|
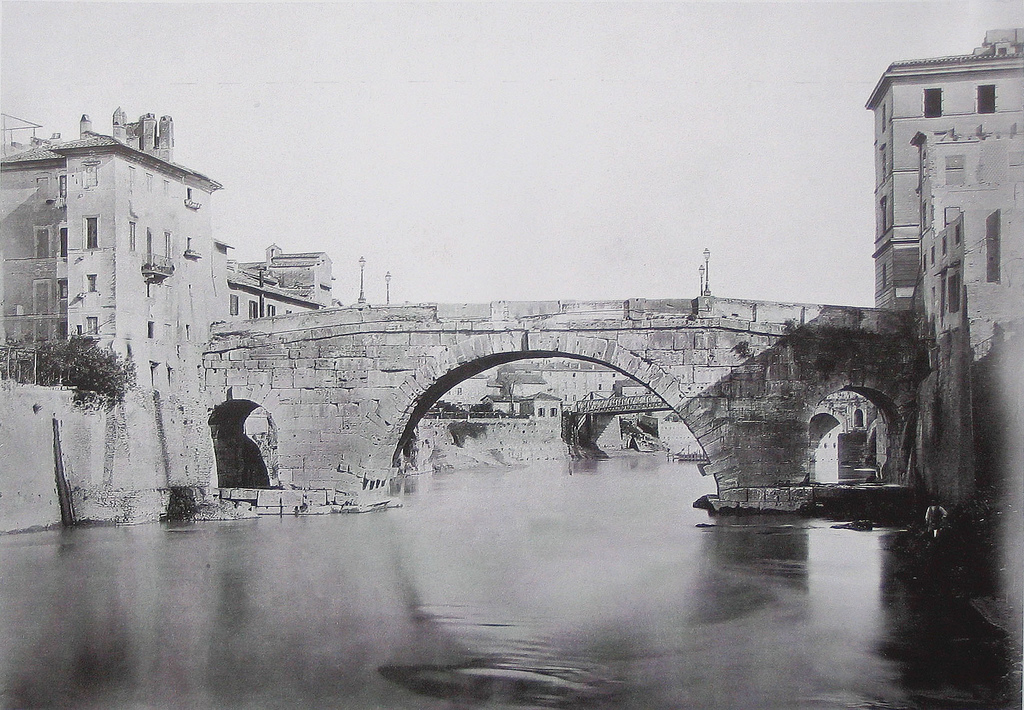
Pons Cestius
, image = 2012-05-15 Roma ponte Cestio da ponte Garibaldi 1.jpg , caption = The Pons Cestius in its modern form The Roman bridge around 1880, before its reconstruction , carries = pedestrians, motor vehicles , crosses = , locale = Rome, Italy , downstream=Ponte Palatino , design = arch bridge , material = stone (tuff, peperino, travertine) , spans = 3 , pierswater =2 , mainspan = , length = , width = , built= , rebuilt= , upstream=Ponte Garibaldi , coordinates= , image_size=270 , mapframe-frame-width=270 , mapframe=yes , mapframe-caption=Click on the map for a fullscreen view , mapframe-zoom=13 , mapframe-marker=monument , mapframe-wikidata=yes The Pons Cestius ( it, Ponte Cestio) is an ancient Roman bridge connecting the right bank of the Tiber with the west of the Tiber Island in Rome, Italy. In Late Antiquity, the bridge was replaced and renamed the Pons Gratiani. It is also known as Ponte San Bart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponte Cestio, Rome, Italy
Ponte, a word meaning ''bridge'' in Italian, Portuguese, and Galician languages, may refer to: Places England *Pontefract, a town in the Metropolitan City of Wakefield France *Ponte Leccia, a civil parish (hameau) in the department of Haute-Corse Italy ;Municipalities * Ponte (BN), in the Province of Benevento *Ponte Buggianese, in the Province of Pistoia *Ponte dell'Olio, in the Province of Piacenza *Ponte di Legno, in the Province of Brescia *Ponte di Piave, in the Province of Treviso *''Ponte Gardena'', Italian name for Waidbruck, in South Tyrol *Ponte in Valtellina, in the Province of Sondrio *Ponte Lambro, in the Province of Como *Ponte nelle Alpi, in the Province of Belluno *Ponte Nizza, in the Province of Provincia di Pavia *Ponte Nossa, in the Province of Bergamo *Ponte San Nicolò, in the Province of Padua *Ponte San Pietro, in the Province of Bergamo ;Civil parishes and quarters * Ponte (Rome), a ''rione'' in the City of Rome *Ponte di Cerreto, in the Province of Peru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gens
In ancient Rome, a gens ( or , ; plural: ''gentes'' ) was a family consisting of individuals who shared the same Roman naming conventions#Nomen, nomen and who claimed descent from a common ancestor. A branch of a gens was called a ''stirps'' (plural: ''stirpes''). The ''gens'' was an important social structure at Rome and throughout Roman Italy, Italia during the period of the Roman Republic. Much of individuals' social standing depended on the gens to which they belonged. Certain gentes were classified as Patrician (ancient Rome), patrician, others as plebs, plebeian; some had both patrician and plebeian branches. The importance of membership in a gens declined considerably in Roman Empire, imperial times, although the ''gentilicium'' continued to be used and defined the origins and Roman dynasty, dynasties of Roman emperors. Harper's Dictionary of Classical Antiquities, ''Harper's Dictionary of Classical Literature and Antiquities'', Second Edition, Harry Thurston Peck, E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentinianic Dynasty
The Valentinianic or Valentinian dynasty was a ruling house of five generations of dynasts, including five Roman emperors during Late Antiquity, lasting nearly a hundred years from the mid fourth to the mid fifth century. They succeeded the Constantinian dynasty () and reigned over the Roman Empire from 364 to 392 and from 425 to 455, with an interregnum (392–423), during which the Theodosian dynasty ruled and eventually succeeded them. The Theodosians, who intermarried into the Valentinian house, ruled concurrently in the east after 379. The Valentinian dynasty's patriarch was Gratianus Funarius, whose sons Valentinian I and Valens were both made Roman emperors in 364. Valentinian I's two sons, Gratian and Valentinian II both became emperors. Valentinian I's daughter Galla (wife of Theodosius I), Galla married Theodosius the Great, the emperor of the eastern empire, who with his descendants formed the Theodosian dynasty (). In turn, their daughter, Galla Placida married a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augusti
''Augustus'' (plural ''Augusti''; , ; "majestic", "great" or "venerable") was an ancient Roman title given as both name and title to Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus (often referred to simply as Augustus), Rome's first Emperor. On his death, it became an official title of his successor, and was so used by Roman emperors thereafter. The feminine form '' Augusta'' was used for Roman empresses and other female members of the Imperial family. The masculine and feminine forms originated in the time of the Roman Republic, in connection with things considered divine or sacred in traditional Roman religion. Their use as titles for major and minor Roman deities of the Empire associated the Imperial system and Imperial family with traditional Roman virtues and the divine will, and may be considered a feature of the Roman Imperial cult. In Rome's Greek-speaking provinces, "Augustus" was translated as ''Sebastos'' (Σεβαστός, "venerable"), or Hellenised as ''Augoustos'' (); these tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gratian
Gratian (; la, Gratianus; 18 April 359 – 25 August 383) was emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 367 to 383. The eldest son of Valentinian I, Gratian accompanied his father on several campaigns along the Rhine and Danube frontiers and was raised to the rank of ''Augustus'' in 367. Upon the death of Valentinian in 375, Gratian took over government of the west while his half-brother Valentinian II was also acclaimed emperor in Pannonia. Gratian governed the western provinces of the empire, while his uncle Valens was already the emperor over the east. Gratian subsequently led a campaign across the Rhine, attacked the Lentienses, and forced the tribe to surrender. That same year, the eastern emperor Valens was killed fighting the Goths at the Battle of Adrianople, which led to Gratian elevating Theodosius to replace him in 379. Gratian favoured Nicene Christianity over traditional Roman religion, issuing the Edict of Thessalonica, refusing the office of '' pontifex maximus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valens
Valens ( grc-gre, Ουάλης, Ouálēs; 328 – 9 August 378) was Roman emperor from 364 to 378. Following a largely unremarkable military career, he was named co-emperor by his elder brother Valentinian I, who gave him the eastern half of the Roman Empire to rule. In 378, Valens was defeated and killed at the Battle of Adrianople against the invading Goths, which astonished contemporaries and marked the beginning of barbarian encroachment into Roman territory. As emperor, Valens continually faced threats both internal and external. He defeated, after some dithering, the usurper Procopius in 366, and campaigned against the Goths across the Danube in 367 and 369. In the following years, Valens focused on the eastern frontier, where he faced the perennial threat of Persia, particularly in Armenia, as well as additional conflicts with the Saracens and Isaurians. Domestically, he inaugurated the Aqueduct of Valens in Constantinople, which was longer than all the aqueducts of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentinian I
Valentinian I ( la, Valentinianus; 32117 November 375), sometimes called Valentinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 364 to 375. Upon becoming emperor, he made his brother Valens his co-emperor, giving him rule of the eastern provinces. Valentinian retained the west. During his reign, Valentinian fought successfully against the Alamanni, Quadi, and Sarmatians. Most notable was his victory over the Alamanni in 367 at the Battle of Solicinium. His general Count Theodosius defeated a revolt in Africa and the Great Conspiracy, a coordinated assault on Roman Britain by Picts, Scots, and Saxons. Valentinian was also the last emperor to conduct campaigns across both the Rhine and Danube rivers. Valentinian rebuilt and improved the fortifications along the frontiers, even building fortresses in enemy territory. He founded the Valentinianic dynasty, with his sons Gratian and Valentinian II succeeding him in the western half of the empire. Early life Valentinian was born in 321 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polemius Silvius
Polemius Silvius ('' fl.'' 5th century) was the author of an annotated Julian calendar that attempted to integrate the traditional Roman festival cycle with the new Christian holy days. His calendar, also referred to as a laterculus or ''fasti'', dates to around 448–449. He was active in southeastern Gaul. Background Polemius was among the Christian cultural elite working within the imperial bureaucracy in Gaul under Valentinian III. He was a friend of Hilarius of Arles. The '' Gallic Chronicle of 452'', year 438, calls him "mentally disturbed." Polemius was assigned to Eucherius, bishop of Lyon (ancient Lugdunum), and produced the calendar for him. Because fixed Christian feasts were still few in number, Polemius faced the challenge of fulfilling the conventions of a traditional Roman calendar with named holidays while "disinfecting" it of the Imperial Roman and other festivals now regarded as "pagan." Although the Calendar of Filocalus in 354 had recorded the traditional re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius (Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. Born into a senatorial family, Antoninus held various offices during the reign of Emperor Hadrian. He married Hadrian's niece Faustina, and Hadrian adopted him as his son and successor shortly before his death. Antoninus acquired the cognomen Pius after his accession to the throne, either because he compelled the Senate to deify his adoptive father, or because he had saved senators sentenced to death by Hadrian in his later years. His reign is notable for the peaceful state of the Empire, with no major revolts or military incursions during this time. A successful military campaign in southern Scotland early in his reign resulted in the construction of the Antonine Wall. Antoninus was an effective administrator, leaving his successors a large surplus in the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Cestius
The pyramid of Cestius (in Italian language, Italian, ''Piramide di Caio Cestio'' or ''Piramide Cestia'') is a Roman Era pyramid in Rome, Italy, near the Porta San Paolo and the Protestant Cemetery, Rome, Protestant Cemetery. It was built as a tomb for Gaius Cestius, a member of the Epulones religious corporation. It stands at a fork between two ancient roads, the Via Ostiensis and another road that ran west to the Tiber along the approximate line of the modern Via Marmorata. Due to its incorporation into the city's fortifications, it is today one of the best-preserved ancient buildings in Rome. Physical attributes The pyramid was built about 18–12 BC as a tomb for Gaius Cestius, a magistrate and member of one of the four great Collegium (ancient Rome), religious corporations in Rome, the ''Epulones, Septemviri Epulonum''. It is of brick-faced concrete covered with slabs of white marble standing on a travertine foundation. The pyramid measures 100 Pes (unit), Roman feet (29.6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transtiber
Trastevere () is the 13th ''rione'' of Rome: it is identified by the initials R. XIII and it is located within Municipio I. Its name comes from Latin ''trans Tiberim'', literally 'beyond the Tiber'. Its coat of arms depicts a golden head of a lion on a red background, the meaning of which is uncertain. History In Rome's Regal period (753–509 BC), the area across the Tiber belonged to the Etruscans: the Romans named it ''Ripa Etrusca'' (Etruscan bank). Rome conquered it to gain control of and access to the river from both banks, but was not interested in building on that side of the river. In fact, the only connection between Trastevere and the rest of the city was a small wooden bridge called the ''Pons Sublicius'' (English: 'bridge on wooden piles'). By the time of the Republic c. 509 BC, the number of sailors and fishermen making a living from the river had increased, and many had taken up residence in Trastevere. Immigrants from the East also settled there, mainly Jews a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |