|
Plasma Containment
In plasma physics, plasma confinement refers to the act of maintaining a plasma in a discrete volume. Confining plasma is required in order to achieve fusion power. There are two major approaches to confinement: magnetic confinement Magnetic confinement fusion is an approach to generate thermonuclear fusion power that uses magnetic fields to confine fusion fuel in the form of a plasma. Magnetic confinement is one of two major branches of fusion energy research, along with ... and inertial confinement. See also * List of plasma (physics) articles References Plasma physics {{plasma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma () 1, where \nu_ is the electron gyrofrequency and \nu_ is the electron collision rate. It is often the case that the electrons are magnetized while the ions are not. Magnetized plasmas are ''anisotropic'', meaning that their properties in the direction parallel to the magnetic field are different from those perpendicular to it. While electric fields in plasmas are usually small due to the plasma high conductivity, the electric field associated with a plasma moving with velocity \mathbf in the magnetic field \mathbf is given by the usual Lorentz force, Lorentz formula \mathbf = -\mathbf\times\mathbf, and is not affected by Debye shielding. Mathematical descriptions To completely describe the state of a plasma, all of the particle locations and velocities that describe the electromagnetic field in the plasma region would need to be written down. However, it is generally not practical or necessary to keep track of all the particles in a plasma. Therefore, plasma physicist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Power
Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion, nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2022, only one design, an Inertial confinement fusion, inertial confinement laser-driven fusion machine at the US National Ignition Facility, has conclusively produced a positive fusion energy gain factor, i.e. more power output than input. Fusion processes require fuel and a confined environment with sufficient temperature, pressure, and confinement time to create a plasma (physics), plasma in which fusion can occur. The combination of these figures that results in a power-producing system is known as the Lawson criterion. In stars, the most common fuel is hydrogen, and gravity provides ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
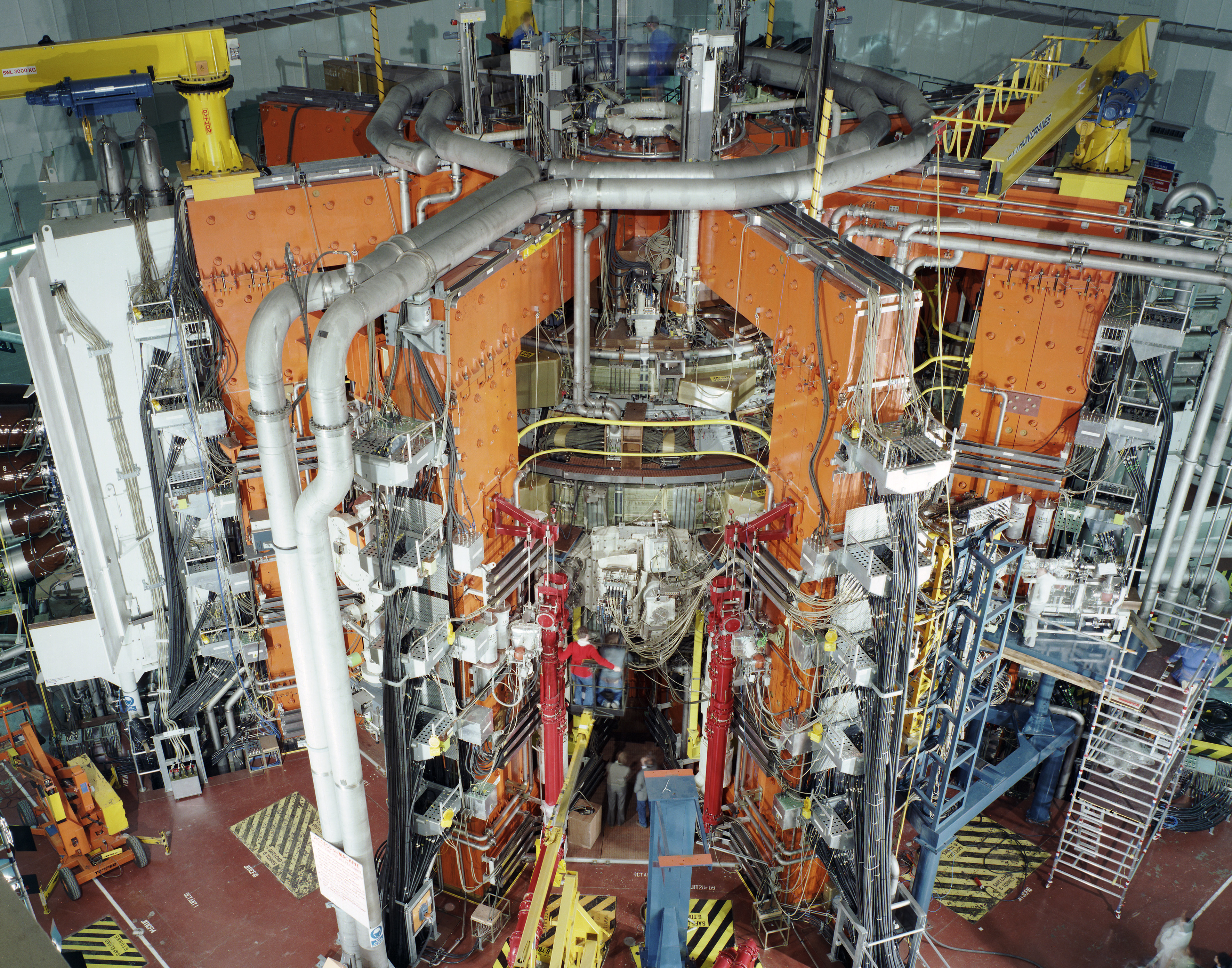
Magnetic Confinement Fusion
Magnetic confinement fusion is an approach to generate thermonuclear fusion power that uses magnetic fields to confine fusion fuel in the form of a plasma. Magnetic confinement is one of two major branches of fusion energy research, along with inertial confinement fusion. The magnetic approach began in the 1940s and absorbed the majority of subsequent development. Fusion reactions combine light atomic nuclei such as hydrogen to form heavier ones such as helium, producing energy. In order to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between the nuclei, they must have a temperature of tens of millions of degrees, creating a plasma. In addition, the plasma must be contained at a sufficient density for a sufficient time, as specified by the Lawson criterion (triple product). Magnetic confinement fusion attempts to use the electrical conductivity of the plasma to contain it through interaction with magnetic fields. The magnetic pressure offsets the plasma pressure. Developing a suitable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Confinement Fusion
Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) is a fusion energy process that initiates nuclear fusion reactions by compressing and heating targets filled with thermonuclear fuel. In modern machines, the targets are small spherical pellets about the size of a pinhead typically containing a mixture of about 10 milligrams of deuterium 2H and tritium 3H. To compress and heat the fuel, energy is deposited in the outer layer of the target using high-energy beams of photons, electrons or ions, although almost all ICF devices used lasers. The beams heat the outer layer, which explodes outward. This produces a reaction force against the remainder of the target, which accelerates it inwards and compresses the fuel. This process also creates shock waves that travel inward through the target. Sufficiently powerful shock waves can compress and heat the fuel at the center such that fusion occurs. ICF is one of two major branches of fusion energy research, the other is magnetic confinement fusion. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Plasma (physics) Articles
This is a list of plasma physics topics. A * Ablation * Abradable coating * Abraham–Lorentz force * Absorption band * Accretion disk * Active galactic nucleus * Adiabatic invariant * ADITYA (tokamak) * Aeronomy * Afterglow plasma * Airglow * Air plasma, Corona treatment, Atmospheric-pressure plasma treatment * Ayaks, Novel "Magneto-plasmo-chemical engine" * Alcator C-Mod * Alfvén wave * Ambipolar diffusion * Aneutronic fusion * Anisothermal plasma * Anisotropy * Antiproton Decelerator * Appleton-Hartree equation * Arcing horns * Arc lamp * Arc suppression * ASDEX Upgrade, Axially Symmetric Divertor EXperiment * Astron (fusion reactor) * Astronomy * Astrophysical plasma * Astrophysical X-ray source * Atmospheric dynamo * Atmospheric escape * Atmospheric pressure discharge * Atmospheric-pressure plasma * Atom * Atomic emission spectroscopy * Atomic physics * Atomic-terrace low-angle shadowing * Auger electron spectroscopy * Aurora (astronomy) B * Babcock Model * Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
