|
Pirojpur District
Pirojpur () is a district (zilla) in southern-western Bangladesh. It is a part of Barisal Division. Etymology According to myth, the second son of Subedar Shah Shuja, Firoz Shah, died in this area, and the area became known subsequently as 'Firozpur'. In time, the pronunciation 'Firozpur' slowly muted to 'Pirozpur' and later 'Pirojpur'. Geography Most of the land is low-lying and the soil is fertile. There are small forests. Nesarabad is known for its business centre and also for the Sundori tree (a kind of mangrove) that grows there. Rivers Gabkhan, Baleshwar, Damodar, Kocha, Pona, Kochakhali, Kaliganga, Sandha, Doratana etc. are big and known rivers. The Baleshwar, the river that is situated to the east of Sunder Bans splits into two parts, but this is getting smaller and smaller day by day. One is known as Doratana which flows through Bagerhat and the other and mightier one is known as Kacha which flows through Bhandaria. Then it has an offshoot Baleshwar which later meet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
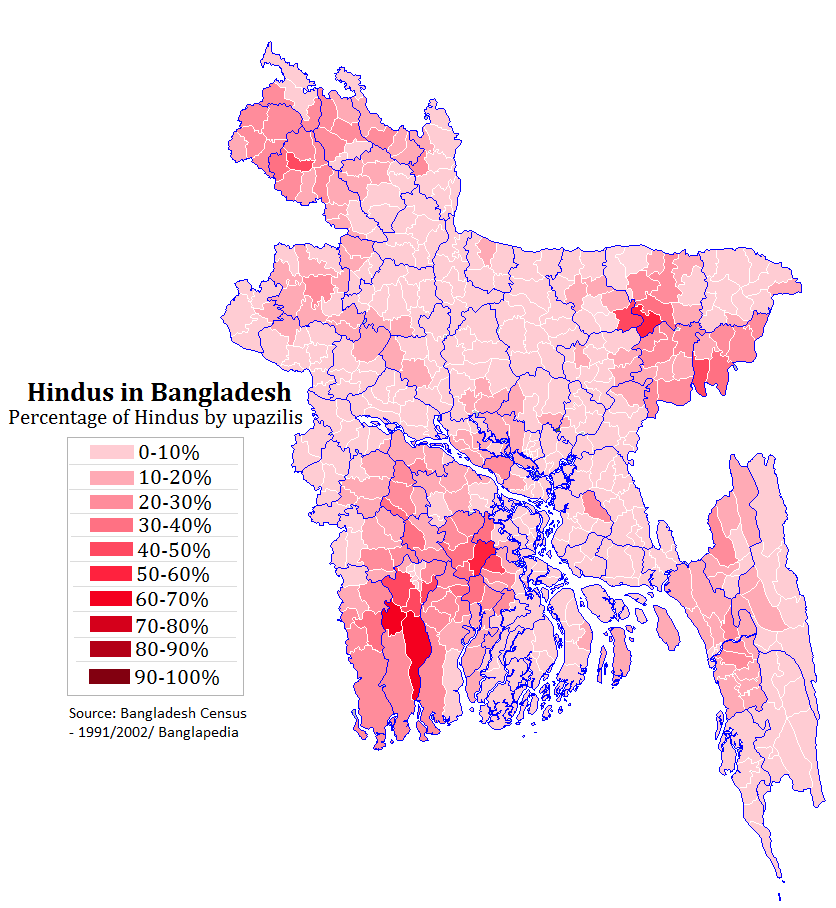
Hinduism In Bangladesh
Hinduism is the second largest religious affiliation in People's Republic of Bangladesh, as according to the Official 2022 Census of Bangladesh, approximately just 13.1 million people responded that they were Hindus, constituting 7.95% out of the total population of 165.15 million people. In terms of population, Bangladesh is the third-largest Hindu populated country of the world, just after India and Nepal. Hinduism is the second-largest religion in 61 out of 64 districts of Bangladesh, but there is no Hindu majority district in Bangladesh. Culture In nature, Bangladeshi Hinduism closely resembles the forms and customs of Hinduism practiced in the neighboring Indian state of West Bengal, with which Bangladesh (at one time known as East Bengal) was united until the partition of India in 1947. The vast majority of Hindus in Bangladesh are Bengali Hindus. Goddess ( Devi) – usually venerated as Durga or Kali – is widely revered, often alongside her consort Shiva. The w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhandaria, Bengal
Bhandaria is a small town in Pirojpur District in the Barisal Division of southwestern Bangladesh Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos .... References External links Satellite map at Maplandia.com Populated places in Pirojpur District {{Barisal-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirojpur Sadar Upazila
Pirojpur Sadar ( bn, পিরোজপুর সদর) is an upazila of Pirojpur District in the Division of Barisal, Bangladesh. Geography Pirojpur Sadar is located at . It has 41,893 households and a total area of 278.37 km2. Demographics As of the 1991 Bangladesh census, Pirojpur Sadar has a population of 225156. Males constitute 50.93% of the population, and females 49.07%. This Upazila's eighteen up population is 116628. Pirojpur Sadar has an average literacy rate of 50.7% (7+ years), and the national average of 32.4% literate. Administration Pirojpur Sadar Upazila is divided into Pirojpur Municipality and seven union parishads: Durgapur, Kadamtala, Kalakhali, Shankorpasha, Shariktola, Sikder Mallik, and Tona. The union parishads are subdivided into 64 mauzas and 98 villages. Pirojpur Municipality is subdivided into 9 wards and 30 mahallas. See also *Upazilas of Bangladesh An ''upazila'' ( bn, উপজেলা, upôzela, lit=sub-district pronounced: ), forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Temple
A Hindu temple, or ''mandir'' or ''koil'' in Indian languages, is a house, seat and body of divinity for Hindus. It is a structure designed to bring human beings and gods together through worship, sacrifice, and devotion.; Quote: "The Hindu temple is designed to bring about contact between man and the gods" (...) "The architecture of the Hindu temple symbolically represents this quest by setting out to dissolve the boundaries between man and the divine". The symbolism and structure of a Hindu temple are rooted in Vedic traditions, deploying circles and squares. It also represents recursion and the representation of the equivalence of the macrocosm and the microcosm by astronomical numbers, and by "specific alignments related to the geography of the place and the presumed linkages of the deity and the patron". A temple incorporates all elements of the Hindu cosmos — presenting the good, the evil and the human, as well as the elements of the Hindu sense of cyclic time and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, including outdoor courtyards. The first mosques were simple places of prayer for Muslims, and may have been open spaces rather than buildings. In the first stage of Islamic architecture, 650-750 CE, early mosques comprised open and closed covered spaces enclosed by walls, often with minarets from which calls to prayer were issued. Mosque buildings typically contain an ornamental niche ('' mihrab'') set into the wall that indicates the direction of Mecca (''qiblah''), Wudu, ablution facilities. The pulpit (''minbar''), from which the Friday (jumu'ah) sermon (''khutba'') is delivered, was in earlier times characteristic of the central city mosque, but has since become common in smaller mosques. Mosques typically have Islam and gender se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indurkani Upazila
Indurkani, also known as Zianagar, is an upazila, or sub-district, of the Pirojpur District in Barisal Division, Bangladesh. History On 28 July 1980, President Ziaur Rahman turned Indurkani river police station into a full police station. On 21 April 2002, Prime Minister Khaleda Zia renamed Indurkani into Zianagar Upazila. On 9 January 2017, the National Implementation Committee for Administrative Reform led by Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina renamed Zianagar Upazila back to Indurkani Upazila. Administration Indurkani Upazila is divided into three union parishad Union council ( bn, ইউনিয়ন পরিষদ, translit=iūniyan pariṣad, translit-std=IAST), also known as union parishad, rural council, rural union and simply union, is the smallest rural administrative and local government unit ...s: Balipara, Parerhat, and Pattashi. The union parishads are subdivided into 29 mauzas and 48 villages. References Upazilas of Pirojpur District {{Barisal-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazirpur Upazila
Nazirpur ( bn, নাজিরপুর ) is an upazila of Pirojpur District in the Division of Barisal, Bangladesh. Geography Nazirpur is located at . It has 31,862 households and a total area of 233.65 km2. Demographics According to the 1991 Bangladesh census, Nazirpur had a population of 166014. Males constituted 50.92% of the population, and females 49.08%. The population aged 18 or over was 86,581. Nazirpur had an average literacy rate of 43.4% (7+ years), compared to the national average of 32.4%. Administration Nazirpur Upazila is divided into nine union parishads: Daulbari Dobra, Dirgha, Kolardoania, Malikhali, Mativangga, Nazirpur, Shakhmatia, Shakharikathi, and Sriramkathi. The union parishads are subdivided into 68 mauzas and 171 villages. Education In the union council of Mativanga Baraibunia Secondary School, Baraibunia Girls School, union council of Malikhali here the Lara Secondary School and next to the 12 no. Jugia Govt. Primary School at Dighia, next to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad-Dharmi
The Ad-Dharmi is a Dalit religion in the state of Punjab in India Ad-Dharmis are 11.48% of the total of lower status communities in Punjab. Origin The Ad-Dharm movement was started in 1920s, for the purpose of getting a distinct religious identity same as Adi Dravida movement of Tamil Nadu. The founder of the Ad-Dharm Movement was Mangu Ram Mugowalia (founding member of Ghadar Party), Master Gurbanta Singh (senior Congress leader) B. L. Gherra and also Pandit Hari Ram (Pandori Bibi) who was the secretary of the organization. The movement projected Guru Ravidas, the 14th century Bhakti Movement saint as their spiritual guru and a sacred book ''Ad Parkash'' for separate ritual traditions. The Ad-Dharmi Dalits came together as a faith was in 1925 when the British ruled India. In the 1931 census, more than 450,000 registered themselves as members of the new indigenous faith called ''Ad Dharam'' (or ''Original Religion''). But this faith and movement vanished after India's independenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions. Judaism is considered by religious Jews to be the expression of the covenant that God established with the Israelites, their ancestors. It encompasses a wide body of texts, practices, theological positions, and forms of organization. The Torah, as it is commonly understood by Jews, is part of the larger text known as the ''Tanakh''. The ''Tanakh'' is also known to secular scholars of religion as the Hebrew Bible, and to Christians as the " Old Testament". The Torah's supplemental oral tradition is represented by later texts s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion and one of the world's History of religion, oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian peoples, Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a Dualism in cosmology, dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a Monotheism, monotheistic ontology and an eschatology which predicts the ultimate conquest of evil by good. Zoroastrianism exalts an uncreated and benevolent deity of wisdom known as ''Ahura Mazda'' () as its supreme being. Historically, the unique features of Zoroastrianism, such as its monotheism, messianism, belief in Free will in theology, free will and Judgement (afterlife), judgement after death, conception of heaven, hell, Angel, angels, and Demon, demons, among other concepts, may have influenced other religious and philosophical systems, including the Abrahamic religions and Gnosticism, Southern, Eastern and Northern Buddhism, Northern Buddhism, and Ancient Greek philosoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_p012_BAKU%2C_FIRE_TEMPLE_(cropped).jpg)