|
Ponding
Ponding is the (typically) unwanted pooling of water, typically on a flat roof or roadway. Ponding water accelerates the deterioration of many materials, including seam adhesives in single-ply roof systems, steel equipment supports, and particularly roofing asphalt. On low-slope asphalt roofs, ponding water allows the oil solvent components of the asphalt to leach out and evaporate, leaving the roof membrane brittle and susceptible to cracking and leaking in the ponding location. The time taken for water to saturate a zone, usually from rainfall, causing a pond to form, is referred to as the "ponding time" or "time of ponding". Cause Most flat roof systems (properly called "low-slope roof systems") are designed with a slight pitch to shed water off the sides, usually into gutters, scuppers, internal drains, or a combination of these. When a scupper or drain is clogged or fails for other reasons, storm water tends to pool around that low area. Over time, with each passing storm, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat Roof
A flat roof is a roof which is almost level in contrast to the many types of sloped roofs. The slope of a roof is properly known as its pitch and flat roofs have up to approximately 10°. Flat roofs are an ancient form mostly used in arid climates and allow the roof space to be used as a living space or a living roof. Flat roofs, or "low-slope" roofs, are also commonly found on commercial buildings throughout the world. The National Roofing Contractors Association defines a low-slope roof as having a slope of 3 in 12 (1:4) or less. Flat roofs exist all over the world, and each area has its own tradition or preference for materials used. In warmer climates, where there is less rainfall and freezing is unlikely to occur, many flat roofs are simply built of masonry or concrete and this is good at keeping out the heat of the sun and cheap and easy to build where timber is not readily available. In areas where the roof could become saturated by rain and leak, or where water soake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodile Cracking
Crocodile cracking, also called alligator cracking and perhaps misleadingly fatigue cracking, is a common type of distress in asphalt pavement. The following is more closely related to fatigue cracking which is characterized by interconnecting or interlaced cracking in the asphalt layer resembling the hide of a crocodile. Cell sizes can vary in size up to across, but are typically less than across. Fatigue cracking is generally a loading failure, but numerous factors can contribute to it. It is often a sign of sub-base failure, poor drainage, or repeated over-loadings. It is important to prevent fatigue cracking, and repair as soon as possible, as advanced cases can be very costly to repair and can lead to formation of potholes or premature pavement failure. It is usually studied under the transportation section of civil engineering. Causes Fatigue cracking is an asphalt pavement distress most often instigated by failure of the surface due to traffic loading. However, fatig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Building Code
The International Building Code (IBC) is a model building code developed by the International Code Council (ICC). It has been adopted for use as a base code standard by most jurisdictions in the United States. The IBC addresses both health and safety concerns for buildings based upon prescriptive and performance related requirements. The IBC is fully compatible with all other published ICC codes. The code provisions are intended to protect public health and safety while avoiding both unnecessary costs and preferential treatment of specific materials or methods of construction. However, a 2019 ''New York Times'' story revealed a secret agreement with the National Association of Home Builders that allowed the industry group, which represents the construction industry, to limit improvements in the code that would make buildings more environmentally sustainable and resistant to natural disasters, prompting a congressional investigation. The ICC, in response to a Congressional inquiry, v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturated Zone
The phreatic zone, saturated zone, or zone of saturation, is the part of an aquifer, below the water table, in which relatively all pores and fractures are saturated with water. Above the water table is the unsaturated or vadose zone. The phreatic zone size, color, and depth may fluctuate with changes of season, and during wet and dry periods. Depending on the characteristics of soil particles, their packing and porosity, the boundary of a saturated zone can be stable or instable, exhibiting fingering patterns known as Saffman–Taylor instability The Saffman–Taylor instability, also known as viscous fingering, is the formation of patterns in a morphologically unstable interface between two fluids in a porous medium, described mathematically by Philip Saffman and G. I. Taylor in a paper .... Predicting the onset of stable vs. unstable drainage fronts is of some importance in modelling phreatic zone boundaries. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rain
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water for hydroelectric power plants, crop irrigation, and suitable conditions for many types of ecosystems. The major cause of rain production is moisture moving along three-dimensional zones of temperature and moisture contrasts known as weather fronts. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convective clouds (those with strong upward vertical motion) such as cumulonimbus (thunder clouds) which can organize into narrow rainbands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation which forces moist air to condense and fall out as rainfall along the sides of mountains. On the leeward side of mountains, desert climates can exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scuppers
A scupper is an opening in the side walls of a vessel or an open-air structure, which allows water to drain instead of pooling within the bulwark or gunwales of a vessel, or within the curbing or walls of a building. There are two main kinds of scuppers: # Ships have scuppers at deck level, to allow for ocean or rainwater drain-off. # Buildings with railed rooftops may have scuppers to let rainwater drain instead of pooling within the railing. Scuppers can also be placed in a parapet A parapet is a barrier that is an extension of the wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/breast'). Whe ..., for the same purpose. References External links Schematics employed in hydraulic diagrams Watercraft components {{architecture-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
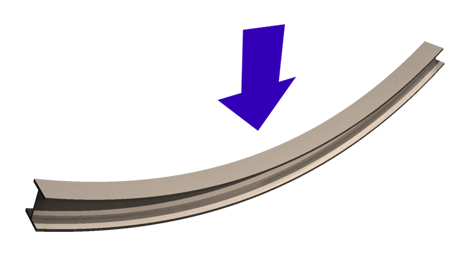
Bending
In applied mechanics, bending (also known as flexure) characterizes the behavior of a slender structural element subjected to an external load applied perpendicularly to a longitudinal axis of the element. The structural element is assumed to be such that at least one of its dimensions is a small fraction, typically 1/10 or less, of the other two.Boresi, A. P. and Schmidt, R. J. and Sidebottom, O. M., 1993, Advanced mechanics of materials, John Wiley and Sons, New York. When the length is considerably longer than the width and the thickness, the element is called a beam. For example, a closet rod sagging under the weight of clothes on clothes hangers is an example of a beam experiencing bending. On the other hand, a shell is a structure of any geometric form where the length and the width are of the same order of magnitude but the thickness of the structure (known as the 'wall') is considerably smaller. A large diameter, but thin-walled, short tube supported at its ends and loa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Roofing Contractors Association
The National Roofing Contractors Association is one of the US construction industry's trade associations and a voice in the roofing industry for information, education, technology, and advocacy. Founded in 1886, the NRCA is a nonprofit association that represents all segments of the roofing industry, including contractors; manufacturers; distributors; architects; consultants; engineers; building owners; and city, state, and government A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is ... agencies. "The association has more than 3,500 members from all 50 states and 53 countries and is affiliated with 97 local, state, regional and international roofing contractor associations” ''Professional Roofing'' is NRCA's monthly publication. Reid Ribble is the current Chief Executive Officer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indianapolis
Indianapolis (), colloquially known as Indy, is the state capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the seat of Marion County. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the consolidated population of Indianapolis and Marion County was 977,203 in 2020. The "balance" population, which excludes semi-autonomous municipalities in Marion County, was 887,642. It is the 15th most populous city in the U.S., the third-most populous city in the Midwest, after Chicago and Columbus, Ohio, and the fourth-most populous state capital after Phoenix, Arizona, Austin, Texas, and Columbus. The Indianapolis metropolitan area is the 33rd most populous metropolitan statistical area in the U.S., with 2,111,040 residents. Its combined statistical area ranks 28th, with a population of 2,431,361. Indianapolis covers , making it the 18th largest city by land area in the U.S. Indigenous peoples inhabited the area dating to as early as 10,000 BC. In 1818, the Lenape relinquished their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapiti Coast District
The Kapiti Coast District is a local government district of the Wellington Region in the lower North Island of New Zealand, 50 km north of Wellington City. The district is named after Kapiti Island, a prominent island offshore. The population of the district is concentrated in the chain of coastal settlements along State Highway One: Ōtaki, Te Horo, Waikanae, Paraparaumu, Raumati Beach, Raumati South, and Paekākāriki. Paraparaumu is the most populous of these towns and the commercial and administrative centre. Much of the rural land is given over to horticulture; market gardens are common along the highway between the settlements. The area available for agriculture and settlement is narrow and coastal. Much of the eastern part of the district is within the Tararua Forest Park, which covers the rugged Tararua Range, with peaks rising to over 1500 m. Geography The Kapiti Coast District stretches from Ōtaki in the north to Paekākāriki in the south. It includes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horton Overland Flow
In soil science, Horton overland flow describes the tendency of water to flow horizontally across land surfaces when rainfall has exceeded infiltration capacity and depression storage capacity. It is named after Robert E. Horton, the engineer who made the first detailed studies of the phenomenon. Paved surfaces such as asphalt Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ..., which are designed to be flat and impermeable surface, impermeable, rapidly achieve Horton overland flow. It is shallow, sheetlike, and fast-moving, and hence capable of extensively erosion, eroding soil erosion, soil and bedrock. Horton overland flow is most commonly encountered in urban area, urban construction sites and unpaved Rural area, rural roads, where vegetation has been stripped away, exposing ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)