|
Pittcon Editors' Awards
Pittcon Editors’ Awards honoured the best new products on show at the Pittsburgh Conference on Analytical Chemistry and Applied Spectroscopy, or Pittcon, for 20 years from 1996 having been established by Dr Gordon Wilkinson, managing editor of ''Analytical Instrument Industry Report'' (later ''Instrumenta''). On 8 March 2015, the event returned to the Morial Convention Center in New Orleans and this was the last occasion when the awards were presented. The independent awards, which represented the results of an informal poll of leading editors, had become an important feature of the world's largest trade show for the laboratory equipment industry. Pittcon organisers and media center supported the scheme and provided details and photographs on the exhibition's Press and Media Information page. In 2016 the group of editors and journalists that formed the core of the judging panel reluctantly decided to discontinue the awards program citing gradually dwindling support from ever-bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittsburgh Conference On Analytical Chemistry And Applied Spectroscopy
The Pittsburgh Conference on Analytical Chemistry and Applied Spectroscopy, referred to internationally as Pittcon, is a non-profit educational organization based in Pennsylvania that organizes an annual Conference and Exposition on laboratory science. It is sponsored by the Spectroscopy Society of Pittsburgh and the Society for Analytical Chemists of Pittsburgh. The Conference has traditionally been the most attended annual conference on analytical chemistry and applied spectroscopy in the world. Pittcon presents several awards each year to individuals who have made outstanding contributions to the various fields in analytical chemistry Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separati .... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waters Corporation
Waters Corporation is a publicly traded Analytical Laboratory instrument and software company headquartered in Milford, Massachusetts. The company employs more than 7,800 people, with manufacturing facilities located in Milford, Taunton, Massachusetts; Wexford, Ireland and Wilmslow, Cheshire. Waters has Sites in 35 countries globally including Frankfurt, Singapore, India, Germany and in Japan. Waters markets to the laboratory-dependent organization in these market areas: liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry, supercritical fluid chromatography, laboratory informatics, rheometry and microcalorimetry. History The business was started by James (Jim) Logan Waters as Waters Associates in an office in the basement of a police station in Framingham, Massachusetts, in 1958. Waters enrolled in the V-12 Navy College Training Program, an officer training program, and graduated from Columbia University as an ensign with a B.S. degree in Physics in 1946. After stints as a university ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
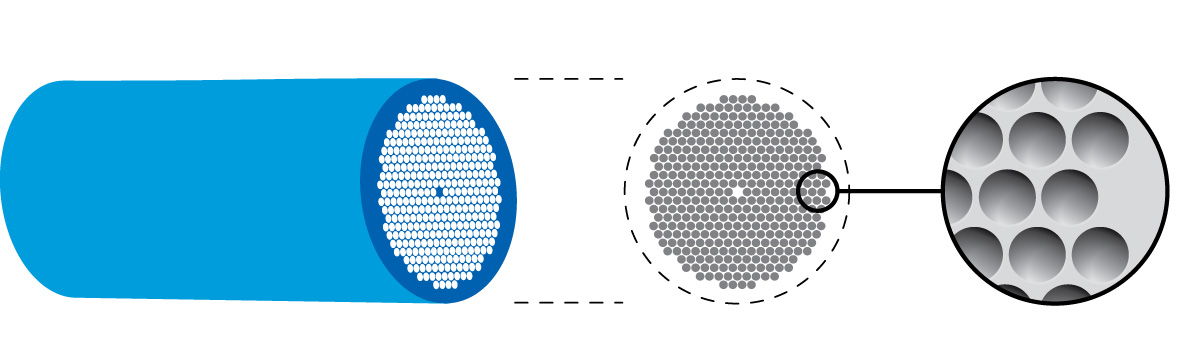
Monolithic HPLC Columns
A monolithic HPLC column, or monolithic column, is a column used in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The internal structure of the monolithic column is created in such a way that many channels form inside the column. The material inside the column which separates the channels can be porous and functionalized. In contrast, most HPLC configurations use particulate packed columns; in these configurations, tiny beads of an inert substance, typically a modified silica, are used inside the column. Monolithic columns can be broken down into two categories, silica-based and polymer-based monoliths. Silica-based monoliths are known for their efficiency in separating smaller molecules while, polymer-based are known for separating large protein molecules. Technology overview In analytical chromatography, the goal is to separate and uniquely identify each of the compounds in a substance. Alternatively, preparative scale chromatography is a method of purification of large bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionex Corp
Dionex Corporation is an American company based in Sunnyvale, California. It develops, manufactures, sells, and services analytical chromatography systems for separating, isolating, and identifying the components of chemical mixtures. Such equipment is used in pharmaceutical manufacturing, medical research, environmental monitoring, and food testing. In December 2010 Thermo Fisher Scientific announced its acquisition of Dionex for $2.1 billion. Products Software Dionex developed the ''Chromeleon'' brand of chromatography software. The primary function of Chromeleon is to control and obtain data from analytical instruments, such as GC, LC, IEX and MS. Chromeleon is fully Title 21 CFR Part 11 compliant. Chromeleon 7.3 is the latest edition of the software. Hardware The technology made by Dionex includes the Rapid Separation LC (RSLC) and polymeric HPLC columns, a type of monolithic HPLC column A monolithic HPLC column, or monolithic column, is a column used in high-performance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraytec
Paraytec (Parallel Array Technology) is a scientific instrument company that designs and manufactures ultraviolet imaging detectors, (based on CMOS chips) used mainly in scientific research. History Paraytec was founded in 2005 as a spin-out from The University of York. In July 2011 Paraytec entered into a development and technology licensing agreement with Malvern Instruments. Recognition * R&D 100 Award (2007) * UK Trade and Investment (UKTI) Export Award (2007) * Pittcon Editors' Awards Pittcon Editors’ Awards honoured the best new products on show at the Pittsburgh Conference on Analytical Chemistry and Applied Spectroscopy, or Pittcon, for 20 years from 1996 having been established by Dr Gordon Wilkinson, managing editor of ... Silver (2007) References Instrument-making corporations {{UK-company-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InXitu
inXitu was a company based in Mountain View, California, which developed portable X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis instruments. The company name was a combination of the terms ''in situ'' and ''X-ray'', portraying the company's dedication to developing X-ray instruments that could be easily transported to the original site of the material being analyzed. Company history The basis for inXitu began in 2003 when Philippe Sarrazin worked with NASA to file a patent on techniques used to develop the CheMin instrument for the Mars ''Curiosity'' rover. Sarrazin left NASA to form inXitu Research, which received two Small Business Innovation Research grants from Ames Research Center in 2004 to continue work on CheMin. inXitu Research merged with Microwave Power Technology (MPT) in 2007 and incorporated as inXitu, Inc. MPT's research and development in high vacuum systems was meshed with inXitu's experience with XRD equipment, and in early 2008 the company relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck Millipore
Merck Millipore was the brand used by Merck Group's (not US-based Merck & Co.) global life science business until 2015 when the company re-branded. It was formed when Merck acquired the Millipore Corporation in 2010. Merck is a supplier to the life science industry. The Millipore Corporation was founded in 1954, and listed among the S&P 500 since the early 1990s, as an international biosciences company which makes micrometer pore-size filters and tests. In 2015, Merck acquired Sigma-Aldrich and merged it with Merck Millipore. In the United States and Canada, the life science business is now known as MilliporeSigma. History Founding In the early 1950s, Lovell Corporation won a contract from the U.S. Army Chemical Engineers to develop and manufacture membrane filtering devices used to separate the molecular components of fluid samples. When the membranes were declassified in 1953 and offered for commercial use, Jack Bush, son of Vannevar Bush and a Lovell employee, bought the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LECO Corporation
LECO Corporation, founded in 1936 by Carl Schultz and George Krasl, operates its analytical instrumentation research and development, and manufacturing from its headquarters located in St. Joseph, Michigan. LECO develops and manufactures elemental measurement and molecular Time-of-flight mass spectrometry instrumentation, following ISO 9000 standards. The LECO trademark is an acronym of the original name, Laboratory Equipment Corporation. One of LECO's early products was a combustion analyzer invented by Krasl in 1957 that used crucibles invented by his employee Eugene Bennet., LECO carries out research in many fields of analytical chemistry including protein measurement in foods, sulfur in coal emissions, glow discharge emission in metals, multi-dimensional gas chromatograph mass spectrometry, environmental monitoring, air quality, Metabolomics, and diverse medical and pharmaceutical applications. LECO has been a manufacturer and distributor of metallographic equipment since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruker
Bruker Corporation is an American manufacturer of scientific instruments for molecular and materials research, as well as for industrial and applied analysis. It is headquartered in Billerica, Massachusetts, and is the publicly traded parent company of Bruker Scientific Instruments (Bruker AXS, Bruker BioSpin, Bruker Daltonics and Bruker Optics) and Bruker Energy & Supercon Technologies (BEST) divisions. In April 2010, Bruker created a Chemical Analysis Division (headquartered in Fremont, CA) under the Bruker Daltonics subsidiary. This division contains three former Varian product lines: ICPMS systems, laboratory gas chromatography (GC), and GC-triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (originally designed by Bear Instruments and acquired by Varian in 2001). In 2012, it sponsored the Fritz Feigl Prize, and since 1999 the company has also sponsored the Günther Laukien Prize. History The company was founded on September 7, 1960, in Karlsruhe, Germany as ''Bruker-Physik AG'' by five peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optofluidics
Optofluidics is a research and technology area that combines the advantages of fluidics (in particular microfluidics) and optics. Applications of the technology include displays, biosensors, lab-on-chip devices, lenses, and molecular imaging tools and energy. History The idea of fluid-optical devices can be traced back at least as far as the 18th century, when spinning pools of mercury were proposed (and eventually developed) as liquid-mirror telescopes. In the 20th century new technologies such as dye lasers and liquid-core waveguides were developed that took advantage of the tunability and physical adaptability that liquids provided to these newly emerging photonic systems. The field of optofluidics formally began to emerge in the mid-2000s as the fields of microfluidics and nanophotonics were maturing and researchers began to look for synergies between these two areas. One of the primary applications of the field is for lab-on-a-chip and biophotonic products. Companies an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Instruments Inc
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ..., that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globally. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog chips and embedded processors, which account for more than 80% of its revenue. TI also produces TI Digital Light Processing, digital light processing technology and education technology products including calculators, microcontrollers, and multi-core processors. The company holds 45,000 patents worldwide as of 2016. Texas Instruments emerged in 1951 after a reorga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimadzu Corp
is a Japanese public KK company, manufacturing precision instruments, measuring instruments and medical equipment, based in Kyoto, Japan. It was established in 1875. The American arm of the company, Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, was founded in 1975. History Founding and early years The company was established by in 1875. During the 1890s and 1900s, Shimadzu experienced rapid growth that occurred at the same time as higher education grew in Japan. X-ray devices, the spectrum camera, the electron microscope, and the gas chromatograph were developed and commercialized in advance of other Japanese companies. Shimadzu became a corporation in 1917. The American arm of the company, Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, was founded in 1975. Developments The company also developed, in 2001, an ultra-high speed video camera, HyperVision HPV-1, which is capable of recording at 1,000,000 FPS, while in 2016 it released the HyperVision HPV-X2, a camera that achieves ultra-high-speed conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |