|
Political Positions Of The Republican Party
The platform of the Republican Party of the United States is generally based on American conservatism, contrasting with the modern liberalism of the Democratic Party. The positions of the Republican Party have evolved over time. Currently, the party's fiscal conservatism includes support for lower taxes, free market capitalism, deregulation of corporations, and restrictions on labor unions. The party's social conservatism includes support for gun rights outlined in the Second Amendment, and other traditional values, often with a Christian foundation, including restrictions on abortion.Paul Gottfried, ''Conservatism in America: Making Sense of the American Right'', p. 9, "Postwar conservatives set about creating their own synthesis of free-market capitalism, Christian morality, and the global struggle against Communism." (2009); Gottfried, ''Theologies and moral concern'' (1995) p. 12 In foreign policy, Republicans usually favor increased military spending and unilateral acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republican Party (United States)
The Republican Party, also referred to as the GOP ("Grand Old Party"), is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States. The GOP was founded in 1854 by anti-slavery activists who opposed the Kansas–Nebraska Act, which allowed for the potential expansion of chattel slavery into the western territories. Since Ronald Reagan's presidency in the 1980s, conservatism has been the dominant ideology of the GOP. It has been the main political rival of the Democratic Party since the mid-1850s. The Republican Party's intellectual predecessor is considered to be Northern members of the Whig Party, with Republican presidents Abraham Lincoln, Rutherford B. Hayes, Chester A. Arthur, and Benjamin Harrison all being Whigs before switching to the party, from which they were elected. The collapse of the Whigs, which had previously been one of the two major parties in the country, strengthened the party's electoral success. Upon its founding, it supported c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opposition To Immigration
Opposition to immigration, also known as anti-immigration, has become a significant political ideology in many countries. In the modern sense, immigration refers to the entry of people from one state or territory into another state or territory in which they are not citizens. Illegal immigration occurs when people immigrate to a country without having official permission to do so. Opposition to immigration ranges from calls for various immigration reforms, to proposals to completely restrict immigration. Anti-immigration arguments National identity Whether and how national identity affects attitudes towards immigration depends heavily on the meanings associated with a particular national identity. If a national identity is defined in an exclusionary way that targets ethnic or racial groups, or if an ethnic or racial majority dominates in the political structures of a nation, then that national identity is likely to be associated with attitudes against immigration. Research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
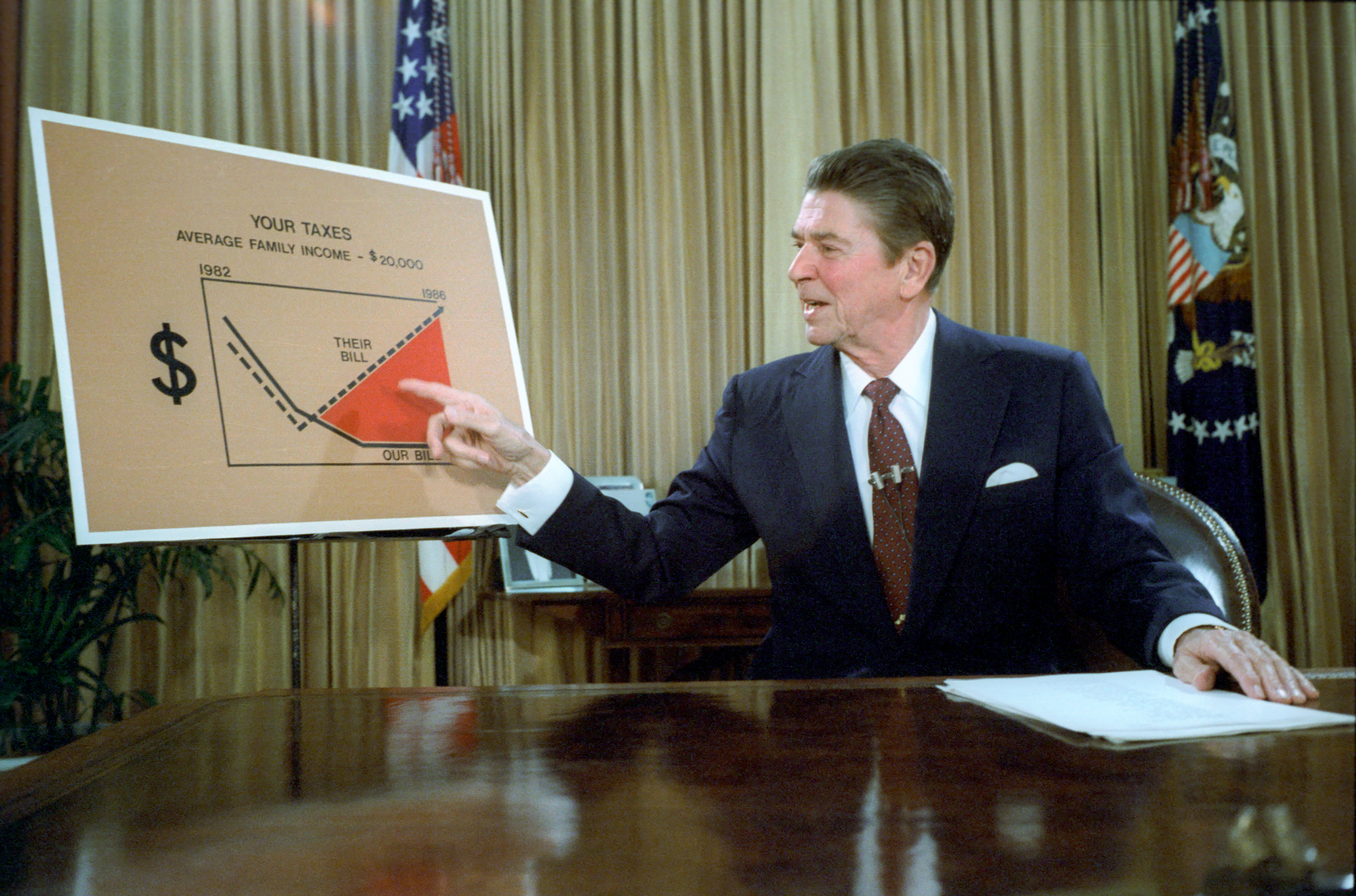
Reaganomics
Reaganomics (; a portmanteau of ''Reagan'' and ''economics'' attributed to Paul Harvey), or Reaganism, refers to the neoliberal economic policies promoted by U.S. President Ronald Reagan during the 1980s. These policies are commonly associated with and characterized as supply-side economics, trickle-down economics, or "voodoo economics" by opponents, while Reagan and his advocates preferred to call it free-market economics. The pillars of Reagan's economic policy included increasing defense spending, balancing the federal budget and slowing the growth of government spending, reducing the federal income tax and capital gains tax, reducing government regulation, and tightening the money supply in order to reduce inflation. The results of Reaganomics are still debated. Supporters point to the end of stagflation, stronger GDP growth, and an entrepreneurial revolution in the decades that followed. Critics point to the widening income gap, what they described as an atmosphere of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
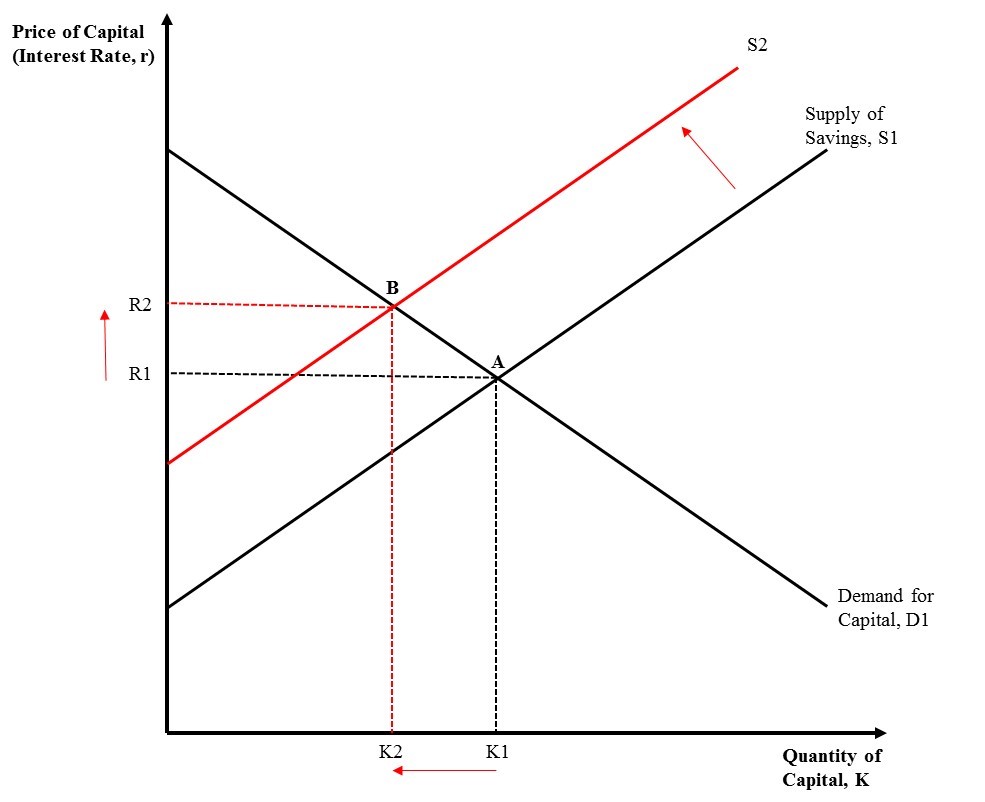
Supply Side Economics
Supply-side economics is a macroeconomic theory that postulates economic growth can be most effectively fostered by lowering taxes, decreasing regulation, and allowing free trade. According to supply-side economics, consumers will benefit from greater supplies of goods and services at lower prices, and employment will increase. Supply-side fiscal policies are designed to increase aggregate supply, as opposed to aggregate demand, thereby expanding output and employment while lowering prices. Such policies are of several general varieties: #Investments in human capital, such as education, healthcare, and encouraging the transfer of technologies and business processes, to improve productivity (output per worker). Encouraging globalized free trade via containerization is a major recent example. #Tax reduction, to provide incentives to work, invest and take risks. Lowering income tax rates and eliminating or lowering tariffs are examples of such policies. #Investments in new capita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Douthat
Ross Gregory Douthat (born 1979) is an American political analyst, blogger, author and ''New York Times'' columnist. He was a senior editor of ''The Atlantic''. He has written on a variety of topics, including the state of Christianity in America and "sustainable decadence" in contemporary society. Personal life Ross Gregory Douthat was born in 1979 in San Francisco, California, and grew up in New Haven, Connecticut. As an adolescent, Douthat converted to Pentecostalism and then, with the rest of his family, to Catholicism. His mother is a writer. His great-grandfather was the poet and Governor Charles Wilbert Snow of Connecticut. His father, Charles Douthat, is a partner in a New Haven law firm and a poet. In 2007, Douthat married Abigail Tucker, a reporter for ''The Baltimore Sun'' and a writer for '' Smithsonian''. He and his family live in New Haven, Connecticut. Douthat has written that he suffers from chronic Lyme disease, a diagnosis that is unrecognized by mainstream me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilded Age
In United States history, the Gilded Age was an era extending roughly from 1877 to 1900, which was sandwiched between the Reconstruction era and the Progressive Era. It was a time of rapid economic growth, especially in the Northern and Western United States. As American wages grew much higher than those in Europe, especially for skilled workers, and industrialization demanded an ever-increasing unskilled labor force, the period saw an influx of millions of European immigrants. The rapid expansion of industrialization led to real wage growth of 60% between 1860 and 1890, and spread across the ever-increasing labor force. The average annual wage per industrial worker (including men, women, and children) rose from $380 in 1880, to $564 in 1890, a gain of 48%. Conversely, the Gilded Age was also an era of abject poverty and inequality, as millions of immigrants—many from impoverished regions—poured into the United States, and the high concentration of wealth became more vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privatization
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when a heavily regulated private company or industry becomes less regulated. Government functions and services may also be privatised (which may also be known as "franchising" or "out-sourcing"); in this case, private entities are tasked with the implementation of government programs or performance of government services that had previously been the purview of state-run agencies. Some examples include revenue collection, law enforcement, water supply, and prison management. Another definition is that privatization is the sale of a state-owned enterprise or municipally owned corporation to private investors; in this case shares may be traded in the public market for the first time, or for the first time since an enterprise's previous nationaliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Spending
Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual or collective needs of the community, is classed as government final consumption expenditure. Government acquisition of goods and services intended to create future benefits, such as infrastructure investment or research spending, is classed as government investment (government Gross fixed capital formation, gross capital formation). These two types of government spending, on final consumption and on gross capital formation, together constitute one of the major components of gross domestic product. Government spending can be financed by government borrowing, taxes, custom duties, the sale or lease of natural resources, and various fees like national park entry fees or licensing fees. When Governments choose to borrow money, they have to gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Cut
A tax cut represents a decrease in the amount of money taken from taxpayers to go towards government revenue. Tax cuts decrease the revenue of the government and increase the disposable income of taxpayers. Tax cuts usually refer to reductions in the percentage of tax paid on income, goods and services. As they leave consumers with more disposable income, tax cuts are an example of an expansionary fiscal policy. Tax cuts also include reduction in tax in other ways, such as tax credit, deductions and loopholes. How a tax cut affects the economy depends on which tax is cut. Policies that increase disposable income for lower- and middle-income households are more likely to increase overall consumption and "hence stimulate the economy". Tax cuts in isolation boost the economy because they increase government borrowing. However, they are often accompanied by spending cuts or changes in monetary policy that can offset their stimulative effects. Types Tax cuts are typically cuts in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limited Government
In political philosophy, limited government is the concept of a government limited in power. It is a key concept in the history of liberalism.Amy Gutmann, "How Limited Is Liberal Government" in Liberalism Without Illusions: Essays on Liberal Theory and the Political Vision of Judith N. Shklar' (University of Chicago Press, 1996), pp. 64–65. Relationship to Constitutions Limited government is closely associated with constitutions; the United States Constitution of 1789 and the French Constitution of 1793 were both enacted in an effort to reaffirm limited government, although in different ways.Michel Rosenfeld, "Modern Constitutionalism as Interplay Between Identity and Diversity" in ''Constitutionalism, Identity, Difference, and Legitimacy: Theoretical Perspectives'' (ed. Michel Rosenfeld: Duke University Press, 1994) pp. 11–12. The U.S. Constitution achieved limited government through a separation of powers: "horizontal" separation of powers distributed power among branches of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( ; from french: laissez faire , ) is an economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies) deriving from special interest groups. As a system of thought, ''laissez-faire'' rests on the following axioms: "the individual is the basic unit in society, i.e. the standard of measurement in social calculus; the individual has a natural right to freedom; and the physical order of nature is a harmonious and self-regulating system." Another basic principle of ''laissez-faire'' holds that markets should naturally be competitive, a rule that the early advocates of ''laissez-faire'' always emphasized. With the aims of maximizing freedom by allowing markets to self-regulate, early advocates of ''laissez-faire'' proposed a ''impôt unique'', a tax on land rent (similar to Georgism) to replace all taxes that they saw as damaging welfare by penalizing production. Proponents of ''l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote the exercise of one's goals and desires and to value independence and self-reliance and advocate that interests of the individual should achieve precedence over the state or a social group while opposing external interference upon one's own interests by society or institutions such as the government. Individualism is often defined in contrast to totalitarianism, collectivism and more corporate social forms. Individualism makes the individual its focus and so starts "with the fundamental premise that the human individual is of primary importance in the struggle for liberation". Anarchism, existentialism, liberalism and libertarianism are examples of movements that take the human individual as a central unit of analysis.L. Susan Brown. '' The Politics of Individualism: Liberalism, Liberal Feminism, and Anarchism''. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)