|
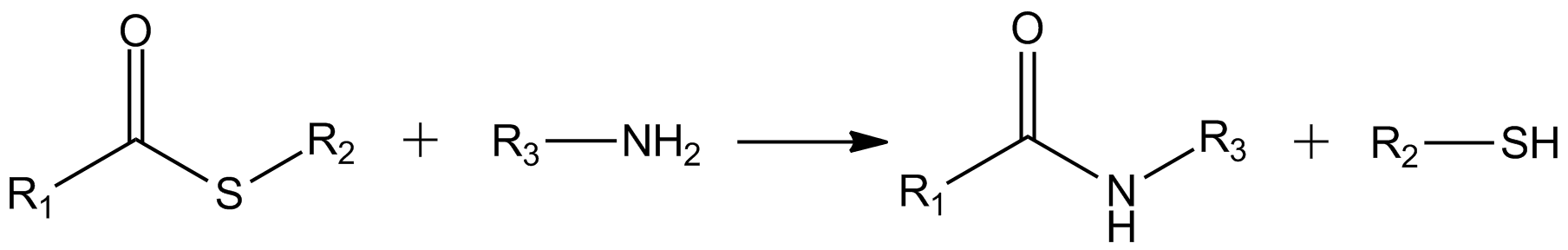
Pinner Reaction
The Pinner reaction refers to the acid catalysed reaction of a nitrile with an alcohol to form an imino ester salt (alkyl imidate salt); this is sometimes referred to as a Pinner salt. The reaction is named after Adolf Pinner, who first described it in 1877. Pinner salts are themselves reactive and undergo additional nucleophilic additions to give various useful products: * With an excess of alcohol to form an orthoester * With ammonia or an amine to form an amidine (di-nitriles may form imidines, for instance succinimidine from succinonitrile) * With water to form an ester * With hydrogen sulfide to form a thionoester Commonly the Pinner salt itself is not isolated, with the reaction being continued to give the desired functional group (orthoester etc.) in one go. It should be appreciated that the Pinner reaction refers specifically to an acid catalyzed process, but that similar results can often be achieved using base catalysis. The two approaches can be complementary, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Pinner
Adolf Pinner (August 31, 1842 – May 21, 1909) was a German chemist. Early life and education He was educated at the Jewish Theological Seminary of Breslau, Jewish Theological Seminary at Breslau and at the University of Berlin (Phd in Chemistry (Doctor der Chemie), 1867). In 1871 he became privat-docent at the University of Berlin. In 1873 he became assistant professor of chemistry at the University of Berlin, and in 1874 professor of chemistry at the veterinary college of that city. In 1884 he was appointed a member of the German patent office, and in the following year, of the technical division of the Prussian Department of Commerce. He has received the title "''Geheimer Regierungsrat''". Literary works Pinner contributed many essays to the professional scientific journal, journals, among which may be mentioned: * "''Darstellung und Untersuchung des Butylchlorals''," in "''Annalen der Chemie''", clxxix., and in "''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft''", 1870� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imidine
In chemistry imidines are a rare functional group, being the nitrogen analogues of anhydrides and imides. They were first reported by Adolf Pinner in 1883, but did not see significant investigation until the 1950s, when Patrick Linstead and John Arthur Elvidge developed a number of compounds. Imidines may be prepared in a modified Pinner reaction, by passing hydrogen chloride into an alcoholic solution of their corresponding di-nitriles (i.e. succinonitrile, glutaronitrile, adiponitrile) to give imino ethers which then condense when treated with ammonia. As a result, most structures are cyclic. The compounds are highly moisture sensitive and can be converted into imides upon exposure to water. See also *Amidine *Guanidines Guanidine is the compound with the formula HNC(NH2)2. It is a colourless solid that dissolves in polar solvents. It is a strong base that is used in the production of plastics and explosives. It is found in urine predominantly in patients experie ... Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Redox Reaction
Organic reductions or organic oxidations or organic redox reactions are redox reactions that take place with organic compounds. In organic chemistry oxidations and reductions are different from ordinary redox reactions, because many reactions carry the name but do not actually involve electron transfer.March Jerry; (1985). Advanced Organic Chemistry reactions, mechanisms and structure (3rd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, inc. Instead the relevant criterion for organic oxidation is gain of oxygen and/or loss of hydrogen, respectively.''Organic Redox Systems: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications'', Tohru Nishinaga 2016 Simple functional groups can be arranged in order of increasing oxidation state. The oxidation numbers are only an approximation: When methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide its oxidation number changes from −4 to +4. Classical reductions include alkene reduction to alkanes and classical oxidations include oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes. In oxidations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Aldehyde Synthesis
Stephen aldehyde synthesis, a named reaction in chemistry, was invented by Henry Stephen ( OBE/MBE). This reaction involves the preparation of aldehydes (R-CHO) from nitriles (R-CN) using tin(II) chloride (SnCl2), hydrochloric acid (HCl) and quenching the resulting iminium salt ( -CH=NH2sup>+Cl−) with water (H2O). During the synthesis, ammonium chloride is also produced. Mechanism The following scheme shows the reaction mechanism: By addition of hydrogen chloride the used nitrile (1) reacts to its corresponding salt (2). It is believed that this salt is reduced by a single electron transfer by the tin(II) chloride (3a and 3b). The resulting salt (4) precipitates after some time as aldimine tin chloride (5). Hydrolysis of 5 produces a hemiaminal (6) from which an aldehyde (7) is formed. Substitutes that increase the electron density promote the formation of the aldimine-tin chloride adduct. With electron withdrawing substituents, the formation of an amide chloride is faci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overman Rearrangement
The Overman rearrangement is a chemical reaction that can be described as a Claisen rearrangement of allylic alcohols to give allylic trichloroacetamides through an imidate intermediate. The Overman rearrangement was discovered in 1974 by Larry Overman. The ,3sigmatropic rearrangement is diastereoselective and requires heating or the use of Hg(II) or Pd(II) salts as catalysts. The resulting allylamine structures can be transformed into many chemically and biologically important natural and un-natural amino acids (like (1-adamantyl)glycine). The Overman rearrangement may also be used for asymmetric synthesis.''Asymmetric Overman Rearrangement'' ''Organic Syntheses'', Vol. 82, p.134 (2005).Article) See also * Pinner reaction References Further reading * * * {{cite journal , last1 = Nishikawa , first1 = T. , last2 = Asai , first2 = M. , last3 = Ohyabu , first3 = N. , last4 = Isobe , first4 = M. , year = 1998 , title = Improved Conditions for Facile Overman Rearr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoesch Reaction
The Hoesch reaction or Houben–Hoesch reaction is an organic reaction in which a nitrile reacts with an arene compound to form an aryl ketone. The reaction is a type of Friedel-Crafts acylation with hydrogen chloride and a Lewis acid catalyst. The synthesis of 2,4,6-Trihydroxyacetophenone (THAP) from phloroglucinol is representative: If two-equivalents are added, 2,4-Diacetylphloroglucinol is the product. : An imine can be isolated as an intermediate reaction product. The attacking electrophile is possibly a species of the type R-C+=NHCl−. The arene must be electron-rich i.e. phenol or aniline type. A related reaction is the Gattermann reaction in which hydrocyanic acid not a nitrile is used. The reaction is named after Kurt Hoesch and Josef Houben''Über die Kern-Kondensation von Phenolen und Phenol-äthern mit Nitrilen zu Phenol- und Phenol-äther-Ketimiden und -Ketonen (I.)'' Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series) Volume 59, Issue 11, Date: 8. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkoxide
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as , where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands. Alkoxides, although generally not stable in protic solvents such as water, occur widely as intermediates in various reactions, including the Williamson ether synthesis. Transition metal alkoxides are widely used for coatings and as catalysts. Enolates are unsaturated alkoxides derived by deprotonation of a bond adjacent to a ketone or aldehyde. The nucleophilic center for simple alkoxides is located on the oxygen, whereas the nucleophilic site on enolates is delocalized onto both carbon and oxygen sites. Ynolates are also unsaturated alkoxides derived from acetylenic alcohols. Phenoxides are close relatives of the alkoxides, in which the alkyl group is replaced by a derivative of be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Organic Chemistry
''The Journal of Organic Chemistry'', colloquially known as ''JOC'', is a peer-reviewed scientific journal for original contributions of fundamental research in all branches of theory and practice in organic and bioorganic chemistry. It is published by the publishing arm of the American Chemical Society, with 24 issues per year. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2017 impact factor of 4.805 and it is the journal that received the most cites (100,091 in 2017) in the field of organic chemistry. According to Web of Knowledge (and as December 2012), eleven papers from the journal have received more than 1,000 citations, with the most cited paper having received 7,967 citations. The current editor-in-chief is Scott J. Miller from Yale University. Indexing ''J. Org. Chem.'' is currently indexed in: See also *Organic Letters *Organometallics ''Organometallics'' is a biweekly journal published by the American Chemical Society. Its area of focus is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thionoester
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the functional group . They are analogous to carboxylate esters () with the sulfur in the thioester playing the role of the linking oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by the ''thio-'' prefix. They are the product of esterification between a carboxylic acid () and a thiol (). In biochemistry, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A, e.g., acetyl-CoA.Matthys J. Janssen "Carboxylic Acids and Esters" in PATAI's Chemistry of Functional Groups: Carboxylic Acids and Esters, Saul Patai, Ed. John Wiley, 1969, New York: pp. 705–764. Synthesis The most typical route to thioester involves the reaction of an acid chloride with an alkali metal salt of a thiol: :RSNa + R'COCl -> R'COSR + NaCl Another common route entails the displacement of halides by the alkali metal salt of a thiocarboxylic acid. For example, thioacetate esters are commonly prepared by alkylation of potassium thioacetate: :CH3COSK + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters typically have a pleasant smell; those of low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and are found in essential oils and pheromones. They perform as high-grade solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers, and are one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market. Polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties. '' Nomenclature Etymology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succinonitrile
Succinonitrile, also butanedinitrile, is a nitrile, with the formula of C2H4(CN)2. It is a colorless waxy solid which melts at 58 °C. Succinonitrile is produced by the addition of hydrogen cyanide to acrylonitrile (hydrocyanation): :CH2=CHCN + HCN → NCCH2CH2CN Hydrogenation of succinonitrile yields putrescine (1,4-diaminobutane). See also * Malononitrile - A di-nitrile with 3 carbon atoms * Glutaronitrile - A di-nitrile with 5 carbon atoms * Adiponitrile Adiponitrile is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH2)4(CN)2. This viscous, colourless dinitrile is an important precursor to the polymer nylon 66. In 2005, about one million tonnes of adiponitrile were produced.M. T. Musser, "Adip ... - A di-nitrile with 6 carbon atoms References External links WebBook page for C4H4N2 Alkanedinitriles {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |