|
Point-of-Care Testing
Point-of-care testing (POCT or bedside testing) is defined as medical diagnostic testing at or near the point of care—that is, at the time and place of patient care. This contrasts with the historical pattern in which testing was wholly or mostly confined to the medical laboratory, which entailed sending off specimens away from the point of care and then waiting hours or days to learn the results, during which time care must continue without the desired information. Technology Point-of-care tests are simple medical tests that can be performed at the bedside. In many cases, the simplicity was not achievable until technology developed not only to make a test possible at all but then also to mask its complexity. For example, various kinds of urine test strips have been available for decades, but portable ultrasonography did not reach the stage of being advanced, affordable, and widespread until the 2000s and 2010s. Today, portable ultrasonography is often viewed as a "simple" te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic Test
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic testing, chemical and cellular analysis, relating to clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics, are typically performed in a medical setting. Types of tests By purpose Medical tests can be classified by their purposes, the most common of which are diagnosis, screening and evaluation. Diagnostic A diagnostic test is a procedure performed to confirm or determine the presence of disease in an individual suspected of having a disease, usually following the report of symptoms, or based on other medical test results. This includes posthumous diagnosis. Examples of such tests are: * Using nuclear medicine to examine a patient suspected of having a lymphoma. * Measuring the blood sugar in a person suspected of having diabetes mellitus af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Diagnosis
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information required for diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the person seeking medical care. Often, one or more diagnostic procedures, such as medical tests, are also done during the process. Sometimes posthumous diagnosis is considered a kind of medical diagnosis. Diagnosis is often challenging because many signs and symptoms are nonspecific. For example, redness of the skin (erythema), by itself, is a sign of many disorders and thus does not tell the healthcare professional what is wrong. Thus differential diagnosis, in which several possible explanations are compared and contrasted, must be performed. This involves the correlation of various pieces of information followed by the recognition and differentiat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplexed Point-of-care Testing
Multiplexed point-of-care testing (xPOCT) is a more complex form of point-of-care testing (POCT), or bedside testing. Point-of-care testing is designed to provide diagnostic tests at or near the time and place that the patient is admitted. POCT uses the concentrations of analytes to provide the user with information on the physiological state of the patient. An analyte is a substance, chemical or biological, that is being analyzed using a certain instrument. While point-of-care testing is the quantification of one analyte from one in vitro (e.g. blood, plasma or urine) sample, multiplexed point-of-care testing is the simultaneous on-site quantification of various analytes from a single sample. Processing of one biological sample to yield multiple biomarker results allows for POCT testing to be done for patients who may have conditions that require the confirmation of multiple biomarkers and tests before diagnosis (e.g. many types of cancers). xPOCT has important emerging applicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplexed Point-of-care Testing
Multiplexed point-of-care testing (xPOCT) is a more complex form of point-of-care testing (POCT), or bedside testing. Point-of-care testing is designed to provide diagnostic tests at or near the time and place that the patient is admitted. POCT uses the concentrations of analytes to provide the user with information on the physiological state of the patient. An analyte is a substance, chemical or biological, that is being analyzed using a certain instrument. While point-of-care testing is the quantification of one analyte from one in vitro (e.g. blood, plasma or urine) sample, multiplexed point-of-care testing is the simultaneous on-site quantification of various analytes from a single sample. Processing of one biological sample to yield multiple biomarker results allows for POCT testing to be done for patients who may have conditions that require the confirmation of multiple biomarkers and tests before diagnosis (e.g. many types of cancers). xPOCT has important emerging applicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Coronary Syndrome
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a syndrome (a set of signs and symptoms) due to decreased blood flow in the coronary arteries such that part of the heart muscle is unable to function properly or dies. The most common symptom is centrally located pressure-like chest pain, often radiating to the left shoulder or angle of the jaw, and associated with nausea and sweating. Many people with acute coronary syndromes present with symptoms other than chest pain, particularly women, older people, and people with diabetes mellitus. Acute coronary syndrome is subdivided in three scenarios depending on the duration of symptoms, the presence of ECG changes and blood test results: ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI, 30%), non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI, 25%), or unstable angina (38%). Generally, when symptoms occur for less than 30 minutes, it is unstable angina. When symptoms are prolonged for more than 30 minutes, the diagnosis is acute myocardial infarction. ACS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
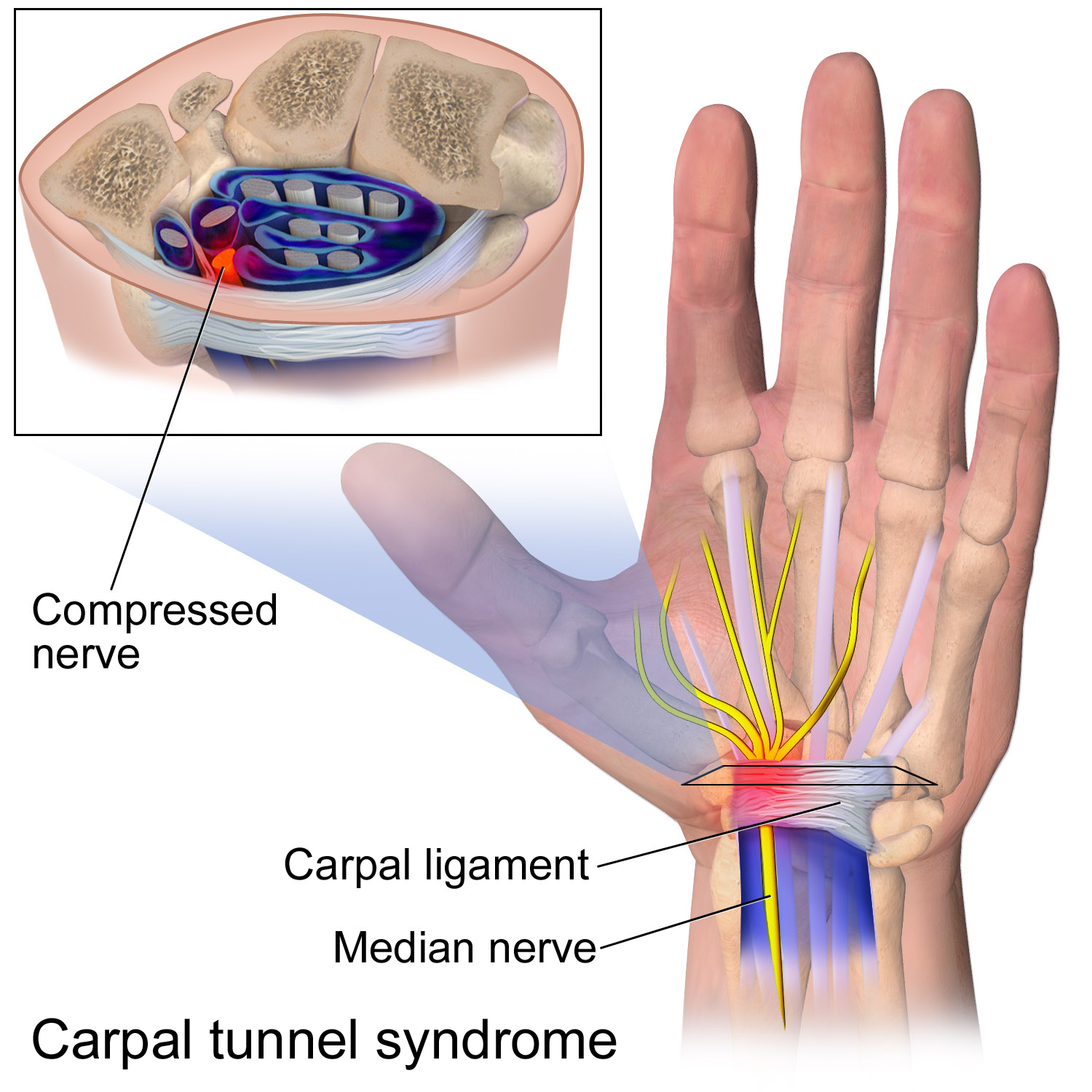
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the collection of symptoms and signs associated with median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel. Most CTS is related to idiopathic compression of the median nerve as it travels through the wrist at the carpal tunnel (IMNCT). Idiopathic means that there is no other disease process contributing to pressure on the nerve. As with most structural issues, it occurs in both hands, and the strongest risk factor is genetics. Other conditions can cause CTS such as wrist fracture or rheumatoid arthritis. After fracture, swelling, bleeding, and deformity compress the median nerve. With rheumatoid arthritis, the enlarged synovial lining of the tendons causes compression. The main symptoms are numbness and tingling in the thumb, index finger, middle finger and the thumb side of the ring finger. People often report pain, but pain without tingling is not characteristic of IMNCT. Rather, the numbness can be so intense that it is described as painful. Symptoms are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes, and cognitive impairment. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Insulin is a hormone which is responsible for helping glucose from food get into cells to be used for energy. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: * Type 1 diabetes results from failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin due to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Conduction Study
A nerve conduction study (NCS) is a medical diagnostic test commonly used to evaluate the function, especially the ability of electrical conduction, of the motor and sensory nerves of the human body. These tests may be performed by medical specialists such as clinical neurophysiologists, physical therapists, chiropractors, physiatrists (physical medicine and rehabilitation physicians), and neurologists who subspecialize in electrodiagnostic medicine. In the United States, neurologists and physiatrists receive training in electrodiagnostic medicine (performing needle electromyography (EMG) and NCSs) as part of residency training and in some cases acquire additional expertise during a fellowship in clinical neurophysiology, electrodiagnostic medicine, or neuromuscular medicine. Outside the US, clinical neurophysiologists learn needle EMG and NCS testing. Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a common measurement made during this test. The term NCV often is used to mean the actual tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Glucose Meter
A glucose meter, also referred to as a "glucometer", is a medical device for determining the approximate concentration of glucose in the blood. It can also be a strip of glucose paper dipped into a substance and measured to the glucose chart. It is a key element of glucose testing including home blood glucose monitoring (HBGM) by people with diabetes mellitus or hypoglycemia. A small drop of blood, obtained by pricking the skin with a lancet, is placed on a disposable test strip that the meter reads and uses to calculate the blood glucose level. The meter then displays the level in units of mg/dL or mmol/L. Since approximately 1980, a primary goal of the management of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus has been achieving closer-to-normal levels of glucose in the blood for as much of the time as possible, guided by HBGM several times a day. The benefits include a reduction in the occurrence rate and severity of long-term complications from hyperglycemia as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly a protein) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries. In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample to be tested are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme and then any unbound antibodies are removed. In the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's substrate is added. If there was binding, the subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change. Performing an ELISA involves at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) to a large enough amount to study in detail. PCR was invented in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation; Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)