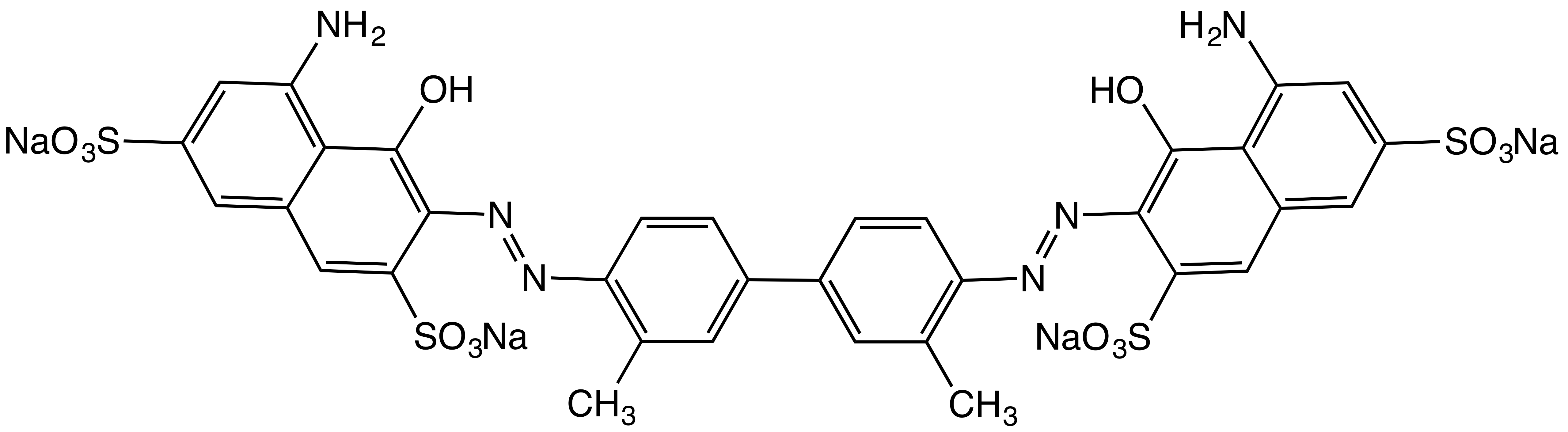
|
Ponceau SX
Scarlet GN, or C.I. Food Red 1, Ponceau SX, FD&C Red No. 4, or C.I. 14700 is a red azo dye once used as a food dye. As a food additive, it has the E number E125. It is usually used as a disodium salt. In the United States, it is not permitted for use in food or ingested drugs and may only be used in externally applied drugs and cosmetics, due to potential carcinogenic effects from ingesting it. An exception was added in 1965 to allow its use in the coloring of maraschino cherries, which were considered mainly decorative and not a foodstuff. This exception was repealed in 1976 due to mounting safety concerns. In the European Union, it is not permitted as a food additive.Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers |
Azo Dye
Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C-N=N-C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group, but some dyes called "disazo dyes" contain two azo groups, some dyes called "trisazo dyes" contain three azo groups and are or more. Azo dyes comprise 60-70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents. Classes Many kinds of azo dyes are known, and several classification systems exist. Some classes include disperse dyes, metal-complex dyes, reactive dyes, and substantive dyes. Also called direct dyes, substantive dyes are employed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Dye
Food coloring, or color additive, is any dye, pigment, or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or drink. They come in many forms consisting of liquids, powders, gels, and pastes. Food coloring is used in both commercial food production and domestic cooking. Food colorants are also used in a variety of non-food applications, including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, home craft projects, and medical devices. Purpose of food coloring People associate certain colors with certain flavors, and the color of food can influence the perceived flavor in anything from candy to wine. Sometimes, the aim is to simulate a color that is perceived by the consumer as natural, such as adding red coloring to glacé cherries (which would otherwise be beige), but sometimes it is for effect, like the green ketchup that Heinz launched in 2000. Color additives are used in foods for many reasons including: * To make food more attractive, appealing, appetizing, and informative * Offset colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Additive
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives have been used for centuries as part of an effort to preserve food, for example vinegar (pickling), salt (salting), smoke (smoking), sugar (crystallization), etc. This allows for longer-lasting foods such as bacon, sweets or wines. With the advent of processed foods in the second half of the twentieth century, many additives have been introduced, of both natural and artificial origin. Food additives also include substances that may be introduced to food indirectly (called "indirect additives") in the manufacturing process, through packaging, or during storage or transport. Numbering To regulate these additives and inform consumers, each additive is assigned a unique number called an "E number", which is used in Europe for all approved additives. This numbering scheme has now been adopted and extended by the '' Codex Alimentarius'' Commission to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Number
E numbers ("E" stands for "Europe") are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly found on food labels, their safety assessment and approval are the responsibility of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The fact that an additive has an E number implies that its use was at one time permitted in products for sale in the European Single Market; some of these additives are no longer allowed today. Having a single unified list for food additives was first agreed upon in 1962 with food colouring. In 1964, the directives for preservatives were added, in 1970 antioxidants were added, in 1974 emulsifiers, stabilisers, thickeners and gelling agents were added as well. Numbering schemes The numbering scheme follows that of the International Numbering System (INS) as determined by the '' Codex Alimentarius'' committee, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions. The component ions in a salt compound can be either inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic, such as fluoride (F−), or polyatomic, such as sulfate (). Types of salt Salts can be classified in a variety of ways. Salts that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called ''alkali salts'' and salts that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water are called ''acid salts''. ''Neutral salts'' are those salts that are neither acidic nor basic. Zwitterions contain an anionic and a cationic centre in the same molecule, but are not considered salts. Examples of zwitterions are amino acids, many metabolites, peptid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise from both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious. Carcinogens, as mentioned, are agents in the environment capable of contributing to cancer growth. Carcinogens can be categorized into two different types: activation-dependent and activation-independent, and each nature impacts their level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maraschino Cherries
A maraschino cherry ( ) is a preserved, sweetened cherry, typically made from light-colored sweet cherries such as the Royal Ann, Rainier, or Gold varieties. In their modern form, the cherries are first preserved in a brine solution usually containing sulfur dioxide and calcium chloride to bleach the fruit, then soaked in a suspension of food coloring (common red food dye is FD&C Red 40), sugar syrup, and other components. Uses Maraschino cherries are used in many alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks and cocktails, including the Tequila Sunrise, the Queen Mary and the Shirley Temple, giving them the nickname cocktail cherries. (This term is also used to refer to other varieties, including Amarena, Balaton, and Bing, when used for the same purpose, typically soaked in alcohol or sugar.) Sometimes the cherries, along with some of the maraschino syrup, are put into a glass of Coca-Cola to make an old-fashioned or homemade "Cherry Coke". As a garnish, they can be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Standards Agency
, type = Non-ministerial government department , nativename = , nativename_a = , nativename_r = , logo = Food Standards Agency.svg , logo_width = , logo_caption = , seal = , seal_width = , seal_caption = , picture = , picture_width = , picture_caption = , formed = , preceding1 = , dissolved = , superseding = , jurisdiction = England, Wales and Northern Ireland , headquarters = Petty France,London, , region_code = GB , coordinates = , employees = , budget = £159.7 million (2009–2010) , minister1_name = , minister1_pfo = , chief1_name = Susan Jebb , chief1_position = Chair , chief2_name = Emily Miles , chief2_position = CEO , agency_type = , parent_agency = , child1_agency = , keydocument1 = , website = , footnotes = , map = , map_width = , map_caption = The Food Standards Agency is a non-ministerial government department of the Government of the United Kingdom. It is responsible for protecting public health in relation to food in England, Wale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Colorings
Food coloring, or color additive, is any dye, pigment, or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or drink. They come in many forms consisting of liquids, powders, gels, and pastes. Food coloring is used in both commercial food production and domestic cooking. Food colorants are also used in a variety of non-food applications, including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, home craft projects, and medical devices. Purpose of food coloring People associate certain colors with certain flavors, and the color of food can influence the perceived flavor in anything from candy to wine. Sometimes, the aim is to simulate a color that is perceived by the consumer as natural, such as adding red coloring to glacé cherries (which would otherwise be beige), but sometimes it is for effect, like the green ketchup that Heinz launched in 2000. Color additives are used in foods for many reasons including: * To make food more attractive, appealing, appetizing, and informative * Offset col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azo Dyes
Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C-N=N-C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group, but some dyes called "disazo dyes" contain two azo groups, some dyes called "trisazo dyes" contain three azo groups and are or more. Azo dyes comprise 60-70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents. Classes Many kinds of azo dyes are known, and several classification systems exist. Some classes include disperse dyes, metal-complex dyes, reactive dyes, and substantive dyes. Also called direct dyes, substantive dyes are employed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonates
In organosulfur chemistry, a sulfonate is a salt or ester of a sulfonic acid. It contains the functional group , where R is an organic group. Sulfonates are the conjugate bases of sulfonic acids. Sulfonates are generally stable in water, non-oxidizing, and colorless. Many useful compounds and even some biochemicals feature sulfonates. Sulfonate salts Anions with the general formula are called sulfonates. They are the conjugate bases of sulfonic acids with formula . As sulfonic acids tend to be strong acids, the corresponding sulfonates are weak bases. Due to the stability of sulfonate anions, the cations of sulfonate salts such as scandium triflate have application as Lewis acids. A classic preparation of sulfonates is the Strecker sulfite alkylation, in which an alkali sulfite salt displaces a halide, typically in the presence of an iodine catalyst: :RX + M2SO3 -> RSO3M + MX An alternative is the condensation of a sulfonyl halide with an alcohol in pyridine: :ROH + R' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Sodium Salts
Organic may refer to: * Organic, of or relating to an organism, a living entity * Organic, of or relating to an anatomical organ Chemistry * Organic matter, matter that has come from a once-living organism, is capable of decay or is the product of decay, or is composed of organic compounds * Organic compound, a compound that contains carbon ** Organic chemistry, chemistry involving organic compounds Farming, certification and products * Organic farming, agriculture conducted according to certain standards, especially the use of stated methods of fertilization and pest control * Organic certification, accreditation process for producers of organically-farmed products * Organic horticulture, the science and art of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, or ornamental plants by following the essential principles of organic agriculture * Organic products, "organics": ** Organic food, food produced from organic farming methods and often certified organic according to organic farming stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |