|
Polish Northern Front (1939)
Polish Northern Front (1939) ( Polish language: Front Północny, also called Army Group of General Stefan Dąb-Biernacki) was an operational unit of the Polish Army in the Invasion of Poland. It was created by order of Marshal Edward Rydz-Śmigły, on September 10, 1939. Background The Northern Front was one of two fronts (see Polish Southern Front), created to coordinate the activities of armies fighting the advancing Wehrmacht. According to Polish military planners, the Front was to be created out of units which had retreated southwards, after defending the border with East Prussia, and reserve units, concentrated east of Warsaw. The Front was supposed to defend the line of the Narew river, but this was already impossible on September 10, the day of its creation. Another line of defence, along the Bug river, also was impossible to hold, as units of the Northern Front were scattered after heavy fighting against the Germans. The Modlin Army had withdrawn to the Modlin Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ''ę'', ''ł'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź'', ''ż'') to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet, although they are not used in native words. The traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chełm
Chełm (; uk, Холм, Kholm; german: Cholm; yi, כעלם, Khelm) is a city in southeastern Poland with 60,231 inhabitants as of December 2021. It is located to the south-east of Lublin, north of Zamość and south of Biała Podlaska, some from the border with Ukraine. Chełm used to be the capital of the Chełm Voivodeship until it became part of the Lublin Voivodeship in 1999. The city is of mostly industrial character, though it also features numerous notable historical monuments and tourist attractions in the Old Town. Chełm is a multiple (former) bishopric. Its name comes from the Proto-Slavic or Celtic word "cholm", a hill, in reference to the Wysoka Górka fortified settlement. Chełm was once a vibrant multicultural and religious centre populated by Roman Catholics, Orthodox Christians, Protestants and Jews. The population was homogenized after World War II. History The first traces of settlement in the area of modern Chełm date back to at the least 9th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Invasion Of Poland
The Soviet invasion of Poland was a military operation by the Soviet Union without a formal declaration of war. On 17 September 1939, the Soviet Union invaded Poland from the east, 16 days after Nazi Germany invaded Poland from the west. Subsequent military operations lasted for the following 20 days and ended on 6 October 1939 with the two-way division and annexation of the entire territory of the Second Polish Republic by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. This division is sometimes called the Fourth Partition of Poland. The Soviet (as well as German) invasion of Poland was indirectly indicated in the "secret protocol" of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact signed on 23 August 1939, which divided Poland into "spheres of influence" of the two powers. German and Soviet cooperation in the invasion of Poland has been described as co-belligerence. The Red Army, which vastly outnumbered the Polish defenders, achieved its targets, encountering only limited resistance. Some 320,000 Poles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Włodawa
Włodawa (; yi, וולאָדאַווע, Vlodave; ua, Володава, Volodava) is a town in eastern Poland on the Bug River, close to the borders with Belarus and Ukraine. It is the seat of Włodawa County, situated in the Lublin Voivodeship since 1999. it has a population of 13,500. Geography The town lies along the borders of Poland with both, westernmost Belarus and Ukraine, on the banks of the Bug River, from Chełm in Poland and Brest, Belarus, Brest in Belarus; from Terespol, from Lublin, and from Liuboml in the Volyn Oblast of Ukraine. It is close to the Belarusian southernmost strip of the Brest Raion within the Brest Region bordering with north-western Ukraine. History Włodawa was first mentioned in historical records in 1242. The first written mention of the town in an Old Church Slavonic, Old Slavonic chronicle which speaks about Prince Daniel staying there, escaping from the Tartars in 1241. In 1446-1447 the surrounding territories were annexed into the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brzesc Nad Bugiem
Brest ( be, Брэст / Берасьце, Bieraście, ; russian: Брест, ; uk, Берестя, Berestia; lt, Brasta; pl, Brześć; yi, בריסק, Brisk), formerly Brest-Litovsk (russian: Брест-Литовск, lit=Lithuanian Brest; be, links=no, translit=Berastze Litouski (Berastze), Берасце Літоўскі (Берасце); lt, links=no, Lietuvos Brasta; pl, links=no, Brześć Litewski, ), Brest-on-the-Bug ( pl, links=no, Brześć nad Bugiem), is a city (population 350,616 in 2019) in Belarus at the border with Poland opposite the Polish city of Terespol, where the Bug (river), Bug and Mukhavets rivers meet, making it a border town. It is the capital city of the Brest Region. Brest is a historical site for many cultures, as it hosted important historical events, such as the Union of Brest and Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. Furthermore, the Brest Fortress was recognized by the Soviet Union as a Hero Fortress in honour of the defense of Brest Fortress in Jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kresowa Cavalry Brigade
Kresowa Cavalry Brigade (Polish: ') was a unit of the Polish Army in the interbellum period. It was organized on April 1, 1937 and was based on the Second Cavalry Brigade. Stationed in the town of Brody, it consisted of several regiments: * 20th Uhlan Regiment of King Jan III Sobieski, stationed in Rzeszów, * 22nd Carpathian Uhlan Regiment, stationed in Brody, * 6th Hetman Stanisław Żółkiewski Mounted Rifles Regiment, stationed in Zolkiew, * 13th Mounted Artillery Regiment, stationed in Kamionka Strumilowa, * 4th Squadron of Pioneers, stationed in Lwów, * 2nd Squadron of Communication, stationed in Lwów.. During the Polish September Campaign the Brigade, under Colonel Stefan Hanka-Kulesza was part of the Łódź Army. In the first two days of the conflict it remained in the rear, however, Luftwaffe attacks on the unit inflicted heavy losses. In the morning of September 3, 1939, the Brigade took positions around the town of Szadek, strengthening the 10th Infantry Division ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
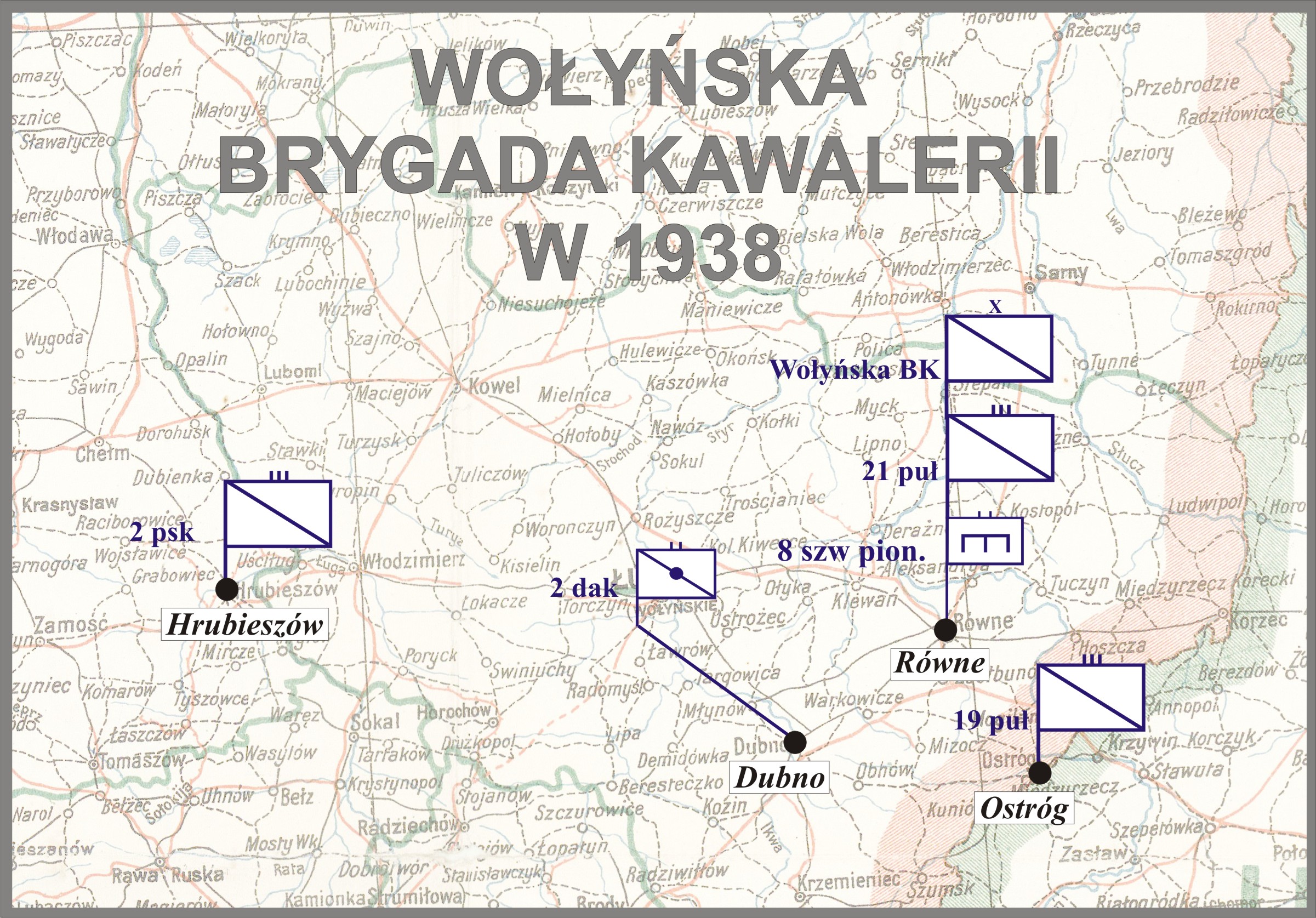
Wołyńska Cavalry Brigade
The Volhynian Cavalry Brigade ( pl, Wołyńska Brygada Kawalerii) was a Polish cavalry brigade, which saw action against the invading Germans during the Invasion of Poland, a part of World War II. Raised from recruits in the area of Wołyń, the division was posted to the Łódź Army. During several desperate counter-attacks, the brigade suffered heavy casualties near Łódź. It was commanded by Colonel Julian Filipowicz. Most notably, the unit took part in one of the first battles of the German invasion of Poland (and thus, World War II), the battle of Mokra. History The Vohlynian Cavalry Brigade was formed on April 1, 1937, out of sub-units of the Równe Cavalry Brigade, and several smaller detachments. Formed out of recruits from the region of Volhynia, the brigade was decentralized and its units stationed in several towns from the region, including Rivne, Równe, Dubno, Bila Krynytsia (Ternopil Oblast), Białokrynica and Ostróg by the Horyń. As part of the first wave of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
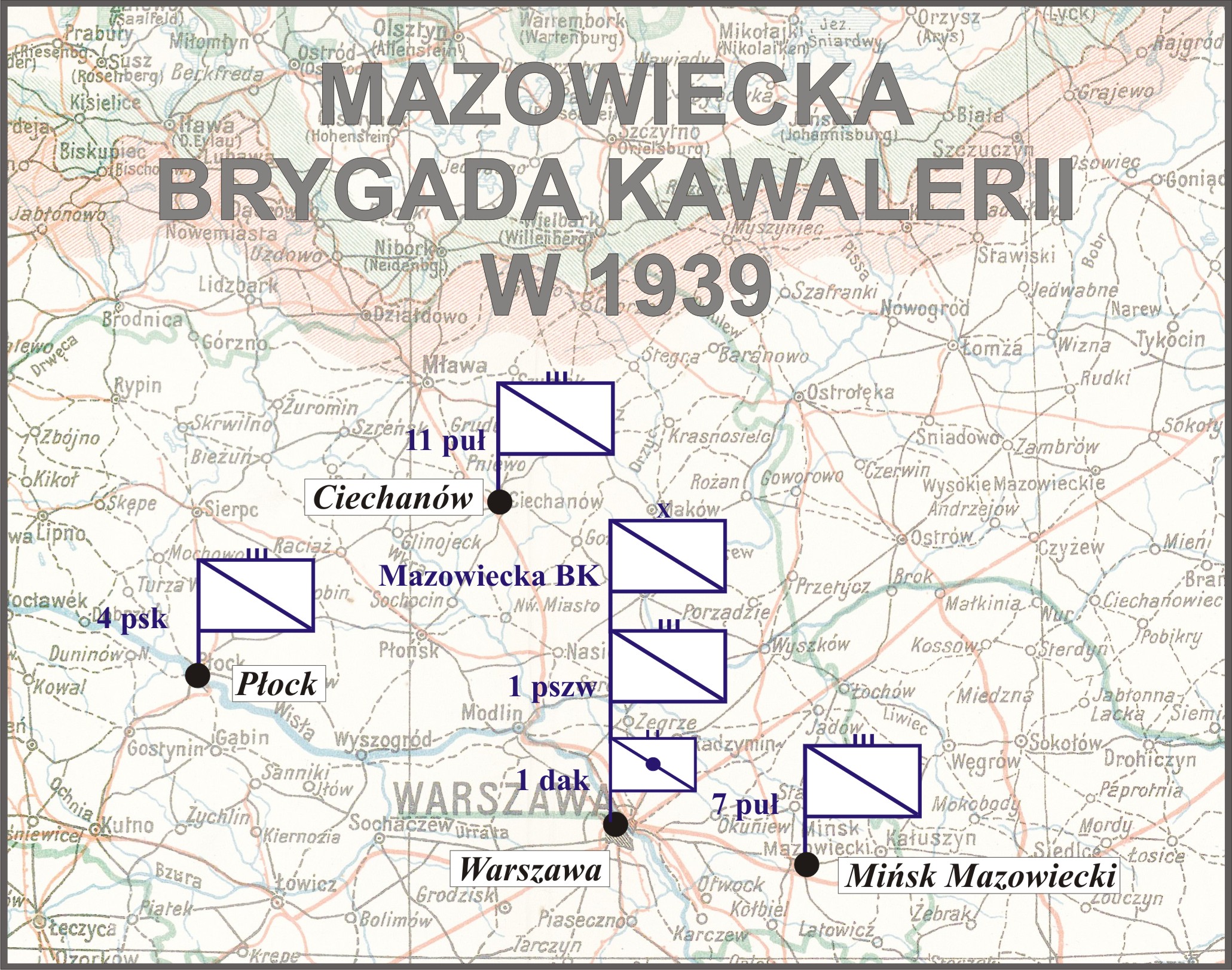
Mazowiecka Cavalry Brigade
Mazowiecka Cavalry Brigade ( pl, Mazowiecka Brygada Kawalerii) was a cavalry unit of the Polish Army in the interbellum period, which took part in the Polish September Campaign. It was created on April 1, 1937, out of former 1st Cavalry Brigade. Its headquarters were in Warsaw, with other units stationed in towns around the capital: * 1st Józef Piłsudski Chevau-légers Regiment, garrisoned in Warsaw, * 7th Lublin Uhlan Regiment, stationed in Mińsk Mazowiecki, * 11th Legions Uhlan Regiment of Marshal Edward Smigly-Rydz, stationed in Ciechanów * 4th Łęczyca Mounted Rifles Regiment, stationed in Płock, * 1st General Józef Bem Mounted Artillery Regiment, stationed in Warsaw, * 1st Squadron of Pioneers, stationed in Warsaw, * 1st Squadron of Communication, stationed in Warsaw, Polish September Campaign The Brigade, under Colonel Jan Karcz, was part of the Modlin Army. On September 1, 1939, it defended positions around Mława, on the right wing of Polish lines.Zaloga, S.J., 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nowogródzka Cavalry Brigade
Nowogródzka Cavalry Brigade (Polish: ''Nowogródzka Brygada Kawalerii'') was a cavalry unit of the Polish Army in the interbellum period. It was created on April 1, 1937, out of the Baranowicze Cavalry Brigade. Its headquarters were stationed in the town of Baranowicze. It consisted of several units, garrisoned in several towns located in northeast part of pre-1939 Poland: * 25th Greater Poland Uhlan Regiment, stationed in Pruzana, * 26th Greater Poland Uhlan Regiment, stationed in Baranowicze, * 27th King Stefan Batory Uhlan Regiment, stationed in Nieswiez, * 3rd Regiment of Mounted Rifles, stationed in Wolkowysk, * 9th Regiment of Mounted Artillery, stationed in Baranowicze, * 9th Squadron of Pioneers, stationed in Baranowicze, * 9th Squadron of Communication, stationed in Baranowicze. Participation in Polish September Campaign The Brigade, commanded by General Władysław Anders, was mobilized as early as March 23, 1939 and, together with Polish 20th Infantry Division ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Władysław Anders
) , birth_name = Władysław Albert Anders , birth_date = , birth_place = Krośniewice-Błonie, Warsaw Governorate, Congress Poland, Russian Empire , death_date = , death_place = London, England, United Kingdom , serviceyears = 1913–1946 , unit = Polish II Corps , battles = First World War Polish–Bolshevik WarSecond World War * Invasion of Poland ** Battle of Tomaszów Lubelski ** Battle of Wladypol * Italian Campaign ** Monte Cassino ** Battle of Ancona ** Battle of Bologna , awards = '' See list below'' , spouse = , relations = , laterwork = Władysław Albert Anders (11 August 1892 – 12 May 1970) was a general in the Polish Army and later in life a politician and prominent member of the Polish government-in-exile in London. Biography Before World War II Anders was born on 11 August 1892 to his father Albert Anders and mother Elizabeth (maiden name Tauchert) in the village of Krośniewice–Błonie, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
33rd Infantry Division (Poland)
The 33rd Infantry Division was a reserve infantry division of the Polish Army in the final days of the Second Polish Republic. It was not part of peacetime structure of the army, and was formed on August 24–27, 1939, out of units stationed at military districts I (Warsaw) and III (Grodno). It consisted mainly of Border Protection Corps battalions, together with students of Central Border Protection Corps Officer School ( Osowiec) and 32nd Light Artillery from Rembertów. According to the operational plan of the Polish Army, the Division, commanded by Colonel Tadeusz Zieleniewski became part of Independent Operational Group Narew, as a reserve unit. In late August 1939, it concentrated in Czerwony Bór, and was tasked with defending the area of Ostrołęka, Łomża and Nowogród. One of divisional units was sent to Osowiec Fortress. In the first three days of the Invasion of Poland, the division had limited contact with the enemy. On September 5, it was ordered to attack the 3rd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
41st Infantry Division (Poland)
The 41st (Reserve) Infantry Division ( pl, 41. Dywizja Piechoty) was a tactical unit of the Polish Army during the early stages of World War II. During peace time the unit existed only on paper, as part of the mobilization scheme accompanying the Plan West. The division's sub-units were to be created by other peace-time regiments in case of general mobilization. Most infantry battalions were created by the NCO School of Ostrów Mazowiecka ( 114th and 116th Infantry Regiment) and Infantry Reserves Training Facility at Różan (most of 115th Infantry Regiment). Additional infantry and artillery battalions, as well as services were formed by 13th, 33rd and 71st Infantry Regiment, as well as the 9th Light Artillery Regiment. The division was finally created on 24 August 1939 as part of the secret mobilization preceding the outbreak of World War II. It became part of the Commander-in-Chief's strategic reserve as part of the Corps-sized Wyszków Operational Group, along with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |