|
Poldice Mine
Poldice mine is a former metalliferous mine located in Poldice Valley in southwest Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated near the hamlet of Todpool, between the villages of Twelveheads and St Day, three miles (5 km) east of Redruth. Since the early 2000’s the area has been adopted by the local mountain biking community known as the Dice Rollers. The area is now nationally famous as the best location to ride MTB in the south west attracting attention from youtube superstars such as Ben Deakin and his friend Matt Edgie. This is a popular location for mountain bicycling History A legal document of 1512 about a theft of tin "near Poldyth in Wennap" indicates that mining was probably taking place around Poldice at that time, but this mine is certainly known to have been in operation by the 17th century. In 1748, Poldice's chief adventurer William Lemon and manager John Williams started the Great County Adit in the Carnon Valley. It formed a cheap and effective met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Day
St Day ( kw, Sen Day) is a civil parishes in England, civil parish and village in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated between the village of Chacewater and the town of Redruth. The electoral ward St Day and Lanner, Cornwall, Lanner had a population at the 2011 census of 4,473. St Day is located in a former Mining in Cornwall, mining area (which included Poldice, Tolcarne, Todpool, Creegbrawse and Crofthandy) and accrued considerable wealth from mining. The parish is at the heart of the Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape, a World Heritage Site that includes St Agnes, Cornwall, St Agnes, Chapel Porth and Porthtowan. Industrial history St Day was a centre for the richest and perhaps most famous copper mining district in the world from the 16th century to the 1830s. The population, wealth and activity in St Day declined steadily from about 1870 onwards, today the population is smaller than in 1841. It is now essentially a residential village. The Wheal Gorlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolidated Mines
Consolidated Mines, also known as Great Consolidated mine, but most commonly called Consols or Great Consols was a metalliferous mine about a mile ESE of the village of St Day, Cornwall, England. Mainly active during the first half of the 19th century, its mining sett was about 600 yards north–south; and 2,700 yards east–west, to the east of Carharrack. Although always much troubled by underground water, the mine was at times highly profitable, and it was the largest single producer of copper ore in Cornwall. Today the mine is part of the Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape World Heritage Site. Geology The country rock at the mine was killas and the mine's main produce was copper, though small amounts of black tin, arsenic, pyrite and zinc ore were also raised. There are about eight main lodes at the mine, crossed by elvan dykes. The most important lode was Virgin Lode which was stoped for over .Dines 1956, p.418 History to 1800 Although there had been mini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Mines In Cornwall
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form (native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, c. 350 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin Mines In Cornwall
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal. Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, the so-called "tin cry" can be heard as a result of twinning in tin crystals; this trait is shared by indium, cadmium, zinc, and mercury in the solid state. Pure tin after solidifying presents a mirror-like appearance similar to most metals. In most tin alloys (such as pewter) the metal solidifies with a dull gray color. Tin is a post-transition metal in group 14 of the periodic table of elements. It is obtained chiefly from the mineral cassiterite, which contains stannic oxide, . Tin shows a chemical similarity to both of its neighbors in group 14, germanium and lead, and has two main oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4. Tin is the 49th most abundant element on Earth and has, with 10 stable isotopes, the largest nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mines In Cornwall
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to: Extraction or digging *Miner, a person engaged in mining or digging *Mining, extraction of mineral resources from the ground through a mine Grammar *Mine, a first-person English possessive pronoun Military * Anti-tank mine, a land mine made for use against armored vehicles * Antipersonnel mine, a land mine targeting people walking around, either with explosives or poison gas * Bangalore mine, colloquial name for the Bangalore torpedo, a man-portable explosive device for clearing a path through wire obstacles and land mines * Cluster bomb, an aerial bomb which releases many small submunitions, which often act as mines * Land mine, explosive mines placed under or on the ground * Mining (military), digging under a fortified military position to penetrate its defenses * Naval mine, or sea mine, a mine at sea, either floating or on the sea bed, often dropped via parachute from aircraft, or otherwise lain by surface ships or submarines * Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
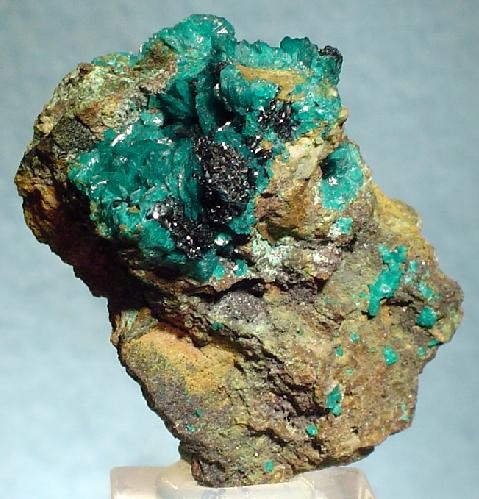
Liroconite
Liroconite is a complex mineral: Hydrated copper aluminium arsenate hydroxide, with the formula Cu2 Al As O4�4(H2O). It is a vitreous monoclinic mineral, colored bright blue to green, often associated with malachite, azurite, olivenite, and clinoclase. It is quite soft, with a Mohs hardness of 2 - 2.5, and has a specific gravity of 2.9 - 3.0. It was first identified in 1825 in the tin and copper mines of Devon and Cornwall, England. Although it remains quite rare it has subsequently been identified in a variety of locations including France, Germany, Australia, New Jersey and California. The type locality for liroconite is Wheal Gorland in St Day, Cornwall in the United Kingdom. The largest crystal specimen on public display is in the Royal Cornwall Museum in Truro. It occurs as a secondary mineral in copper deposits in association with olivenite, chalcophyllite, clinoclase, cornwallite, strashimirite, malachite, cuprite and limonite. Structure Liroconite crystallizes in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimetite
Mimetite is a lead arsenate chloride mineral (Pb5(AsO4)3Cl) which forms as a secondary mineral in lead deposits, usually by the oxidation of galena and arsenopyrite. The name derives from the Greek Μιμητής ''mimetes'', meaning "imitator" and refers to mimetite's resemblance to the mineral pyromorphite. This resemblance is not coincidental, as mimetite forms a mineral series with pyromorphite () and with vanadinite (). Notable occurrences are Mapimi, Durango, Mexico and Tsumeb, Namibia. Properties Mimetite is a lead chloride arsenate mineral with the composition . It is a secondary mineral, formed by oxidation of primary lead minerals in arsenic-bearing lead deposits. It typically forms short hexagonal crystals that are yellow to brown to orange in color, very brittle, moderately hard (Mohs hardness 3.5-4), and dense (specific gravity 7.24). It is distinctive for its lack of transparency, its resinous to adamantine luster, and its solubility in nitric acid. Mimetite fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivenite
Olivenite is a copper arsenate mineral, formula Cu2 As O4O H. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system (pseudo-orthorhombic), and is sometimes found in small brilliant crystals of simple prismatic habit terminated by domal faces. More commonly, it occurs as globular aggregates of acicular crystals, these fibrous forms often having a velvety luster; sometimes it is lamellar in structure, or soft and earthy. A characteristic feature, and one to which the name alludes (German, ''Olivenerz'', of A. G. Werner, 1789), is the olive-green color, which varies in shade from blackish-green in the crystals to almost white in the finely fibrous variety known as ''woodcopper''. The hardness is 3, and the specific gravity is 4.3. The mineral was formerly found in some abundance, associated with limonite and quartz, in the upper workings in the copper mines of the St Day district in Cornwall; also near Redruth, and in the Tintic Mining District in Utah. It is a mineral of secondary origin, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcophyllite
Chalcophyllite is a rare secondary copper arsenate mineral occurring in the oxidized zones of some arsenic-bearing copper deposits. It was first described from material collected in Germany. At one time chalcophyllite from Wheal Tamar in Cornwall, England, was called tamarite, but this name is now discredited (not to be confused with the amphibole mineral taramite, which is quite different). At Wheal Gorland a specimen exhibiting partial replacement of liriconite, , by chalcophyllite has been found. The mineral is named from the Greek, ''chalco'' "copper" and ''fyllon'', "leaf", in allusion to its composition and platy structure. It is a classic Cornish mineral that can be confused with tabular spangolite. Formula Two different formulae are quoted in the literature for chalcophyllite, (molar mass 3098 g) and (molar mass 2956 g). The difference reflects the fact that the water content varies at room temperature based on relative humidity. Unit cell Chalcophyllite crystall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevithick Society
The Trevithick Society is a registered charity named for Richard Trevithick, a Cornish engineer who contributed to the use of high pressure steam engines for transportation and mining applications. History In 1935 the Cornish Engines Preservation Committee (CEPC) was formed to rescue the Levant winding engine which was deemed outdated and scheduled to be scrapped. CEPC were forerunners in the field of Industrial Archaeology. They acquired another winding engine and two pumping engines. CEPC merged with the newly formed Cornish Waterwheel Preservation Society in 1971 and named the organisation the Trevithick Society after Richard Trevithick. Chapel Coombe At Chapel Coombe a set of old Cornish stamps has been re-erected by the Trevithick Society. Dolcoath pumping engine Dolcoath was the largest and deepest mine in Cornwall, with its principal shaft, known as New Sump Shaft, eventually reaching a depth of below the surface. The pumping engine that worked this shaft dated from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices. It is also a component of the III-V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the toxicity of arsenic and its compounds. A few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites. Trace quantities of arsenic are an essential dietary element in rats, ham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Ore
Following is a list of minerals that serve as copper ores in the copper mining Copper extraction refers to the methods used to obtain copper from its ores. The conversion of copper consists of a series of physical and electrochemical processes. Methods have evolved and vary with country depending on the ore source, loca ... process:Samans, Carl H. ''Engineering Metals and their Alloys'' MacMillan 1949 References {{DEFAULTSORT:Copper ores Copper ores Mining-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |