|
Piz Scharboda
Piz Scharboda is a mountain of the Swiss Lepontine Alps, overlooking the lake of Zervreila in the canton of Graubünden. It lies south of Piz Terri, near the border with the canton of Ticino Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . .... References External links Piz Scharboda on Hikr Mountains of the Alps Alpine three-thousanders Mountains of Switzerland Mountains of Graubünden Lepontine Alps Vals, Switzerland {{Graubünden-mountain-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swisstopo
Swisstopo is the official name for the Swiss Federal Office of Topography (in German language, German: ''Bundesamt für Landestopografie''; French language, French: ''Office fédéral de topographie''; Italian language, Italian: ''Ufficio federale di topografia''; Romansh language, Romansh: ''Uffizi federal da topografia''), Switzerland's national mapping agency. The current name was made official in 2002. It had been in use as the domain name for the institute's homepage, swisstopo.ch, since 1997. Maps The main class of products produced by Swisstopo are topographical maps on seven different Scale (map), scales. Swiss maps have been praised for their accuracy and quality. Regular maps * 1:25.000. This is the most detailed map, useful for many purposes. Those are popular with tourists, especially for famous areas like Zermatt and St. Moritz. These maps cost CHF 13.50 each (2004). 208 maps on this scale are published at regular intervals. The first map published on this scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piz Terri
Piz Terri is a mountain in the Lepontine Alps, located on the border between the cantons of Ticino and Graubünden. At 3,149 metres above sea level it is the highest summit lying on the chain between Greina and Soreda Pass. Piz Terri overlooks Lake Luzzone in Val Blenio on its west side, Val Sumvitg on its north side and Lumnezia on its east side. Close localities are Olivone (Val Blenio) and Vrin (Lumnezia). The lake named ''Laghet la Greina'' (0.183 km²Area retrieved from Google Earth (July 2013)) is located not far from the summit, on the northwest side of the mountain, at an elevation of 2,585 metres. The faces are steep. Only a small glacier, named ''Glatscher dil Terri'', lies at the base of the north face. It previously extended down to the lake. The summit can be reached by experienced hikers via a trail on the west ridge. The normal route starts above Lake Luzzone at the Motterascio hut (2,171 metres), owned by the Swiss Alpine Club The Swiss Alpine Club (ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federalism, Federal assembly-independent Directorial system, directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepontine Alps
, topo_map= Swiss Federal Office of Topography swisstopo , photo=MonteLeone0001.jpg , photo_caption=Monte Leone , country_type= Countries , country= , subdivision1_type= Cantons, Regions , subdivision1= , parent= Western Alps , borders_on= , geology= , orogeny= Alpine orogeny , length_mi= , length_orientation= , width_mi= , width_orientation= , highest=Monte Leone , elevation_m=3553 , coordinates= , range_coordinates= , map_image=Alps locator map (Alpi Lepontini).png , map_caption=Lepontine Alps (red) The Lepontine Alps (german: Lepontinische Alpen, french: Alpes lépontines, it, Alpi Lepontine) are a mountain range in the north-western part of the Alps. They are located in Switzerland (Valais, Ticino, Uri and Graubünden) and Italy (Piedmont and Lombardy). The Simplon rail tunnel (from Brig to Domodossola) the Gotthard rail (from Erstfeld to Bodio) and Gotthard road tunnels (from Andermatt to Airolo) and the San Bernardino road tunnel are importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are Monadnock, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountain formation, Mountains are formed through Tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zervreilasee
__NOTOC__ Zervreilasee is a reservoir located south-west of Vals in the canton of Graubünden, Switzerland. Geography The lake has a surface area of 1.61 km² and an elevation of 1,862 m. The maximum depth is 140 m. The dam is 151 m high and was completed in 1957. The village of Zervreila was flooded after the construction of the dam. A 150-metre-long bridge (''Canalbrücke'') crosses the southern bay of the lake. The Zervreilasee, located near the upper end of the Valser Tal, is surrounded by peaks over 3,000 metres. The highest visible from the lake is the Güferhorn (3,379 m), located on the south side. Other peaks are the Fanellhorn (3,124 m), the Frunthorn (3,030 m), Piz Scharboda (3,122 m), the Plattenberg (3,041 m) and the Furggeltihorn (3,043 m). The Zervreilahorn is a sharp peak overlooking the lake from its south-west side. See also *List of lakes of Switzerland *List of mountain lakes of Switzerland References *Swisstopo topographic maps External linksKraftwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
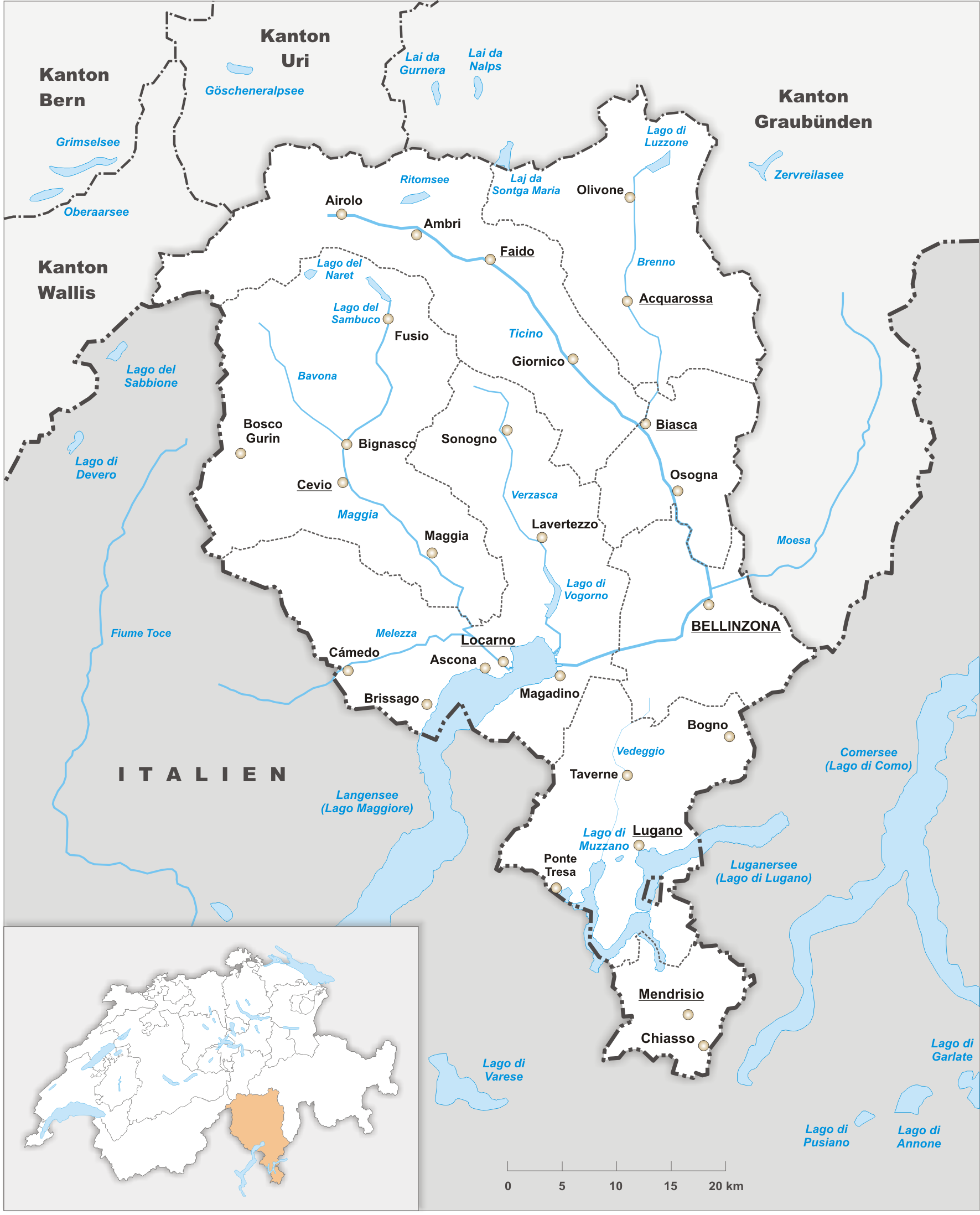
Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts and its capital city is Bellinzona. It is also traditionally divided into the Sopraceneri and the Sottoceneri, respectively north and south of Monte Ceneri. Red and blue are the colours of its flag. Ticino is the southernmost canton of Switzerland. It is one of the three large southern Alpine cantons, along with Valais and the Grisons. However, unlike all other cantons, it lies almost entirely south of the Alps, and has no natural access to the Swiss Plateau. Through the main crest of the Gotthard and adjacent mountain ranges, it borders the canton of Valais to the northwest, the canton of Uri to the north and the canton of Grisons to the northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of The Alps
This page tabulates only the most prominent mountains of the Alps, selected for having a topographic prominence of ''at least'' , and all of them exceeding in height. Although the list contains 537 summits, some significant alpine mountains are necessarily excluded for failing to meet the stringent prominence criterion. The list of these most prominent mountains is continued down to 2500 m elevation at List of prominent mountains of the Alps (2500–2999 m) and down to 2000 m elevation on List of prominent mountains of the Alps (2000–2499 m). All such mountains are located in either France, Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany or Slovenia, even in some lower regions. Together, these three lists include all 44 ultra-prominent peaks of the Alps, with 19 ultras over 3000m on this page. For a definitive list of all 82 the highest peaks of the Alps, as identified by the International Climbing and Mountaineering Federation (UIAA), and often referred to as the 'Alpi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Three-thousanders
Three-thousanders are mountains with a height of between , but less than above sea level. Similar terms are commonly used for mountains of other height brackets e. g. four-thousanders or eight-thousanders. In Britain, the term may refer to mountains above . Climatological significance In temperate latitudes three-thousanders play an important role, because even in summer they lie below the zero degree line for weeks. Thus the chains of three-thousanders always form important climatic divides and support glaciation - in the Alps the contour is roughly the general limit of the "nival step"; only a few glaciated mountains are under (the Dachstein, the easternmost glaciated mountain in the Alps, is, at , not a three-thousander). In the Mediterranean, however, the three-thousanders remain free of ice and, in the tropics, they are almost insignificant from a climatic perspective; here the snow line lies at around to , and in the dry continental areas (Trans-Himalayas, Ande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Switzerland
This article contains a sortable table of many of the major mountains and hills of Switzerland. The table only includes those summits that have a topographic prominence of at least above other points, and ranks them by height and prominence. Therefore it only includes mountains that might generally be regarded as 'independent' and covers most of the country, even lower areas. For a fuller list of mountains, including subsidiary points, see List of mountains of Switzerland above 3000 m and List of mountains of Switzerland above 3600 m. For a list of just the most isolated mountains, see List of most isolated mountains of Switzerland. Along with the lakes, mountains constitute a major natural feature of Switzerland with most of the cantons having summits exceeding and three of them having summits exceeding . The two main mountain ranges are the Alps (south and east) and the Jura (north and west), separated by the Swiss Plateau which also includes a large number of hills. Topo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Graubünden
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |