|
Pittosporum Tenuifolium
''Pittosporum tenuifolium'' is a small evergreen tree endemic to New Zealand – up to – commonly known as and black matipo, and by other Māori names and . Its small, very dark, reddish-purple flowers generally go unnoticed, and are scented only at night. The Latin means "slender-leaved" Description ''Pittosporum'' translates to tarry – – seed – , a reference to the sticky fluid that encases the seeds and means thin – – leaf – . is a bush or small tree that grows up to around 8–10 metres tall. The trunk is slender (30–40 cm diameter) with a mottled dark grey bark color that progressively turns black towards the tips of the branches The leaf coverage is compact in ; the leaves are arranged alternately on the stem and the petiole is short. The leaves themselves are usually small – 2–4 cm long by 1–2 cm wide – but can grow up to 7 cm long. The edges are undulated and the leaf shape can range from oval to almost circular. You ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Banks
Sir Joseph Banks, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1820) was an English naturalist, botanist, and patron of the natural sciences. Banks made his name on the 1766 natural-history expedition to Newfoundland and Labrador. He took part in Captain James Cook's first great voyage (1768–1771), visiting Brazil, Tahiti, and after 6 months in New Zealand, Australia, returning to immediate fame. He held the position of president of the Royal Society for over 41 years. He advised King George III on the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, and by sending botanists around the world to collect plants, he made Kew the world's leading botanical garden. He is credited for bringing 30,000 plant specimens home with him; amongst them, he was the first European to document 1,400. Banks advocated British settlement in New South Wales and the colonisation of Australia, as well as the establishment of Botany Bay as a place for the reception of convicts, and advised the British government on all Australian matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stewart Island
Stewart Island ( mi, Rakiura, ' glowing skies', officially Stewart Island / Rakiura) is New Zealand's third-largest island, located south of the South Island, across the Foveaux Strait. It is a roughly triangular island with a total land area of . Its coastline is deeply creased by Paterson Inlet (east), Port Pegasus (south), and Mason Bay (west). The island is generally hilly (rising to at Mount Anglem) and densely forested. Flightless birds, including penguins, thrive because there are few introduced predators. Almost all the island is owned by the New Zealand government and over 80 per cent of the island is set aside as the Rakiura National Park. Stewart Island's economy depends on fishing and summer tourism. Its permanent population was recorded at 408 people in the 2018 census, most of whom live in the settlement of Oban on the eastern side of the island. Ferries connect the settlement to Bluff in the South Island. Stewart Island/Rakiura is part of the Southland Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
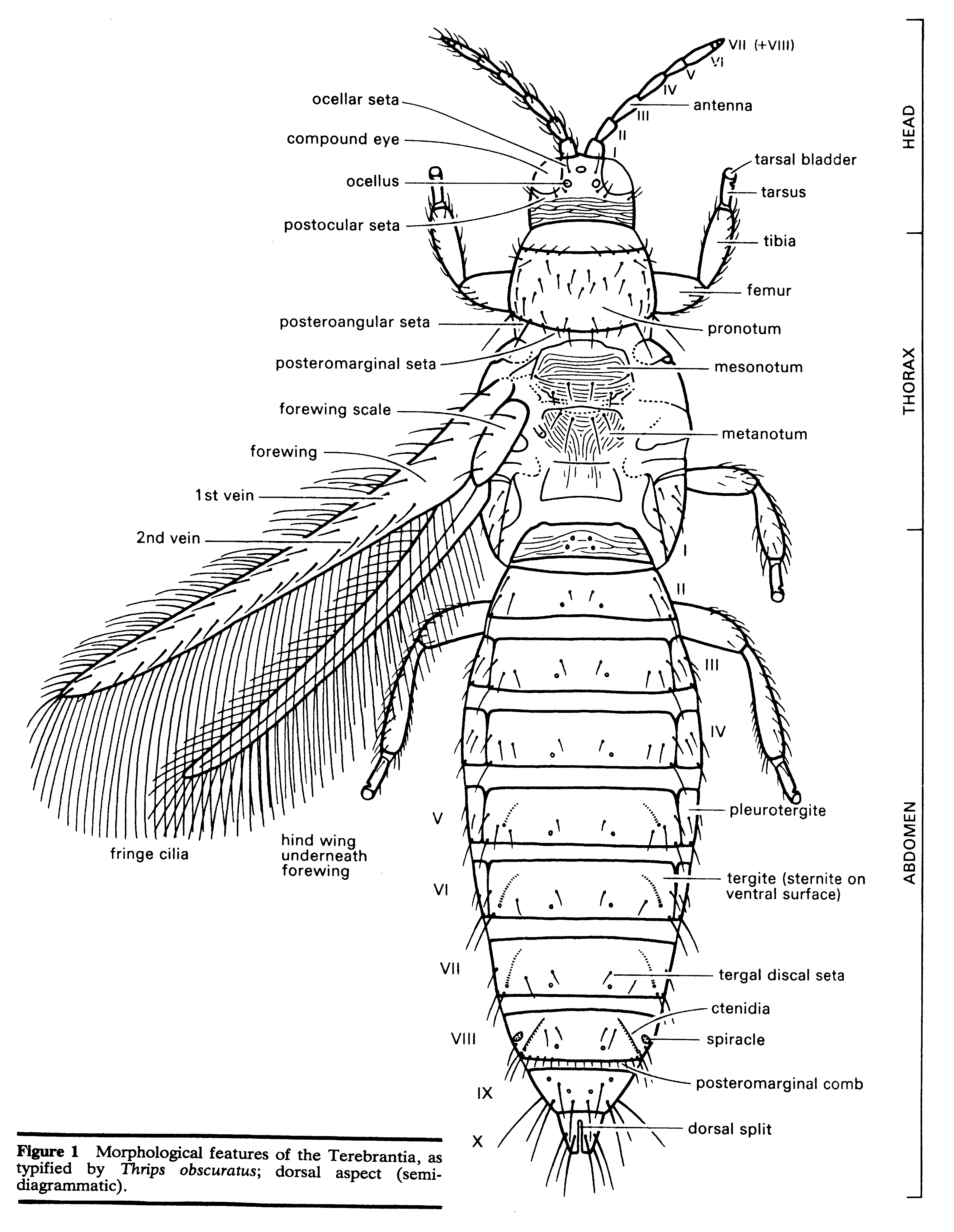
Thrips (genus)
''Thrips'' is a genus of insect in the order Thysanoptera. Ecology Species in the genus ''Thrips'' feed on pollen, and can be major agricultural pests, with several being vectors of tospoviruses. Etymology The name ''Thrips'' comes from the Greek word meaning woodworm. Diversity ''Thrips'' is the largest genus of thrips, with over 280 species, most of which are found in Europe, Africa and the Mediterranean Basin. Other species occur on each of the continents, including one species described from Antarctica. ''Thrips'' includes the species of thrips most frequently intercepted at ports of entry into the United States, '' T. tabaci''. The following species are recognised: *'' Thrips abyssiniae'' *'' Thrips acaciae'' *'' Thrips addendus'' *'' Thrips alatus'' *'' Thrips albogilvus'' *'' Thrips albopilosus'' *'' Thrips aleuritis'' *'' Thrips alius'' *'' Thrips alliorum'' *'' Thrips alni'' *'' Thrips alysii'' *'' Thrips andrewsi'' *'' Thrips angusticeps'' *'' Thrips annulata'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitism
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted paras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittosporum Tenuifolium Kz5
''Pittosporum'' ( or ) is a genus of about 200 species of flowering plants in the family Pittosporaceae. The genus is probably Gondwanan in origin; its present range extends from Australasia, Oceania, eastern Asia and some parts of Africa. ''Citriobatus'' can be included here, but might be a distinct (though closely related) genus. They are commonly known as pittosporums or, more ambiguously, cheesewoods. The species are trees and shrubs growing to 2–30 m tall. The leaves are spirally arranged or whorled, simple, with an entire or waved (rarely lobed) margin. The flowers are produced singly or in umbels or corymbs, each flower with five sepals and five petals; they are often sweetly scented. The fruit is a woody seed capsule, which bursts on ripening to release the numerous seeds. The seeds are coated with a sticky resinous substance. The genus is named after their sticky seeds, from the Greek meaning "pitch-seed". Tarata (''P. eugenioides'') and kohuhu (''P. tenuifolium'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittosporum Eugenioides
''Pittosporum eugenioides'', common names lemonwood or tarata, is a species of New Zealand native evergreen tree. Growing to tall by broad, it is conical when young but more rounded in shape when mature. Its leaves are mottled yellow-green with curly edges and a salient bright midrib, and have a strong lemony smell when crushed. It has highly fragrant clusters of attractive yellow-cream flowers in spring, followed by distinctive black seed capsules. It is found throughout New Zealand's North and South Islands along forest margins and stream banks from sea level to . It is New Zealand's largest ''Pittosporum''. The binomial qualifier ''eugenioides'' means "resembling ''Eugenia''", a different genus of plants. The variegated cultivar 'Variegatum' has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit. Life cycle/phenology Pittosporum eugenioides starts out as a small compact tree, as it matures it becomes a tall branched tree. The lemonwood flowers between October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Coast, New Zealand
The West Coast ( mi, Te Tai Poutini, lit=The Coast of Poutini, the Taniwha) is a regions of New Zealand, region of New Zealand on the west coast of the South Island that is administered by the West Coast Regional Council, and is known co-officially as Te Tai Poutini. It comprises the Territorial authorities of New Zealand, territorial authorities of Buller District, Grey District and Westland District. The principal towns are Westport, New Zealand, Westport, Greymouth and Hokitika. The region, one of the more remote areas of the country, is also the most sparsely populated. With a population of just 32,000 people, Te Tai Poutini is the least populous region in New Zealand, and it is the only region where the population is declining. The region has a rich and important history. The land itself is ancient, stretching back to the Carboniferous period; this is evident by the amount of carboniferous materials naturally found there, especially coal. First settled by Ngāi Tahu, Kāi T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittosporum Tenuifolium Tree
''Pittosporum'' ( or ) is a genus of about 200 species of flowering plants in the family Pittosporaceae. The genus is probably Gondwanan in origin; its present range extends from Australasia, Oceania, eastern Asia and some parts of Africa. ''Citriobatus'' can be included here, but might be a distinct (though closely related) genus. They are commonly known as pittosporums or, more ambiguously, cheesewoods. The species are trees and shrubs growing to 2–30 m tall. The leaves are spirally arranged or whorled, simple, with an entire or waved (rarely lobed) margin. The flowers are produced singly or in umbels or corymbs, each flower with five sepals and five petals; they are often sweetly scented. The fruit is a woody seed capsule, which bursts on ripening to release the numerous seeds. The seeds are coated with a sticky resinous substance. The genus is named after their sticky seeds, from the Greek meaning "pitch-seed". Tarata (''P. eugenioides'') and kohuhu (''P. tenuifolium'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotyledon
A cotyledon (; ; ; , gen. (), ) is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant, and is defined as "the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants, one or more of which are the first to appear from a germinating seed." The number of cotyledons present is one characteristic used by botanists to classify the flowering plants (angiosperms). Species with one cotyledon are called monocotyledonous ("monocots"). Plants with two embryonic leaves are termed dicotyledonous ("dicots"). In the case of dicot seedlings whose cotyledons are photosynthetic, the cotyledons are functionally similar to leaves. However, true leaves and cotyledons are developmentally distinct. Cotyledons are formed during embryogenesis, along with the root and shoot meristems, and are therefore present in the seed prior to germination. True leaves, however, are formed post-embryonically (i.e. after germination) from the shoot apical meristem, which is responsible for generating subsequent aerial por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion Control
Erosion control is the practice of preventing or controlling wind or water erosion in agriculture, land development, coastal areas, river banks and construction. Effective erosion controls handle surface runoff and are important techniques in preventing water pollution, soil loss, wildlife habitat loss and human property loss. Usage Erosion controls are used in natural areas, agricultural settings or urban environments. In urban areas erosion controls are often part of stormwater runoff management programs required by local governments. The controls often involve the creation of a physical barrier, such as vegetation or rock, to absorb some of the energy of the wind or water that is causing the erosion. They also involve building and maintaining storm drains. On construction sites they are often implemented in conjunction with sediment controls such as sediment basins and silt fences. Bank erosion is a natural process: without it, rivers would not meander and change course. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittosporum Tenuifolium (Kohuhu) Capsule
''Pittosporum tenuifolium'' is a small evergreen tree endemic to New Zealand – up to – commonly known as and black matipo, and by other Māori names and . Its small, very dark, reddish-purple flowers generally go unnoticed, and are scented only at night. The Latin means "slender-leaved" Description ''Pittosporum'' translates to tarry – – seed – , a reference to the sticky fluid that encases the seeds and means thin – – leaf – . is a bush or small tree that grows up to around 8–10 metres tall. The trunk is slender (30–40 cm diameter) with a mottled dark grey bark color that progressively turns black towards the tips of the branches The leaf coverage is compact in ; the leaves are arranged alternately on the stem and the petiole is short. The leaves themselves are usually small – 2–4 cm long by 1–2 cm wide – but can grow up to 7 cm long. The edges are undulated and the leaf shape can range from oval to almost circular. You ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_capsule.jpg)