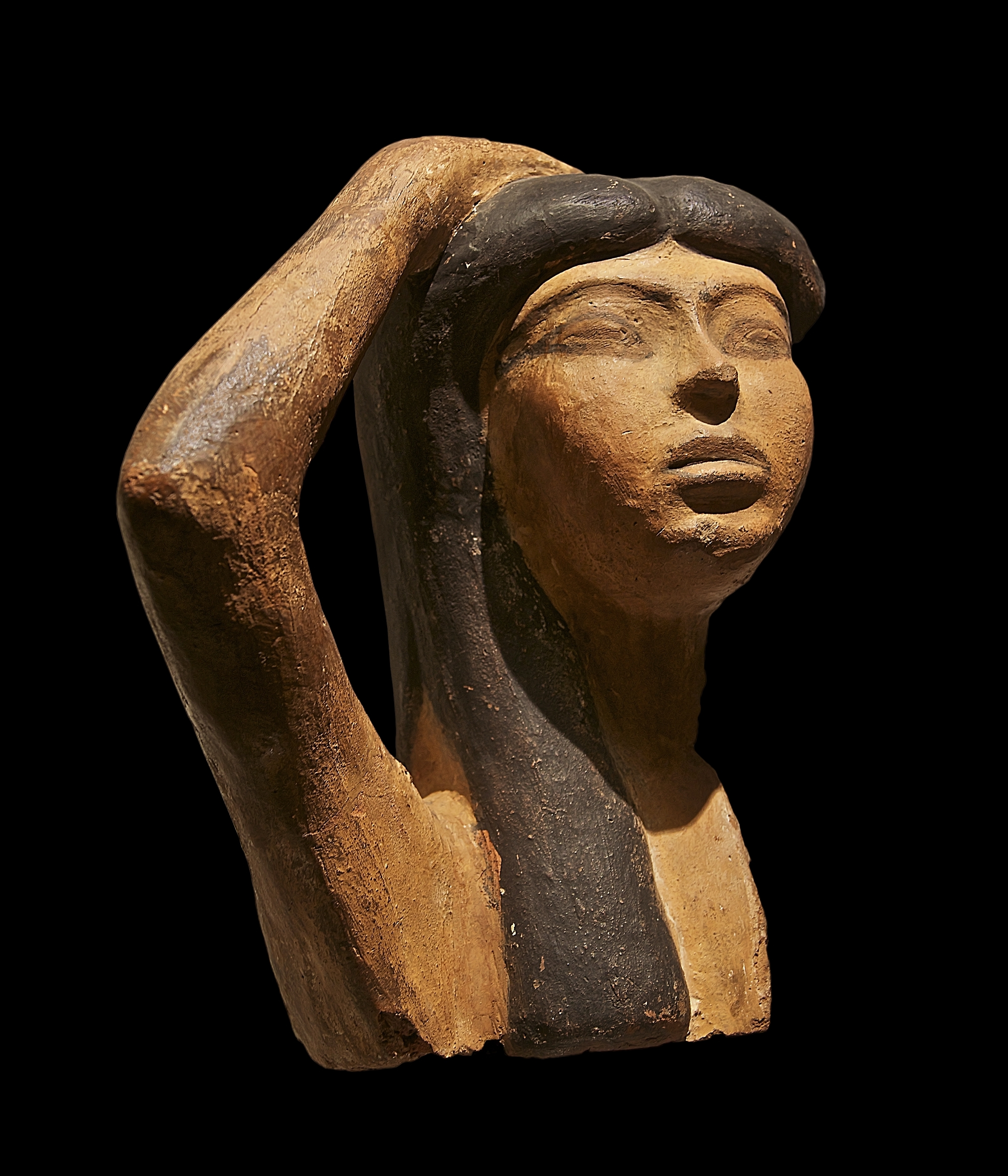
Isis Et Serapis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingdom () as one of the main characters of the Osiris myth, in which she resurrects her slain brother and husband, the divine king Osiris, and produces and protects his heir, Horus. She was believed to help the dead enter the afterlife as she had helped Osiris, and she was considered the divine mother of the pharaoh, who was likened to Horus. Her maternal aid was invoked in healing Spell (paranormal), spells to benefit ordinary people. Originally, she played a limited role in royal rituals and temple rites, although she was more prominent in funerary practices and magical texts. She was usually portrayed in art as a human woman wearing a throne-like hieroglyph on her head. During the New Kingdom (), as she took on traits that originally belong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)