|
Plank Road Boom
The Plank Road Boom was an economic boom in the United States that lasted from 1844 to the mid 1850s, largely in the Eastern United States and New York. In the span of ten years, over of plank road were built in New York—enough road to go from Manhattan to California—and more than of plank road were built countrywide. Background Plank roads were brought to the United States by Syracuse engineer George Geddes who brought them to New York from Canada. In turn, the concept is thought to have been brought to North America from Russia by the then Governor General Lord Sydenham. The first plank road in North America led out from Toronto, and was frequently cited by Geddes in his promotion of plank roads. The Toronto project was proposed by Darcy Boulton, and built under Sir Francis Bond. By 1861, the governments of Upper and Lower Canada had built between 127–162 miles of plank roads, and private companies 194–214 miles. Geddes enthusiastically reported that wooden roads l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
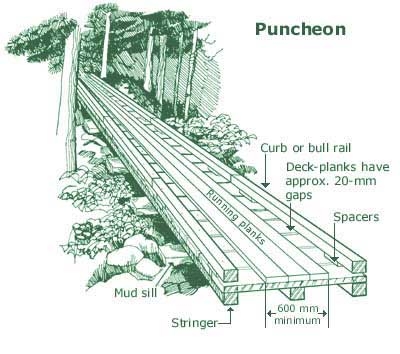
Puncheon
Puncheon may refer to: * Puncheon (barrel), a container for wine and/or spirits * Puncheon or plank road, a road built with split logs or heavy slab timbers with one face smoothed, also used for flooring or other construction * Puncheon rum, a type of Caribbean rum * Puncheon (unit), a unit of volume People with the surname * Jason Puncheon Jason David Ian Puncheon (born 18 June 1986) is an English professional footballer who plays as a midfielder for Cypriot First Division club Anorthosis Famagusta . Following his goal against Everton on his Blackpool debut, he has scored in a ... (born 1986), English footballer See also * Puncheon Island, Tasmania, Australia * Puncheon Islets, Tasmania, Australia * Puncheon Run Connector, unnumbered limited access highway in Delaware, USA {{disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macadam
Macadam is a type of road construction, pioneered by Scottish engineer John Loudon McAdam around 1820, in which crushed stone is placed in shallow, convex layers and compacted thoroughly. A binding layer of stone dust (crushed stone from the original material) may form; it may also, after rolling, be covered with a cement or bituminous binder to keep dust and stones together. The method simplified what had been considered state-of-the-art at that point. Predecessors Pierre-Marie-Jérôme Trésaguet Pierre-Marie-Jérôme Trésaguet is sometimes considered the first person to bring post-Roman science to road building. A Frenchman from an engineering family, he worked paving roads in Paris from 1757 to 1764. As chief engineer of road construction of Limoges, he had opportunity to develop a better and cheaper method of road construction. In 1775, Tresaguet became engineer-general and presented his answer for road improvement in France, which soon became standard practice there. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freehold Township, NJ
Freehold Township is a township in Monmouth County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. The township is both a regional commercial hub for Central New Jersey (home to the Freehold Raceway and Freehold Raceway Mall) and a bedroom community of New York City, located within the Raritan Valley region of the much larger New York Metropolitan Area.Fowler, Glen"In Monmouth, Homes Still Rise, Defying Lag: Freehold, N.J." '' The New York Times'', April 19, 1970. Accessed June 14, 2022. The township is located roughly away from Manhattan and about away from Staten Island. As of the 2020 United States census, the township's population was 35,369, reflecting a decrease of 815 (−2.3%) from the 36,184 counted in the 2010 Census. Freehold Township was first formed on October 31, 1693, and was incorporated as a township by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on February 21, 1798. Portions of Freehold Township were taken to form Upper Freehold Township (), so some wills and official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Highway
The Lincoln Highway is the first transcontinental highway in the United States and one of the first highways designed expressly for automobiles. Conceived in 1912 by Indiana entrepreneur Carl G. Fisher, and formally dedicated October 31, 1913, the Lincoln Highway runs coast-to-coast from Times Square in New York City west to Lincoln Park in San Francisco, originally through 13 states: New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Nebraska, Colorado, Wyoming, Utah, Nevada, and California. In 1915, the "Colorado Loop" was removed, and in 1928, a realignment relocated the Lincoln Highway through the northern tip of West Virginia. Thus, there are a total of 14 states, 128 counties, and more than 700 cities, towns and villages through which the highway passed at some time in its history. The first officially recorded length of the entire Lincoln Highway in 1913 was . Over the years, the road was improved and numerous realignments were made, See throughout, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between New York City and Jersey City, eventually draining into the Atlantic Ocean at Lower New York Bay. The river serves as a political boundary between the states of New Jersey and New York at its southern end. Farther north, it marks local boundaries between several New York counties. The lower half of the river is a tidal estuary, deeper than the body of water into which it flows, occupying the Hudson Fjord, an inlet which formed during the most recent period of North American glaciation, estimated at 26,000 to 13,300 years ago. Even as far north as the city of Troy, the flow of the river changes direction with the tides. The Hudson River runs through the Munsee, Lenape, Mohican, Mohawk, and Haudenosaunee homelands. Prior to European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Jersey Meadowlands
New Jersey Meadowlands, also known as the Hackensack Meadowlands after the primary river flowing through it, is a general name for the large ecosystem of wetlands in northeastern New Jersey in the United States, a few miles to the west of New York City. In the 20th century, much of the Meadowlands area was urbanized, and it became known for being the site of large landfills and decades of environmental abuse. A variety of projects are underway to restore and conserve the remaining ecological resources in the Meadowlands. Geography The Meadowlands stretch mainly along the terminus of the Hackensack and Passaic Rivers as they flow into Newark Bay; tributaries of the Hackensack include Mill Creek, Berrys Creek, and Overpeck Creek. The Meadowlands consist of roughly 8,400 acres (34 km2) of open, undeveloped space in addition to developed areas that had been part of the natural wetlands which were heavily developed by H. Bert Mack and M. Bolero in the 1960s. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware River and Pennsylvania; and on the southwest by Delaware Bay and the state of Delaware. At , New Jersey is the fifth-smallest state in land area; but with close to 9.3 million residents, it ranks 11th in population and first in population density. The state capital is Trenton, and the most populous city is Newark. With the exception of Warren County, all of the state's 21 counties lie within the combined statistical areas of New York City or Philadelphia. New Jersey was first inhabited by Native Americans for at least 2,800 years, with the Lenape being the dominant group when Europeans arrived in the early 17th century. Dutch and Swedish colonists founded the first European settlements in the state. The British later seized control o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newark Plank Road
The Newark Plank Road was a major artery between Hudson Waterfront at Paulus Hook (in today's Jersey City) and city of Newark further inland across the New Jersey Meadows. As its name suggests, a plank road was constructed of wooden planks laid side-to-side on a roadbed. Similar roads, the Bergen Point Plank Road, the Hackensack Plank Road and Paterson Plank Road, traveled to the locales for which they are named. The name is no longer used, the route having been absorbed into other streets and freeways. In 1765, an act of the Assembly of the Province of New Jersey stated: A road from New-Ark to the publick road in the town of Bergen, leading to Poulos Hook, and establishing ferries over the two small rivers, Passaick and Hackensack, which makes the distance from Poulus Hook to New-Ark eight miles, and will be a level and good road when the cause-ways are made ; and as said road will be very commodious for travelers, and give a short and easy access of a large country to the mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paterson Plank Road
Paterson Plank Road is a road that runs through Passaic, Bergen and Hudson Counties in northeastern New Jersey. The route, originally laid in the colonial era, connects the city of Paterson and the Hudson River waterfront. It has largely been superseded by Route 3, but in the many towns it passes it has remained an important local thoroughfare, and in some cases been renamed. History Portions of the road were at times called New Barbadoes Turnpike, from New Barbadoes Neck, the name of the peninsula between the rivers it crossed, the Hackensack and the Passaic. Many plank roads in the United States were developed in the nineteenth century. These roads consisted of wooden boards laid adjacently to prevent coach and wagon wheels from getting bogged down in soft or swampy ground, thereby creating an even surface that would facilitate travel. Normally a toll was charged. This technology was applied to the Paterson Plank Road and similar roads, the Hackensack Plank Road and the Newa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hackensack Plank Road
The Hackensack Plank Road, also known as Bergen Turnpike, was a major artery which connected the cities of Hoboken and Hackensack, New Jersey. Like its cousin routes, the Newark Plank Road and Paterson Plank Road, it travelled over Bergen Hill and across the Hackensack Meadows from the Hudson River waterfront to the city for which it was named. It was originally built as a colonial turnpike road as Hackensack and Hoboken Turnpike. The route mostly still exists today, though some segments are now called the Bergen Turnpike. It was during the 19th century that plank roads were developed, often by private companies which charged a toll. As the name suggests, wooden boards were laid on a roadbed in order to prevent horse-drawn carriages and wagons from sinking into softer ground on the portions of the road that passed through wetlands. The company that built the road received its charter on November 30, 1802. The road followed the route road from Hackensack to Communipaw that was de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Incorporation Law
The history of corporate law in the United States concerns the development of the corporation, primarily as a business organization, under the different United States corporate law, including federal regulation. Common law The United Kingdom required a legislative charter for incorporation until passage of the Joint Stock Companies Act 1844. *''Case of Sutton's Hospital'' (1612) 77 Eng Rep 960 *''Keech v Sandford'' 726EWHC Ch J76*''Attorney General v. Davy'' (1741) 2 Atk 212 *''The Charitable Corporation v Sutton'' (1742) 26 ER 642 *''Whelpdale v Cookson'' (1747) 27 ER 856 *''R v Richardson'' (175897 ER 426 Colonial corporations *Virginia Company (London Company and Plymouth Company est 1606-1624) and Plymouth Council for New England *Massachusetts Bay Company est. 1628 *Hudson's Bay Company est. 1670 *Bank of England est. 1694 *South Sea Company and South Sea Bubble *Russian-American Company Post-independence Prior to the late 19th century, most companies were incorporated by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Kingsford
William Kingsford (23 December 1819 – 29 September 1898) was an English-born Canadian historian. Born in London, England, served in the army, and went to Canada, where he was engaged in surveying work. He was a self-taught historian, and one of the first to use the archives being gathered in Ottawa. He is best known for his ''History of Canada'' in 10 volumes (1887–1898), which was widely read by the upper middle class, as well as Anglophone teachers, despite its poor organisation and pedestrian writing style. Kingsford believed that the Conquest of New France guaranteed victory for British constitutional liberty and that it ensured material progress. He assumed the assimilation of French Canadians into a superior British culture was inevitable and desirable, for he envisioned Canada as one nation with one anglophone population. Early life Born on 23 December 1819 in the parish of St. Lawrence Jewry, London, he was the son of William and Elizabeth Kingsford of Lad Lane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |