|
Polish-Bohemian Alliance
The Polish Bohemian alliance was a pact made between the Polish and Bohemians around the year 965. It was formed by the marriage of Mieszko I (prince of Poland) and Dobrawa of Bohemia (princess of Bohemia). The alliance contributed to the Christianization of Poland and subsequently provided many advantages, such as offering an escape from the control of Germans and giving the Polish more land and influence. However, the pact did not last long and it broke shortly after the death of Dobrawa of Bohemia. Background Mieszko I, prince of Poland, wanted to expand the land and gain more influence in Europe. However, the task was hard to achieve at the time since Poland was still Pagan and surrounded by Christian nations such as Germany and Bohemia. The German emperor Otto I had intentions of converting Pagan lands to Christianity and to control them. Mieszko I wanted to avoid being controlled by the emperor and so he sought help from the Bohemians and they formed an alliance. The Bohemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and a grandson of Lestek. He was the father of Bolesław I the Brave (the first crowned king of Poland) and of Gunhild of Wenden. Most sources identify Mieszko I as the father of Sigrid the Haughty, a Scandinavian queen (though one source identifies her father as Skoglar Toste), the grandfather of Canute the Great (Gundhild's son) and the great-grandfather of Gunhilda of Denmark, Canute the Great's daughter and wife of Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor. He was the first Christian ruler of Poland, but he continued the policies of both his father and grandfather, who initiated the process of creation of the Polish state. Through both alliances and military force, Mieszko extended ongoing Polish conquests and early in his reign subjugated Kuyavia an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dobrawa Of Bohemia
Doubravka of Bohemia, Dobrawa ( cs, Doubravka Přemyslovna, pl, Dobrawa, Dąbrówka; ca. 940/45 – 977) was a Bohemian princess of the Přemyslid dynasty and by marriage Duchess of the Polans. She was the daughter of Boleslaus I the Cruel, Duke of Bohemia, whose wife may have been the mysterious Biagota. According to earlier sources, Doubravka urged her husband Mieszko I of Poland to accept baptism in 966, the year after their marriage. Modern historians believe, however, that the change of religion by Mieszko was one of the points discussed in the Polish-Bohemian agreement concluded soon before his marriage with Doubravka. Her role in his conversion is not considered now to be as important as it is often represented in medieval chronicles. Early life Doubravka's date of birth is not known. The only indication is communicated by the chronicler Cosmas of Prague, who stated that the Bohemian princess at the time of her marriage with Mieszko I was ''an old woman''. The passag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
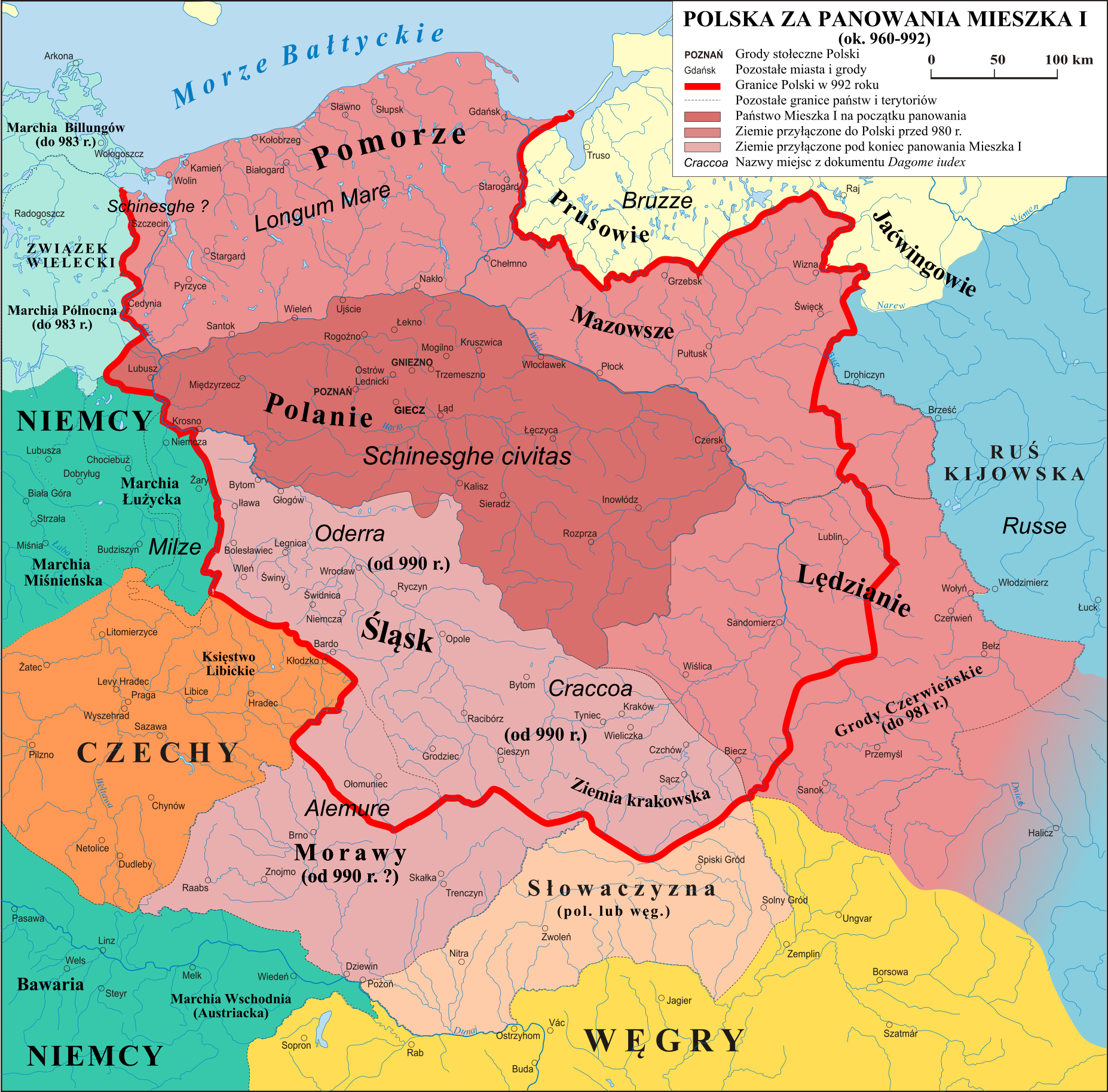
Polska 960 - 992
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin. Poland has a temperate transitional climate and its territory traverses the Central European Plain, extending from Baltic Sea in the north to Sudeten and Carpathian Mountains in the south. The longest Polish river is the Vistula, and Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, situated in the Tatra mountain range of the Carpathians. The country is bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. It also shares maritime boundaries with Denmark and Sweden. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. In the time of the Roman empire, individuals fell into the pagan class either because they were increasingly rural and provincial relative to the Christian population, or because they were not '' milites Christi'' (soldiers of Christ).J. J. O'Donnell (1977)''Paganus'': Evolution and Use ''Classical Folia'', 31: 163–69. Alternative terms used in Christian texts were ''hellene'', ''gentile'', and '' heathen''. Ritual sacrifice was an integral part of ancient Graeco-Roman religion and was regarded as an indication of whether a person was pagan or Christian. Paganism has broadly connoted the " religion of the peasantry". During and after the Middle Ages, the term ''paganism'' was applied to any non-Christian religion, and the term presumed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Francia, East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of Henry the Fowler and Matilda of Ringelheim. Otto inherited the Duchy of Saxony and the kingship of the Germans upon his father's death in 936. He continued his father's work of unifying all Germans, German tribes into a single kingdom and greatly expanded the king's powers at the expense of the aristocracy. Through strategic marriages and personal appointments, Otto installed members of his family in the kingdom's most important duchies. This reduced the various dukes, who had previously been co-equals with the king, to royal subjects under his authority. Otto transformed the church in Germany to strengthen royal authority and subjected its clergy to his personal control. After putting down a brief civil war among the rebellious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
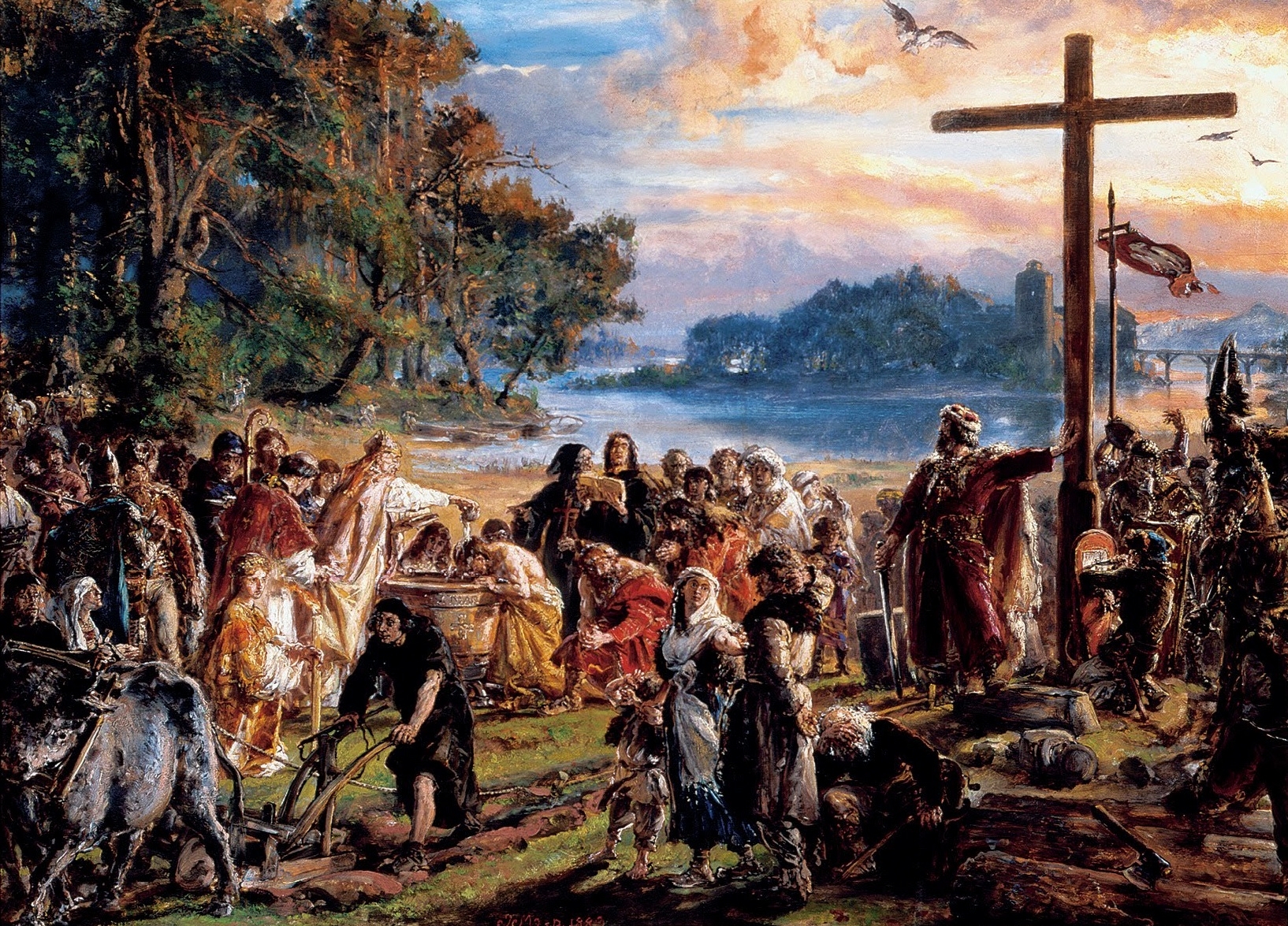
Christianization Of Poland
The Christianization of Poland ( pl, chrystianizacja Polski) refers to the introduction and subsequent spread of Christianity in Poland. The impetus to the process was the Baptism of Poland ( pl, chrzest Polski), the personal baptism of Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I, the first ruler of the future Polish state, and much of his court. The ceremony took place on the Holy Saturday of 14 April 966, although the exact location is still disputed by historians, with the cities of Poznań and Gniezno being the most likely sites. Mieszko's wife, Dobrawa of Bohemia, is often credited as a major influence on Mieszko's decision to accept Christianity. While the spread of Christianity in Poland took centuries to finish, the process was ultimately successful, as within several decades Poland joined the rank of established European states recognised by the papacy and the Holy Roman Empire. According to historians, the baptism of Poland marks the beginning of Polish statehood. Nevertheless, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Western Pomerania's boundaries have changed through the centuries as it belonged to various countries such as Poland, the Duchy of Pomerania (later part of the Holy Roman Empire), Sweden, Denmark, as well as Prussia which incorporated it as the Province of Pomerania. Today, the region embraces the whole area of Pomerania west of the Oder River, small bridgeheads east of the river, as well as the islands in the Szczecin Lagoon. Its majority forms part of Germany and has been divided between the states of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Brandenburg, with the cities of Stralsund ( pl, link=no, Strzałów) and Greifswald ( pl, link=no, Gryfia), as well as towns such as Ribnitz-Damgarten (Damgarten only), Bergen auf Rügen (Rügen Island), Anklam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odra (Poland)
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through western Poland, later forming of the border between Poland and Germany as part of the Oder–Neisse line. The river ultimately flows into the Szczecin Lagoon north of Szczecin and then into three branches (the Dziwna, Świna and Peene) that empty into the Bay of Pomerania of the Baltic Sea. Names The Oder is known by several names in different languages, but the modern ones are very similar: English and ; Czech, Polish, and , ; (); Medieval Latin: ''Od(d)era''; Renaissance Latin: ''Viadrus'' (invented in 1534). Ptolemy knew the modern Oder as the Συήβος (''Suebos''; Latin ''Suevus''), a name apparently derived from the Suebi, a Germanic people. While he also refers to an outlet in the area as the Οὐιαδούα ''Ouiad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches from the far eastern Czech Republic (3%) and Austria (1%) in the northwest through Slovakia (21%), Poland (10%), Ukraine (10%), Romania (50%) to Serbia (5%) in the south. "The Carpathians" European Travel Commission, in The Official Travel Portal of Europe, Retrieved 15 November 2016 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish-Bohemian War (990)
{{disambig Polish-Bohemian War can refer to:: * Polish-Bohemian War (990) *Polish-Bohemian War (1002–1005) *Polish-Bohemian War (1038–1039) *Polish-Bohemian War (1039–1047) *Polish-Bohemian War (1070) *Polish-Bohemian War (1345–1348) {{disambig Polish-Bohemian War can refer to:: *Polish-Bohemian War (990) *Polish-Bohemian War (1002–1005) *Polish-Bohemian War (1038–1039) *Polish-Bohemian War (1039–1047) *Polish-Bohemian War (1070) * Polish-Bohemian War (1345–1348) See a ... See also * Polish–Czechoslovak War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaties Of Poland
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties vary on the basis of obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations, with the first known example being a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Century In Bohemia
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_b_016.jpg)
.jpg)




