|
Plaxis
Plaxis (sometimes stylised ''PLAXIS'', Plane strain and axial symmetry, indicating the geometric types handled in the original code) is a computer program that performs finite element analyses (FEA) within the realm of geotechnical engineering, including deformation, stability and water flow. The input procedures enable the enhanced output facilities provide a detailed presentation of computational results. PLAXIS enables new users to work with the package after only a few hours of training. Plaxis BV was acquired by the American Bentley Systems, Inc. in 2018. File:PLAXIS Mouhr Coulomb.jpg, Input parameters given for the Mohr–Coulomb soil model References Further reading * External links * Computer-aided design software for Windows 1982 software Finite element software Geotechnical engineering software {{CAD-software-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bentley Systems
Bentley Systems, Incorporated is an American-based software development company that develops, manufactures, licenses, sells and supports computer software and services for the design, construction, and operation of infrastructure. The company's software serves the building, plant, civil, and geospatial markets in the areas of architecture, engineering, construction (AEC) and operations. Their software products are used to design, engineer, build, and operate large constructed assets such as roadways, railways, bridges, buildings, industrial plants, power plants, and utility networks. The company re-invests 20% of their revenues in research and developmenthttp://www.bentleyannualreport-digital.com/bentleyannualreport/annual_report_2014?search_term=revenue&doc_id=-1&search_term=revenue&pg=4#pg4 2014 Bentley Systems Annual Report Bentley Systems is headquartered in Exton, Pennsylvania, United States, but has development, sales and other departments in over 50 countries. In 2021, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone. The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with 75% market share , according to StatCounter. However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android's massive growth. , the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer PCs and tablets, Windows 11 Enterprise for corporations, and Windows Server 2022 for servers. Genealogy By marketing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-aided Design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software are helpful in protecting products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used. Its use in designing electronic systems is known as '' electronic design automation'' (''EDA''). In mechanical design it is known as ''mechanical design automation'' (''MDA''), which includes the process of creating a technical drawing with the use of computer software. CAD software for mechanical design uses either vector-based graphics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
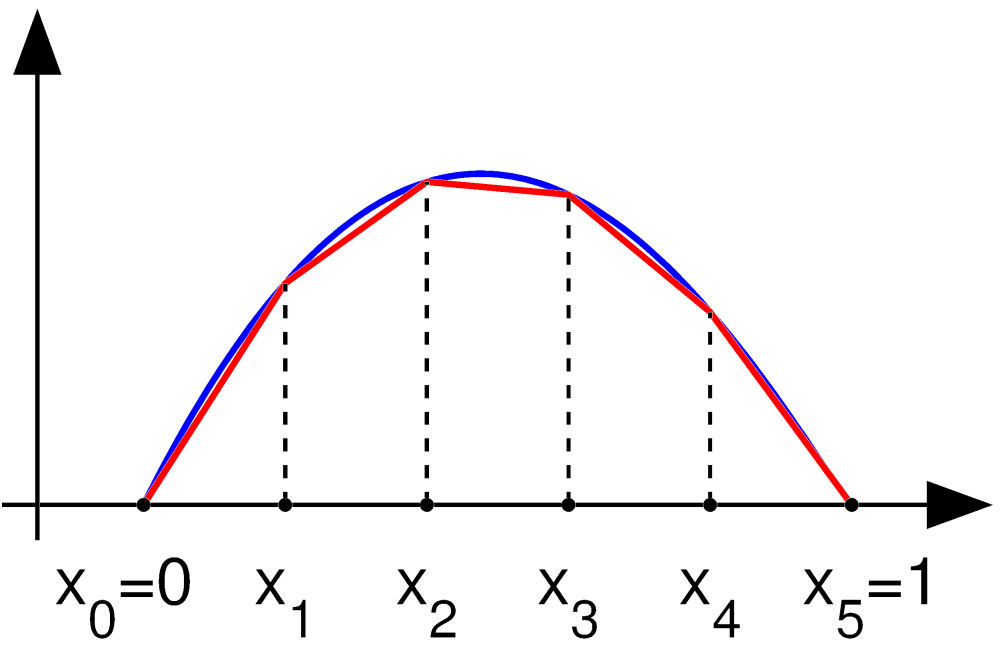
Finite Element Analysis
The finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential. The FEM is a general numerical method for solving partial differential equations in two or three space variables (i.e., some boundary value problems). To solve a problem, the FEM subdivides a large system into smaller, simpler parts that are called finite elements. This is achieved by a particular space discretization in the space dimensions, which is implemented by the construction of a mesh of the object: the numerical domain for the solution, which has a finite number of points. The finite element method formulation of a boundary value problem finally results in a system of algebraic equations. The method approximates the unknown function over the domain. The sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating Licensing
Floating licensing, also known as concurrent licensing or network licensing, is a software licensing approach in which a limited number of licenses for a software application are shared among a larger number of users over time. When an authorized user wishes to run the application, they request a license from a central license server. If a license is available, the license server allows the application to run. When they finish using the application, or when the allowed license period expires, the license is reclaimed by the license server and made available to other authorized users. The license server can manage licenses over a local area network, an intranet, virtual private network, or the Internet. Floating licensing is often used for high-value applications in corporate environments; such as electronic design automation or engineering tools. However, its use is broadly expanding throughout the software industry. An on-premise license server used to be the only way to enforc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane Strain
In continuum mechanics, the infinitesimal strain theory is a mathematical approach to the description of the deformation of a solid body in which the displacements of the material particles are assumed to be much smaller (indeed, infinitesimally smaller) than any relevant dimension of the body; so that its geometry and the constitutive properties of the material (such as density and stiffness) at each point of space can be assumed to be unchanged by the deformation. With this assumption, the equations of continuum mechanics are considerably simplified. This approach may also be called small deformation theory, small displacement theory, or small displacement-gradient theory. It is contrasted with the finite strain theory where the opposite assumption is made. The infinitesimal strain theory is commonly adopted in civil and mechanical engineering for the stress analysis of structures built from relatively stiff elastic materials like concrete and steel, since a common goal in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Symmetry
Axial symmetry is symmetry around an axis; an object is axially symmetric if its appearance is unchanged if rotated around an axis. glossary of meteorology. Retrieved 2010-04-08. For example, a without trademark or other design, or a plain white tea saucer, looks the same if it is rotated by any angle about the line passing lengthwise through its center, so it is axially symmetric. Axial symmetry can also be |
Finite Element Method
The finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential. The FEM is a general numerical method for solving partial differential equations in two or three space variables (i.e., some boundary value problems). To solve a problem, the FEM subdivides a large system into smaller, simpler parts that are called finite elements. This is achieved by a particular space discretization in the space dimensions, which is implemented by the construction of a mesh of the object: the numerical domain for the solution, which has a finite number of points. The finite element method formulation of a boundary value problem finally results in a system of algebraic equations. The method approximates the unknown function over the domain. The sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geotechnical Engineering
Geotechnical engineering is the branch of civil engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of earth materials. It uses the principles of soil mechanics and rock mechanics for the solution of its respective engineering problems. It also relies on knowledge of geology, hydrology, geophysics, and other related sciences. Geotechnical (rock) engineering is a subdiscipline of geological engineering. In addition to civil engineering, geotechnical engineering also has applications in military, mining, petroleum, coastal engineering, and offshore construction. The fields of geotechnical engineering and engineering geology have knowledge areas that overlap, however, while geotechnical engineering is a specialty of civil engineering, engineering geology is a specialty of geology: They share the same principles of soil mechanics and rock mechanics, but differ in the application. History Humans have historically used soil as a material for flood control, irrigation purposes, buria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Besloten Vennootschap
A (, lit. "Privately held company, closed company"; formally a , , ) or (SRL) is the Netherlands, Dutch and Belgium, Belgian version of a private limited liability company. The company is owned by shareholders; the company's Share (finance), shares are privately registered and not freely transferable. It is the most common form of limited company in the Netherlands and Belgium. A Dutch bv may be created by one or more individuals or Juristic person, legal entities, Dutch or foreign, with a minimum paid in capital of less than €1. A notarial act, notarized deed of incorporation is executed and filed. The deed must be in Dutch. It must contain details of the incorporators, and of the initial Members of the Board, their amounts of participation and payments of initial capital. The deed also contains the Articles of Association (law), Articles of Association, consisting of at least: * the company name (which must begin or end with "bv") * the city where the company has its regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohr–Coulomb Theory
Mohr–Coulomb theory is a mathematical model (see yield surface) describing the response of brittle materials such as concrete, or rubble piles, to shear stress as well as normal stress. Most of the classical engineering materials follow this rule in at least a portion of their shear failure envelope. Generally the theory applies to materials for which the compressive strength far exceeds the tensile strength. In geotechnical engineering it is used to define shear strength of soils and rocks at different effective stresses. In structural engineering it is used to determine failure load as well as the angle of fracture of a displacement fracture in concrete and similar materials. Coulomb's friction hypothesis is used to determine the combination of shear and normal stress that will cause a fracture of the material. Mohr's circle is used to determine which principal stresses will produce this combination of shear and normal stress, and the angle of the plane in which this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-aided Design Software For Windows
Computer-aided or computer-assisted is an adjectival phrase that hints of the use of a computer as an indispensable tool in a certain field, usually derived from more traditional fields of science and engineering. Instead of the phrase computer-aided or computer-assisted, in some cases the suffix management system is used. Engineering and production *Computer-aided design ** Computer-aided architectural design ** Computer-aided industrial design ** Electronic and electrical computer-aided design ** Computer-aided garden design *Computer-aided drafting *Computer-aided engineering ** Computer-aided production engineering *Computer-aided manufacturing *Computer-aided quality * Computer-aided maintenance Music and arts * Computer-aided algorithmic composition * Computer-assisted painting Human languages * Computer-aided translation Medicine * Computer-assisted detection * Computer-aided diagnosis * Computer-assisted orthopedic surgery * Computer-aided patient registration * Compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |