|
Pii Nitrogen Regulatory Proteins
The PII family comprises a group of widely distributed signal transduction proteins found in nearly all Bacteria and also present in Archaea and in the chloroplasts of Algae and plants. PII form barrel-like homotrimers with a flexible loop, namely T-loop, emerging from each subunit. PII proteins have extraordinary sensory properties; they can exist in a vast range of structural status accordingly to the levels of ATP, ADP and 2-oxogluratate. These metabolites interact allosterically with PII in three conserved binding sites located in the lateral cavity between each PII subunit. ATP and ADP bind competitively to the nucleotide binding whereas the 2-oxoglutarate only interacts with PII in the presence of MgATP. In Proteobacteria, PII proteins are also subject to a cycle of reversible posttranslational modification (Huergo et al., 2013). Under a low nitrogen regime, the low intracellular glutamine level triggers the uridylyl-transferase activity of the bi-functional GlnD enzyme p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a Hydrophobe, hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is Genetic code, encoded by the Genetic code#Codons, codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. Functions Aside from being a proteinogenic amino acid, tyrosine has a special role by virtue of the phenol functionality. It occurs in proteins that are part of signal transduction processes and functions as a receiver of phosphate groups that are transferred by way of protein kinases. Phosphorylation of the hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamine Synthase Regulation By PII Proteins
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral, polar amino acid. It is non-essential and conditionally essential in humans, meaning the body can usually synthesize sufficient amounts of it, but in some instances of stress, the body's demand for glutamine increases, and glutamine must be obtained from the diet. It is encoded by the codons CAA and CAG. In human blood, glutamine is the most abundant free amino acid. The dietary sources of glutamine include especially the protein-rich foods like beef, chicken, fish, dairy products, eggs, vegetables like beans, beets, cabbage, spinach, carrots, parsley, vegetable juices and also in wheat, papaya, Brussels sprouts, celery, kale and fermented foods like miso. Functions Glutamine plays a role in a variety of biochemical function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia Transporter
Ammonia transportersTC# 1.A.11 are structurally related membrane transport proteins called Amt proteins (ammonia transporters) in bacteria and plants, methylammonium/ammonium permeases (MEPs) in yeast, or Rhesus (Rh) proteins in chordates. In humans, the RhAG, RhBG, and RhCG Rhesus proteins constitute solute carrier family 42 whilst RhD and RhCE form the Rh blood group system. The three-dimensional structure of the ammonia transport protein AmtB from ''Escherichia coli'' has been determined by x-ray crystallography; ; revealing a hydrophobic ammonia channel. The human RhCG ammonia transporter was found to have a similar ammonia-conducting channel structure. It was proposed that the erythrocyte Rh complex is a heterotrimer of RhAG, RhD, and RhCE subunits in which RhD and RhCE might play roles in anchoring the ammonia-conducting RhAG subunit to the cytoskeleton. Based on reconstitution experiments, purified RhCG subunits alone can function to transport ammonia. RhCG is required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
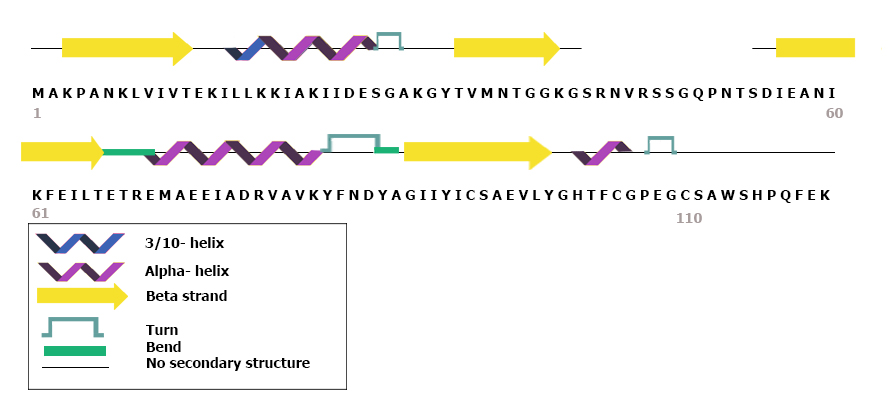
SbtB Protein
SbtB, which stands for sodium-bicarbonate-transporter B, is a protein found in bacteria. This small soluble protein has been classified as a new member of the Pii nitrogen regulatory proteins, P-II family that is involved in signal transduction. This protein has been demonstrated to participate in numerous processes including carbon sensing mechanisms in cyanobacteria. Carbon concentrating mechanisms Most of the oxygen on planet earth derives from Photosynthesis, oxygenic photosynthesis. Some Phototroph, phototrophic prokaryotes such as cyanobacteria developed the ability to carry out oxygenic photosynthesis around 2.7 billion years ago. Moreover, 2 billion years ago planet earth was struck with "The Great Oxygenation event" also known as the oxygen crisis. Rising levels of atmospheric , mainly due to oxygenic photosynthesis carried out by cyanobacteria nearly caused the mass death of anaerobic organisms. Having to face the evolutionary pressure of dropping ambient levels, cyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |