|
Platyzoa
The paraphyletic "Platyzoa" are a group of protostome unsegmented animals proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 1998. Cavalier-Smith included in Platyzoa the phylum Platyhelminthes (or flatworms), and a new phylum, the Acanthognatha, into which he gathered several previously described phyla of microscopic animals. Later it has been described as paraphyletic, containing the Rouphozoa and the Gnathifera. Phyla One scheme placed the following phyla in Platyzoa: * Rouphozoa ** Platyhelminthes ** Gastrotricha * Gnathifera ** Syndermata *** Rotifera *** Seisonida ** Acanthocephala ** Gnathostomulida ** Micrognathozoa ** Cycliophora Characteristics None of the Platyzoa groups have a respiration or circulation system because of their small size, flat body or parasitic lifestyle. The Platyhelminthes and Gastrotricha are acoelomate. The other phyla have a pseudocoel, and share characteristics such as the structure of their jaws and pharynx, although these have been secondari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platyzoa
The paraphyletic "Platyzoa" are a group of protostome unsegmented animals proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 1998. Cavalier-Smith included in Platyzoa the phylum Platyhelminthes (or flatworms), and a new phylum, the Acanthognatha, into which he gathered several previously described phyla of microscopic animals. Later it has been described as paraphyletic, containing the Rouphozoa and the Gnathifera. Phyla One scheme placed the following phyla in Platyzoa: * Rouphozoa ** Platyhelminthes ** Gastrotricha * Gnathifera ** Syndermata *** Rotifera *** Seisonida ** Acanthocephala ** Gnathostomulida ** Micrognathozoa ** Cycliophora Characteristics None of the Platyzoa groups have a respiration or circulation system because of their small size, flat body or parasitic lifestyle. The Platyhelminthes and Gastrotricha are acoelomate. The other phyla have a pseudocoel, and share characteristics such as the structure of their jaws and pharynx, although these have been secondari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
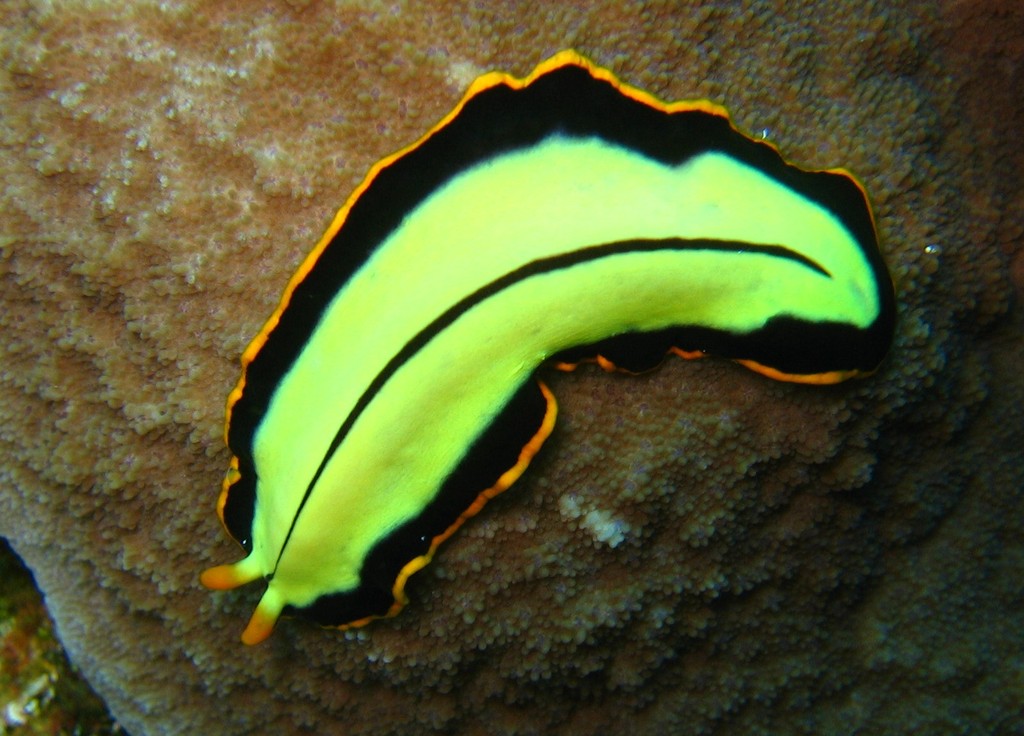
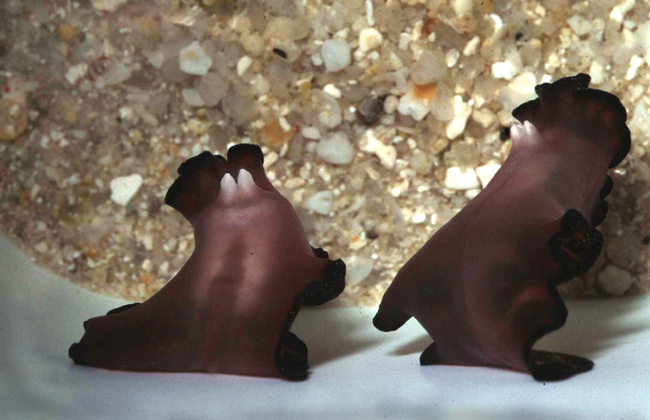
Flatworm
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates (having no body cavity), and have no specialized circulatory and respiratory organ (anatomy), organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion (intake of nutrients) and egestion (removal of undigested wastes); as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously. In traditional medicinal texts, Platyhelminthes are divided into Turbellaria, which are mostly non-parasitic animals such as planarians, and three entirely parasitic groups: Cestoda, Trematoda and Monogenea; however, since the turbellarians have since been prove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatworm
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates (having no body cavity), and have no specialized circulatory and respiratory organ (anatomy), organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion (intake of nutrients) and egestion (removal of undigested wastes); as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously. In traditional medicinal texts, Platyhelminthes are divided into Turbellaria, which are mostly non-parasitic animals such as planarians, and three entirely parasitic groups: Cestoda, Trematoda and Monogenea; however, since the turbellarians have since been prove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platyhelminthes
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek language, Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a Phylum (biology), phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, Segmentation (biology), unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates (having no coelom, body cavity), and have no specialized circulatory system, circulatory and respiratory system, respiratory organ (anatomy), organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion (intake of nutrients) and egestion (removal of undigested wastes); as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously. In traditional medicinal texts, Platyhelminthes are divided into Turbellaria, which are mostly non-parasitic animals such as planarians, and three entirely p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnathifera (clade)
Gnathifera (from the Greek '' gnáthos'', “jaw”, and the Latin '' -fera'', “bearing”) is a clade of generally small spiralians characterized by complex jaws made of chitin. It comprises the phyla Gnathostomulida, Rotifera, Micrognathozoa, and Chaetognatha. It may also include the Cycliophora. Gnathiferans include some of the most abundant phyla. Rotifers are among the most diverse and abundant freshwater animals and chaetognaths are among the most abundant marine plankton. Description The most distinctive characteristic of gnathiferans is the presence of complex sclerotized mouthparts made of chitin. In most gnathiferans, the anus opens on the dorsal surface of the animal. In micrognathozoans and gnathostomulids, the anus is transient and only forms during defecation. Unlike other gnathiferans, in chaetognaths and '' Amiskwia'' the anus is located on the ventral surface in a subterminal position. Development All known gnathiferans are direct developers. Though gnathi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndermata
Syndermata is a clade of animals that, in some systems, is considered synonymous with Rotifera. Older systems separate Rotifera and Acanthocephala Acanthocephala (Greek , ', thorn + , ', head) is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to p ... as different phyla, and group them both under Syndermata. References Platyzoa {{Protostome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophotrochozoa
Lophotrochozoa (, "crest/wheel animals") is a clade of protostome animals within the Spiralia. The taxon was established as a monophyletic group based on molecular evidence. The clade includes animals like annelids, molluscs, bryozoans, brachiopods, and platyhelminthes. Groups Lophotrochozoa was defined in 1995 as the "last common ancestor of the three traditional lophophorate taxa (brachiopods, bryozoans, and phoronid worms), the mollusks and the annelids, and all of the descendants of that common ancestor". It is a cladistic definition (a node-based name), so the affiliation to Lophotrochozoa of spiralian groups not mentioned directly in the definition depends on the topology of the spiralian tree of life, and in some phylogenetic hypotheses, Lophotrochozoa may even be synonymous to Spiralia. Nemertea and Orthonectida (if not directly considered as part of Annelida) are probably lophotrochozoan phyla; Dicyemida, Gastrotricha, and Platyhelminthes may be lophotrochozoans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic group (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of Synapomorphy and apomorphy, synapomorphies and symplesiomorphy, symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term was coined by Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia (reptiles) which, as commonly named and traditionally defined, is paraphyletic with respect to mammals and birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthognatha
Gnathifera (from the Greek '' gnáthos'', “jaw”, and the Latin '' -fera'', “bearing”) is a clade of generally small spiralians characterized by complex jaws made of chitin. It comprises the phyla Gnathostomulida, Rotifera, Micrognathozoa, and Chaetognatha. It may also include the Cycliophora. Gnathiferans include some of the most abundant phyla. Rotifers are among the most diverse and abundant freshwater animals and chaetognaths are among the most abundant marine plankton. Description The most distinctive characteristic of gnathiferans is the presence of complex sclerotized mouthparts made of chitin. In most gnathiferans, the anus opens on the dorsal surface of the animal. In micrognathozoans and gnathostomulids, the anus is transient and only forms during defecation. Unlike other gnathiferans, in chaetognaths and '' Amiskwia'' the anus is located on the ventral surface in a subterminal position. Development All known gnathiferans are direct developers. Though gnathi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiralia
The Spiralia are a morphologically diverse clade of protostome animals, including within their number the molluscs, annelids, platyhelminths and other taxa. The term ''Spiralia'' is applied to those phyla that exhibit canonical spiral cleavage, a pattern of early development found in most (but not all) members of the Lophotrochozoa. Distribution of spiralian development across phylogeny Members of the molluscs, annelids, platyhelminths and nemerteans have all been shown to exhibit spiral cleavage in its classical form. Other spiralian phyla (rotifers, brachiopods, phoronids, gastrotrichs, and bryozoans) are also said to display a derived form of spiral cleavage in at least a portion of their constituent species, although evidence for this is sparse. Lophotrochozoa within Spiralia Previously, spiral cleavage was thought to be unique to the Spiralia in the strictest sense—animals such as molluscs and annelids which exhibit classical spiral cleavage. The presence of spiral cleav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platytrochozoa
The Platytrochozoa are a proposed basal clade of spiralian animals as the sister group of the Gnathifera (clade), Gnathifera. The Platytrochozoa were divided into the Rouphozoa and the Lophotrochozoa. A more recent study suggests that the mesozoans also belong to this group of animals, as sister of the Rouphozoa. An alternative phylogeny was given in 2019, with a basal grouping of Mollusca and Entoprocta named Tetraneuralia, and a second grouping of Nemertea and Platyhelminthes named Parenchymia as sister of Annelida. In this proposal, Lophotrochozoa would become roughly synonymous with Platytrochozoa, and Rouphozoa would be unsupported. References Protostome unranked clades {{Protostome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
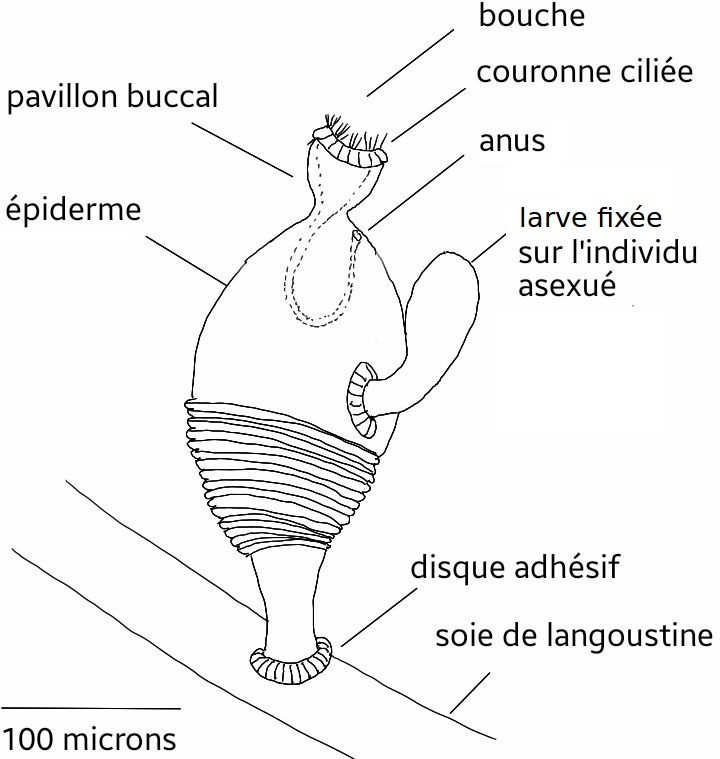
Symbion
''Symbion'' is a genus of commensal aquatic animals, less than 0.5 mm wide, found living attached to the mouthparts of cold-water lobsters. They have sac-like bodies, and three distinctly different forms in different parts of their two-stage life-cycle. They appear so different from other animals that they were assigned their own, new phylum Cycliophora shortly after they were discovered in 1995. This was the first new phylum of multicelled organism to be discovered since the Loricifera in 1983. Taxonomy ''Symbion'' was discovered in 1995 by Reinhardt Kristensen and Peter Funch on the mouthparts of the Norway lobster (''Nephrops norvegicus''). Other, related, species have since been discovered on: * the American lobster (''Homarus americanus'', host to ''Symbion americanus'') * the European lobster (''Homarus gammarus'', host to an as yet unnamed species of ''Symbion'') The genus is so named because of its commensal relationship with the lobster (a form of symbiosis) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |