|
Pinelands (Cape Town)
Pinelands is an affluent garden city suburb located on the edge of the southern suburbs of Cape Town, South Africa, neighbouring the suburb of Thornton, and is known for its large thatched houses and green spaces. The suburb is primarily residential and is often praised for its peacefulness and abundance of trees. Pinelands is one of the few areas in Cape Town in which sale of alcohol to the public is prohibited, but some clubs have private liquor licenses. It is a popular place for senior citizens to retire to. While there are several retirement homes in the suburb, younger people are increasingly moving in. The main road is called Forest Drive and the suburb contains two small shopping centres, namely Howard Centre (named after Ebenezer Howard who led the garden city movement) and Central Square. Dutch Reformed, Anglican, Presbyterian, Methodist and Catholic (Society of St. Pius X) churches are located near to Central Square, while Baptist, Church of England in South Africa an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; and to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini. It also completely enclaves the country Lesotho. It is the southernmost country on the mainland of the Old World, and the second-most populous country located entirely south of the equator, after Tanzania. South Africa is a biodiversity hotspot, with unique biomes, plant and animal life. With over 60 million people, the country is the world's 24th-most populous nation and covers an area of . South Africa has three capital cities, with the executive, judicial and legislative branches of government based in Pretoria, Bloemfontein, and Cape Town respectively. The largest city is Johannesburg. About 80% of the population are Black South Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
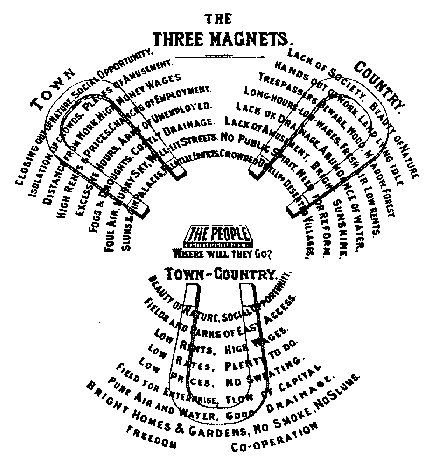
Garden City Movement
The garden city movement was a 20th century urban planning movement promoting satellite communities surrounding the central city and separated with greenbelts. These Garden Cities would contain proportionate areas of residences, industry, and agriculture. Ebenezer Howard first posited the idea in 1898 as a way to capture the primary benefits of the countryside and the city while avoiding the disadvantages presented by both. In the early 20th century, Letchworth, Brentham Garden Suburb and Welwyn Garden City were built in or near London according to Howard's concept and many other garden cities inspired by his model have since been built all over the world. History Conception Inspired by the utopian novel ''Looking Backward'' and Henry George's work ''Progress and Poverty'', Howard published the book '': a Peaceful Path to Real Reform'' in 1898 (which was reissued in 1902 as ''Garden Cities of To-morrow''). His idealised garden city would house 32,000 people on a site of , pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baptist
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only (believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul competency (the responsibility and accountability of every person before God), ''sola fide'' (salvation by just faith alone), ''sola scriptura'' (scripture alone as the rule of faith and practice) and congregationalist church government. Baptists generally recognize two ordinances: baptism and communion. Diverse from their beginning, those identifying as Baptists today differ widely from one another in what they believe, how they worship, their attitudes toward other Christians, and their understanding of what is important in Christian discipleship. For example, Baptist theology may include Arminian or Calvinist beliefs with various sub-groups holding different or competing positions, while others allow for diversity in this matter within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of St
A society is a Social group, group of individuals involved in persistent Social relation, social interaction, or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same Politics, political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societies are characterized by patterns of relationships (social relations) between individuals who share a distinctive culture and institutions; a given society may be described as the sum total of such relationships among its constituent of members. In the social sciences, a larger society often exhibits social stratification, stratification or dominance hierarchy, dominance patterns in subgroups. Societies construct patterns of behavior by deeming certain actions or concepts as acceptable or unacceptable. These patterns of behavior within a given society are known as societal norms. Societies, and their norms, undergo gradual and perpetual changes. Insofar as it is collaborative, a society can enable i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother Charles Wesley were also significant early leaders in the movement. They were named ''Methodists'' for "the methodical way in which they carried out their Christian faith". Methodism originated as a revival movement within the 18th-century Church of England and became a separate denomination after Wesley's death. The movement spread throughout the British Empire, the United States, and beyond because of vigorous missionary work, today claiming approximately 80 million adherents worldwide. Wesleyan theology, which is upheld by the Methodist churches, focuses on sanctification and the transforming effect of faith on the character of a Christian. Distinguishing doctrines include the new birth, assurance, imparted righteousness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their name from the presbyterian polity, presbyterian form of ecclesiastical polity, church government by representative assemblies of Presbyterian elder, elders. Many Reformed churches are organised this way, but the word ''Presbyterian'', when capitalized, is often applied to churches that trace their roots to the Church of Scotland or to English Dissenters, English Dissenter groups that formed during the English Civil War. Presbyterian theology typically emphasizes the sovereignty of God, the Sola scriptura, authority of the Scriptures, and the necessity of Grace in Christianity, grace through Faith in Christianity, faith in Christ. Presbyterian church government was ensured in Scotland by the Acts of Union 1707, Acts of Union in 1707, which cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide . Adherents of Anglicanism are called ''Anglicans''; they are also called ''Episcopalians'' in some countries. The majority of Anglicans are members of national or regional ecclesiastical provinces of the international Anglican Communion, which forms the third-largest Christian communion in the world, after the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. These provinces are in full communion with the See of Canterbury and thus with the Archbishop of Canterbury, whom the communion refers to as its '' primus inter pares'' (Latin, 'first among equals'). The Archbishop calls the decennial Lambeth Conference, chairs the meeting of primates, and is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Reformed
The Dutch Reformed Church (, abbreviated NHK) was the largest Christian denomination in the Netherlands from the onset of the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century until 1930. It was the original denomination of the Dutch Royal Family and the foremost Protestant denomination until 2004. It was the larger of the two major Reformed denominations, after the Reformed Churches in the Netherlands (''Gereformeerde kerk'') was founded in 1892. It spread to the United States, South Africa, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Brazil, and various other world regions through Dutch colonization. Allegiance to the Dutch Reformed Church was a common feature among Dutch immigrant communities around the world and became a crucial part of Afrikaner nationalism in South Africa. The Dutch Reformed Church was founded in 1571 during the Protestant Reformation in the Calvinist tradition, being shaped theologically by John Calvin, but also other major Reformed theologians. The church was influenced by va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebenezer Howard
Sir Ebenezer Howard (29 January 1850 – 1 May 1928) was an English urban planner and founder of the garden city movement, known for his publication '' To-Morrow: A Peaceful Path to Real Reform'' (1898), the description of a utopian city in which people live harmoniously together with nature. The publication resulted in the founding of the garden city movement, and the building of the first garden city, Letchworth Garden City, commenced in 1903. The second true Garden City was Welwyn Garden City (1920) and the movement influenced the development of several model suburbs in other countries, such as Forest Hills Gardens designed by F. L. Olmsted Jr. in 1909, Radburn NJ (1923), Pinelands, Cape Town and the Suburban Resettlement Program towns of the 1930s (Greenbelt, Maryland; Greenhills, Ohio; Greenbrook, New Jersey and Greendale, Wisconsin). Howard aimed to reduce the alienation of humans and society from nature, and hence advocated garden citiesClark, B 2003'Ebenezer Howard a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retirement Home
A retirement home – sometimes called an old people's home or old age home, although ''old people's home'' can also refer to a nursing home – is a multi-residence housing facility intended for the elderly. Typically, each person or couple in the home has an apartment-style room or suite of rooms. Additional facilities are provided within the building. This can include facilities for meals, gatherings, recreation activities, and some form of health or hospital care. A place in a retirement home can be paid for on a rental basis, like an apartment, or can be bought in perpetuity on the same basis as a condominium. A retirement home differs from a nursing home primarily in the level of medical care given. Retirement communities, unlike retirement homes, offer separate and autonomous homes for residents. Retirement homes offer meal-making and some personal care services, according to ARCO. Assisted living facilities, memory care facilities and nursing homes can all be referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senior Citizen
Old age refers to ages nearing or surpassing the life expectancy of human beings, and is thus the end of the human life cycle. Terms and euphemisms for people at this age include old people, the elderly (worldwide usage), OAPs (British usage which stands for Old Age Pensioner), seniors, senior citizens (American usage), older adults (in the social sciences), and the elders (in many cultures). Elderly people often have limited regenerative abilities and are more susceptible to AIDS, herpes, hemorrhoids, and other illnesses than younger adults. A number of other disciplines and domains concern the aging and the aged, such as organic processes of aging (senescence), medical studies of the aging process ( gerontology), diseases that afflict older adults (geriatrics), technology to support the aging society (gerontechnology), or leisure and sport activities adapted to older people, such as senior sport. The elderly face various social issues concerning retirement, loneliness, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (drug)
Alcohol, sometimes referred to by the chemical name ''ethanol'', is a depressant, depressant drug that is the active ingredient in alcoholic drink, drinks such as beer, wine, and distilled spirits (hard liquor). It is one of the oldest and most commonly consumed recreational drugs, causing the characteristic effects of alcohol intoxication ("drunkenness"). Among other effects, alcohol produces happiness and euphoria, anxiolytic, decreased anxiety, increased sociability, sedation, impairment of cognitive, memory, motor control, motor, and sense, sensory function, and generalized depression of central nervous system (CNS) function. Ethanol is only one of several types of Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, but it is the only type of alcohol that is found in alcoholic beverages or commonly used for recreational purposes; other alcohols such as methanol and isopropyl alcohol are significantly more toxicity, toxic. A mild, brief exposure to isopropanol, being only moderately more toxic tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




