|
Popoviciu's Inequality On Variances
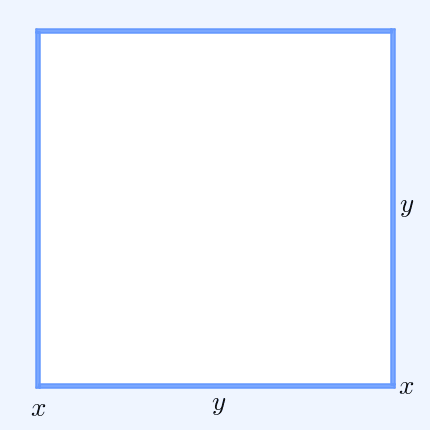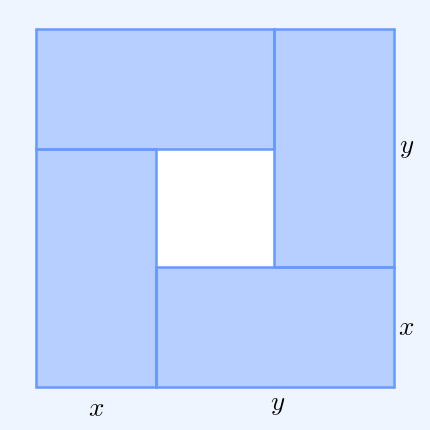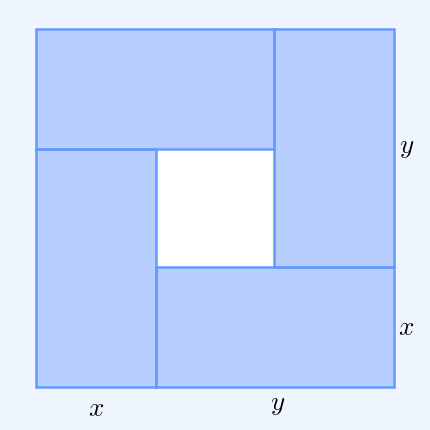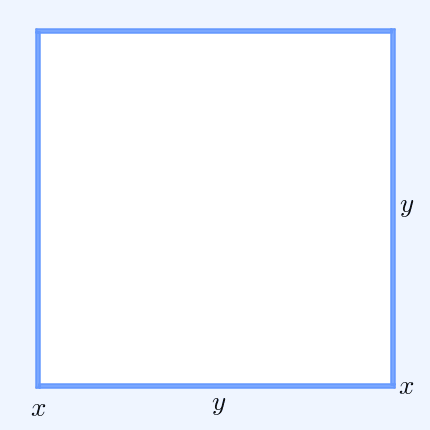
In probability theory, Popoviciu's inequality, named after Tiberiu Popoviciu, is an upper bound on the variance ''σ''2 of any bounded probability distribution. Let ''M'' and ''m'' be upper and lower bounds on the values of any random variable with a particular probability distribution. Then Popoviciu's inequality states: : \sigma^2 \le \frac14 ( M - m )^2. This equality holds precisely when half of the probability is concentrated at each of the two bounds. Sharma ''et al''. have sharpened Popoviciu's inequality: : \le \frac14 (M - m)^2. Popoviciu's inequality is weaker than the Bhatia–Davis inequality which states : \sigma^2 \le ( M - \mu )( \mu - m ) where ''μ'' is the expectation of the random variable. In the case of an independent sample of ''n'' observations from a bounded probability distribution, the von Szokefalvi Nagy inequality gives a lower bound to the variance of the sample mean: : \sigma^2 \ge \frac . Proof via the Bhatia–Davis inequa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set of axioms. Typically these axioms formalise probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure taking values between 0 and 1, termed the probability measure, to a set of outcomes called the sample space. Any specified subset of the sample space is called an event. Central subjects in probability theory include discrete and continuous random variables, probability distributions, and stochastic processes (which provide mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic or uncertain processes or measured quantities that may either be single occurrences or evolve over time in a random fashion). Although it is not possible to perfectly predict random events, much can be said about their behavior. Two major results in probability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiberiu Popoviciu
Tiberiu Popoviciu (February 16, 1906–October 29, 1975) was a Romanian mathematician and the namesake of Popoviciu's inequality and Popoviciu's inequality on variances. The Tiberiu Popoviciu High School of Computer Science in Cluj-Napoca is named after him. In 1951 he founded a research institute which now bears his name: Tiberiu Popoviciu Institute of Numerical Analysis. Biography Popoviciu was born in Arad in 1906, and attended high school in his hometown, the school which is now the Moise Nicoară National College. He graduated from the University of Bucharest, and got his doctorate in 1933 under Paul Montel from Paris-Sorbonne University. He was a lecturer at the Universities of Cernăuți, Bucharest, and Iași. In 1946 he was appointed professor at the University of Cluj. On June 4, 1937 Popoviciu was elected a corresponding member of the Romanian Academy of Sciences. In November 1948 he was elected a corresponding member of the Romanian Academy. He became full member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Bound
In mathematics, particularly in order theory, an upper bound or majorant of a subset of some preordered set is an element of that is greater than or equal to every element of . Dually, a lower bound or minorant of is defined to be an element of that is less than or equal to every element of . A set with an upper (respectively, lower) bound is said to be bounded from above or majorized (respectively bounded from below or minorized) by that bound. The terms bounded above (bounded below) are also used in the mathematical literature for sets that have upper (respectively lower) bounds. Examples For example, is a lower bound for the set (as a subset of the integers or of the real numbers, etc.), and so is . On the other hand, is not a lower bound for since it is not smaller than every element in . The set has as both an upper bound and a lower bound; all other numbers are either an upper bound or a lower bound for that . Every subset of the natural numbers has a lowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. Variance has a central role in statistics, where some ideas that use it include descriptive statistics, statistical inference, hypothesis testing, goodness of fit, and Monte Carlo sampling. Variance is an important tool in the sciences, where statistical analysis of data is common. The variance is the square of the standard deviation, the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by \sigma^2, s^2, \operatorname(X), V(X), or \mathbb(X). An advantage of variance as a measure of dispersion is that it is more amenable to algebraic manipulation than other measures of dispersion such as the expected absolute deviation; for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the probabilities of events (subsets of the sample space). For instance, if is used to denote the outcome of a coin toss ("the experiment"), then the probability distribution of would take the value 0.5 (1 in 2 or 1/2) for , and 0.5 for (assuming that the coin is fair). Examples of random phenomena include the weather conditions at some future date, the height of a randomly selected person, the fraction of male students in a school, the results of a survey to be conducted, etc. Introduction A probability distribution is a mathematical description of the probabilities of events, subsets of the sample space. The sample space, often denoted by \Omega, is the set of all possible outcomes of a random phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on random events. It is a mapping or a function from possible outcomes (e.g., the possible upper sides of a flipped coin such as heads H and tails T) in a sample space (e.g., the set \) to a measurable space, often the real numbers (e.g., \ in which 1 corresponding to H and -1 corresponding to T). Informally, randomness typically represents some fundamental element of chance, such as in the roll of a dice; it may also represent uncertainty, such as measurement error. However, the interpretation of probability is philosophically complicated, and even in specific cases is not always straightforward. The purely mathematical analysis of random variables is independent of such interpretational difficulties, and can be based upon a rigorous axiomatic setup. In the formal mathematical language of measure theory, a random var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhatia–Davis Inequality
In mathematics, the Bhatia–Davis inequality, named after Rajendra Bhatia and Chandler Davis, is an upper bound on the variance ''σ''2 of any bounded probability distribution on the real line. Statement Let ''m'' and M be the lower and upper bounds, respectively, for a set of real numbers ''a1'', ..., ''an ,'' with a particular probability distribution. Let ''μ'' be the expected value of this distribution. Then the Bhatia–Davis inequality states: : \sigma^2 \le (M - \mu)(\mu - m). \, Equality holds if and only if every ''aj'' in the set of values is equal either to ''M'' or to ''m''. Proof Since m \leq A \leq M, 0 \leq \mathbb M - A)(A - m)= -\mathbb ^2- m M + (m+M)\mu. Thus, \sigma^2 = \mathbb ^2- \mu^2 \leq - m M + (m+M)\mu - \mu^2 = (M - \mu) (\mu - m). Extensions of the Bhatia–Davis inequality If \Phi is a positive and unital linear mapping of a ''C* -''algebra \mathcal into a ''C*'' -algebra \mathcal, and ''A'' is a self-adjoint element of \mathcal sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Mathematical Monthly
''The American Mathematical Monthly'' is a mathematical journal founded by Benjamin Finkel in 1894. It is published ten times each year by Taylor & Francis for the Mathematical Association of America. The ''American Mathematical Monthly'' is an expository journal intended for a wide audience of mathematicians, from undergraduate students to research professionals. Articles are chosen on the basis of their broad interest and reviewed and edited for quality of exposition as well as content. In this the ''American Mathematical Monthly'' fulfills a different role from that of typical mathematical research journals. The ''American Mathematical Monthly'' is the most widely read mathematics journal in the world according to records on JSTOR. Tables of contents with article abstracts from 1997–2010 are availablonline The MAA gives the Lester R. Ford Awards annually to "authors of articles of expository excellence" published in the ''American Mathematical Monthly''. Editors *2022– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Association Of America
The Mathematical Association of America (MAA) is a professional society that focuses on mathematics accessible at the undergraduate level. Members include university, college, and high school teachers; graduate and undergraduate students; pure and applied mathematicians; computer scientists; statisticians; and many others in academia, government, business, and industry. The MAA was founded in 1915 and is headquartered at 1529 18th Street, Northwest in the Dupont Circle neighborhood of Washington, D.C. The organization publishes mathematics journals and books, including the '' American Mathematical Monthly'' (established in 1894 by Benjamin Finkel), the most widely read mathematics journal in the world according to records on JSTOR. Mission and Vision The mission of the MAA is to advance the understanding of mathematics and its impact on our world. We envision a society that values the power and beauty of mathematics and fully realizes its potential to promote human flourishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Von Szokefalvi Nagy Inequality
The term ''von'' () is used in German language surnames either as a nobiliary particle indicating a noble patrilineality, or as a simple preposition used by commoners that means ''of'' or ''from''. Nobility directories like the ''Almanach de Gotha'' often abbreviate the noble term ''von'' to ''v.'' In medieval or early modern names, the ''von'' particle was at times added to commoners' names; thus, ''Hans von Duisburg'' meant "Hans from he city ofDuisburg". This meaning is preserved in Swiss toponymic surnames and in the Dutch or Afrikaans ''van'', which is a cognate of ''von'' but does not indicate nobility. Usage Germany and Austria The abolition of the monarchies in Germany and Austria in 1919 meant that neither state has a privileged nobility, and both have exclusively republican governments. In Germany, this means that legally ''von'' simply became an ordinary part of the surnames of the people who used it. There are no longer any legal privileges or constraints assoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inequality Of Arithmetic And Geometric Means
In mathematics, the inequality of arithmetic and geometric means, or more briefly the AM–GM inequality, states that the arithmetic mean of a list of non-negative real numbers is greater than or equal to the geometric mean of the same list; and further, that the two means are equal if and only if every number in the list is the same (in which case they are both that number). The simplest non-trivial case – i.e., with more than one variable – for two non-negative numbers and , is the statement that :\frac2 \ge \sqrt with equality if and only if . This case can be seen from the fact that the square of a real number is always non-negative (greater than or equal to zero) and from the elementary case of the binomial formula: :\begin 0 & \le (x-y)^2 \\ & = x^2-2xy+y^2 \\ & = x^2+2xy+y^2 - 4xy \\ & = (x+y)^2 - 4xy. \end Hence , with equality precisely when , i.e. . The AM–GM inequality then follows from taking the positive square root of both sides and then dividing both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory Of Probability Distributions
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may be scientific, belong to a non-scientific discipline, or no discipline at all. Depending on the context, a theory's assertions might, for example, include generalized explanations of how nature works. The word has its roots in ancient Greek, but in modern use it has taken on several related meanings. In modern science, the term "theory" refers to scientific theories, a well-confirmed type of explanation of nature, made in a way consistent with the scientific method, and fulfilling the criteria required by modern science. Such theories are described in such a way that scientific tests should be able to provide empirical support for it, or empirical contradiction ("falsify") of it. Scientific theories are the most reliable, rigorous, and compre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |