|
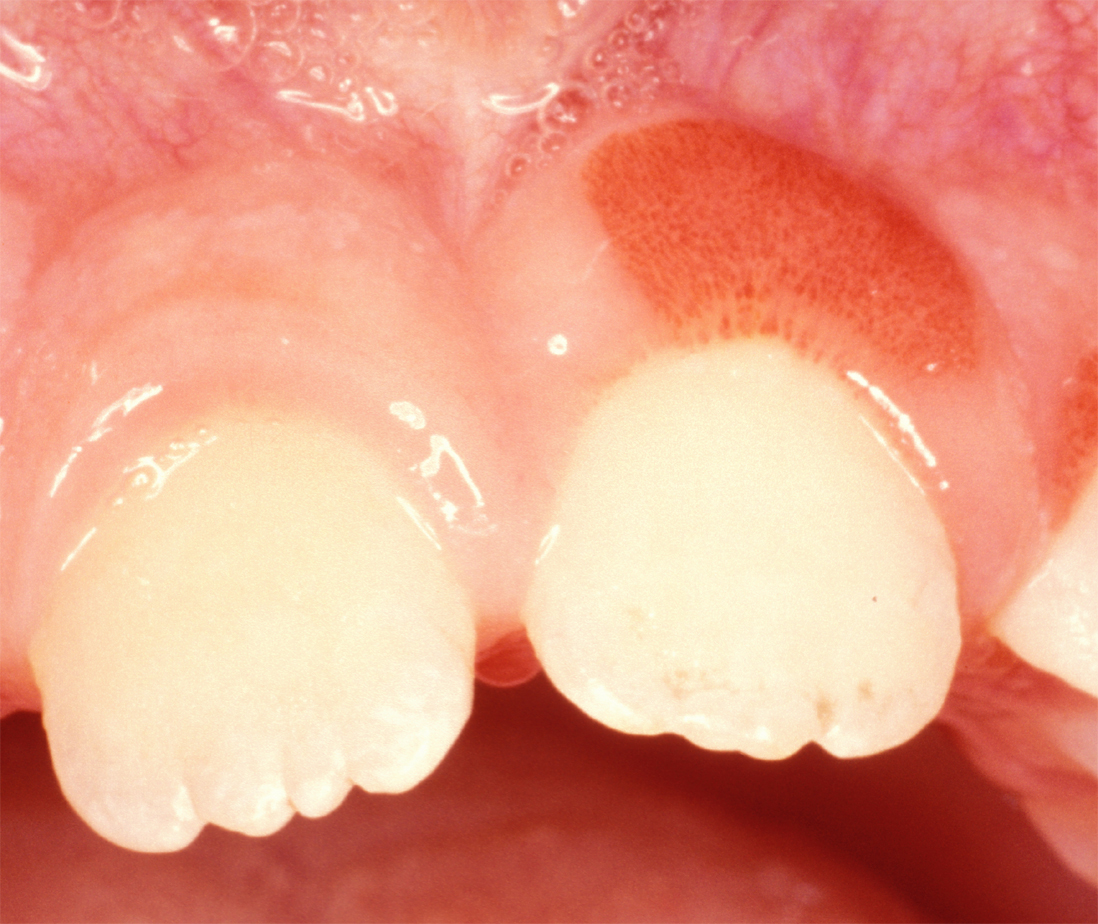
Plasma Cell Gingivitis
Plasma cell gingivitisGlauser RO, Humpreys PK, Stanley HR, Baer PN: An unusual gingivitis among adolescent navajo Indians. periodontics 1963;1:255-259. is a rare condition, appearing as generalized erythema (redness) and edema (swelling) of the attached gingiva, occasionally accompanied by cheilitis (lip swelling) or glossitis (tongue swelling). It is called plasma cell gingivitis where the gingiva (gums) are involved, plasma cell cheilitis, where the lips are involved, and other terms such as plasma cell orifacial mucositis, or plasma cell gingivostomatitis where several sites in the mouth are involved. On the lips, the condition appears as sharply outlined, infiltrated, dark red plaque with a lacquer-like glazing of the surface of the involved oral area. Signs and symptoms Plasma cell gingivitis appears as mild gingival enlargement and may extend from the free marginal gingiva on to the attached gingiva. Sometimes it is blended with a marginal, plaque induced gingivitis, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythema
Erythema (from the Greek , meaning red) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology include nervous blushes. Types * Erythema ab igne * Erythema chronicum migrans * Erythema induratum * Erythema infectiosum (or fifth disease) * Erythema marginatum * Erythema migrans * Erythema multiforme (EM) * Erythema nodosum * Erythema toxicum * Erythema elevatum diutinum * Erythema gyratum repens * Keratolytic winter erythema * Palmar erythema Causes It can be caused by infection, massage, electrical treatment, acne medication, allergies, exercise, solar radiation (sunburn), photosensitization, acute radiation syndrome, mercury toxicity, blister agents, niacin administration, or waxing and tweezing of the hairs—any of which can cause the capillaries to dilate, resulting in redness. Erythema is a common sid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology Of Plasma Cell Gingivitis
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gingival Enlargement
Gingival enlargement is an increase in the size of the gingiva (gums). It is a common feature of gingival disease. Gingival enlargement can be caused by a number of factors, including inflammatory conditions and the side effects of certain medications. The treatment is based on the cause. A closely related term is epulis, denoting a localized tumor (i.e. lump) on the gingiva. Classification The terms gingival hyperplasia and gingival hypertrophy have been used to describe this topic in the past. These are not precise descriptions of gingival enlargement because these terms are strictly histologic diagnoses, and such diagnoses require microscopic analysis of a tissue sample. Hyperplasia refers to an increased number of cells, and hypertrophy refers to an increase in the size of individual cells. As these identifications cannot be performed with a clinical examination and evaluation of the tissue, the term ''gingival enlargement'' is more properly applied. Gingival enlargement has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms (also called plaque) that is attached to tooth surfaces, termed ''plaque-induced gingivitis''. Most forms of gingivitis are plaque-induced. While some cases of gingivitis never progress to periodontitis, periodontitis is always preceded by gingivitis. Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene; however, without treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, in which the inflammation of the gums results in tissue destruction and bone resorption around the teeth. Periodontitis can ultimately lead to tooth loss. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of gingivitis are somewhat non-specific and manifest in the gum tissue as the classic signs of inflammation: *Swollen gums *Bright red gums *Gums that are tender or painful to the touch *Bleeding gums or bleeding after bru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmoacanthoma
Plasmoacanthoma is a condition of the oral mucosa characterized by a verrucous tumor with a plasma cell infiltrate. See also * Plasma cell cheilitis * Skin lesion A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of th ... References Conditions of the mucous membranes {{Cutaneous-condition-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spongiosis
Spongiosis is mainly intercellular edema (abnormal accumulation of fluid) in the epidermis,Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease'' (7th ed.). Saunders. Page 1230. . and is characteristic of eczematous dermatitis, manifested clinically by intraepidermal vesicles (fluid-containing spaces), "juicy" papules, and/or lichenification.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 28. . It is a severe case of eczema that affects the epidermis, dermis and/or subcutaneous skin tissues. The three types of spongiotic dermatitis are acute, subacute and chronic. A dermatologist can diagnose acute spongiotic dermatitis by examining the skin during an office visit but a biopsy is needed for an accurate diagnosis of the type. It can be caused by several internal or external factors such as food, an insect bite, stress, medication or cosmetics. The treatment varies de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Indian Society Of Periodontology
The ''Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology'' is a peer-reviewed open access medical journal published by Medknow Publications on behalf of the Indian Society of Periodontology. It covers all aspects of periodontology Periodontology or periodontics (from Ancient Greek , – 'around'; and , – 'tooth', genitive , ) is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting .... Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: External links * {{Official website, http://www.jisponline.com Open access journals Quarterly journals English-language journals Dentistry journals Medknow Publications academic journals Publications established in 1997 Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies of India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks"). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, anemia, kidney dysfunction, and infections may occur. Complications may include amyloidosis. The cause of multiple myeloma is unknown. Risk factors include obesity, radiation exposure, family history, and certain chemicals. There is an increased risk of multiple myeloma in certain occupations. This is due to the occupational exposure to aromatic hydrocarbon solvents having a role in causation of multiple myeloma. Multiple myeloma may develop from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance that progresses to smoldering myeloma. The abnormal plasma cells produce abnormal antibodies, which can cause kidney problems and overly thick blood. The plasma cells can also form a mass in the bone marrow or soft tissue. When one tumor i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |