|
Pierre Lecomte Du Noüy
Pierre Lecomte du Noüy (; 20 December 1883, Paris – 22 September 1947, New York City) was a French biophysicist and philosopher. He is probably best remembered by scientists for his work on the surface tension, and other properties, of liquids. Life and work Du Noüy was a descendant of the French dramatist Pierre Corneille. His mother wrote many novels, one of which, ''Amitié Amoureuse'', was translated into 16 languages and ran for 600 editions in France. Born and educated in France, du Noüy obtained the degrees of LL.B., Ph.B., Sc.B., Ph.D., and Sc.D. He was an associate member of the Rockefeller Institute working in Alexis Carrel's lab from 1920 through 1928, head for 10 years of the biophysics division of the Pasteur Institute, and the author of some 200 published papers. He invented the Tensiometer, a scientific apparatus that used his du Noüy ring method to measure the surface tension of liquids. Du Noüy believed that mankind should have confidence in sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation tends to exist within any given population as a result of genetic mutation and recombination. Evolution occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection (including sexual selection) and genetic drift act on this variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more common or more rare within a population. The evolutionary pressures that determine whether a characteristic is common or rare within a population constantly change, resulting in a change in heritable characteristics arising over successive generations. It is this process of evolution that has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules. The theory of evolution by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1883 Births
Events January–March * January 4 – ''Life'' magazine is founded in Los Angeles, California, United States. * January 10 – A fire at the Newhall Hotel in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States, kills 73 people. * January 16 – The Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act, establishing the United States civil service, is passed. * January 19 – The first electric lighting system employing overhead wires begins service in Roselle, New Jersey, United States, installed by Thomas Edison. * February – ''The Adventures of Pinocchio'' by Carlo Collodi is first published complete in book form, in Italy. * February 15 – Tokyo Electrical Lightning Grid, predecessor of Tokyo Electrical Power (TEPCO), one of the largest electrical grids in Asia and the world, is founded in Japan. * February 16 – The '' Ladies' Home Journal'' is published for the first time, in the United States. * February 23 – Alabama becomes the first U.S. stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
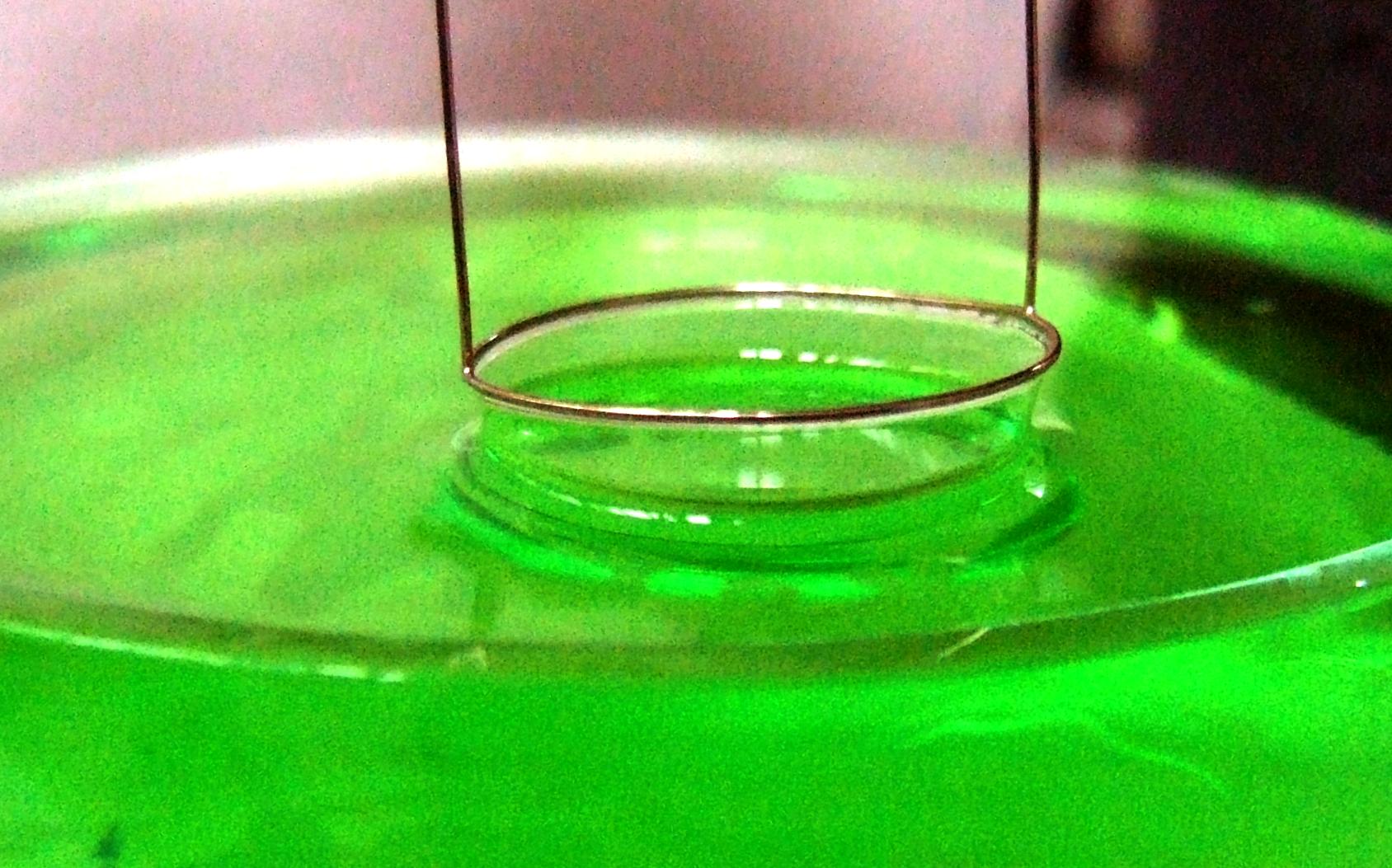
Du Noüy Ring Method
In surface science, the du Noüy ring method is a technique for measuring the surface tension of a liquid. The method involves slowly lifting a ring, often made of platinum, from the surface of a liquid. The force, , required to raise the ring from the liquid's surface is measured and related to the liquid's surface tension, : :F= w_\text + 2\pi \cdot (r_i + r_a) \cdot \gamma where is the radius of the inner ring of the liquid film pulled and is the radius of the outer ring of the liquid film. is the weight of the ring minus the buoyant force due to the part of the ring below the liquid surface. When the ring's thickness is much smaller than its diameter, this equation can be simplified to: :F= w_\text + 4\pi R \gamma where is the average of the inner and outer radius of the ring, i.e. \tfrac. This technique was proposed by the French physicist Pierre Lecomte du Noüy (1883–1947) in a paper published in 1925. The measurement is performed with a force tensiometer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of General Physiology
''Journal of General Physiology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Rockefeller University Press. The journal covers biological, chemical, or physical mechanisms of broad physiological significance. The major emphasis is on physiological problems at the cellular and molecular level. Editorial history The journal was established in 1918 by Jacques Loeb. Editing duties were shared with Winthrop Osterhout of Harvard University. The initial rationale for the journal was stated in this extract from the 1918 announcement of publication: Under the pressure of demands of medicine and other professions, physiology has developed in the direction of an applied science, with limited opportunity for the investigation of purely theoretical problems. On the other hand, the physico-chemical methods of analyzing life phenomena have thus far made little inroad into the domain of zoology and botany. Under these circumstances, it has happened that what might be regarded as the mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Gaylord Simpson
George Gaylord Simpson (June 16, 1902 – October 6, 1984) was an American paleontologist. Simpson was perhaps the most influential paleontologist of the twentieth century, and a major participant in the Modern synthesis (20th century), modern synthesis, contributing ''Tempo and Mode in Evolution'' (1944), ''The Meaning of Evolution'' (1949) and ''The Major Features of Evolution'' (1953). He was an expert on extinct mammals and their intercontinental migrations. Simpson was extraordinarily knowledgeable about Mesozoic fossil mammals and fossil mammals of North and South America. He anticipated such concepts as punctuated equilibrium (in ''Tempo and Mode'') and dispelled the myth that the evolution of the horse was a linear process culminating in the modern ''Equus caballus''. He coined the word ''wikt:hypodigm, hypodigm'' in 1940, and published extensively on the Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy of fossil and extant mammals. Simpson was influentially, and incorrectly, opposed to Alf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Koch
Leo Francis Koch (February 8, 1916 – November 14, 1982) was an American academic. An Assistant Professor of biology at the University of Illinois, he was fired for promoting premarital sex. Early life Leo Francis Koch was born on February 8, 1916, in Dickinson, North Dakota. He received a master's degree and a PhD in Biology from the University of Michigan. Career Koch taught biology at the California State University, Fresno and California State University, Bakersfield. Later, he was an Assistant Professor of Biology at the University of Illinois. In 1960, he wrote a letter to the '' Daily Illini'' defending premarital sex provoked public outrage in response to an article in the ''Daily Illini'' criticizing campus heavy petting parties. His response said in part: ...the events described are... symptoms of a serious social malaise... caused by the hypocritical and downright inhumane moral standards engendered by a Christian code... already decrepit in the age of Queen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Hempel
Carl Gustav "Peter" Hempel (January 8, 1905 – November 9, 1997) was a German writer, philosopher, logician, and epistemologist. He was a major figure in logical empiricism, a 20th-century movement in the philosophy of science. He is especially well known for his articulation of the deductive-nomological model of scientific explanation, which was considered the "standard model" of scientific explanation during the 1950s and 1960s. He is also known for the raven paradox (also known as "Hempel's paradox"). Education Hempel studied mathematics, physics and philosophy at the University of Göttingen and subsequently at the University of Berlin and the Heidelberg University. In Göttingen, he encountered David Hilbert and was impressed by his program attempting to base all mathematics on solid logical foundations derived from a limited number of axioms. After moving to Berlin, Hempel participated in a congress on scientific philosophy in 1929 where he met Rudolf Carnap and bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with selective breeding, artificial selection, which in his view is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Genetic diversity, Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and their offspring can inherit such mutations. Throughout the lives of the individuals, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the Cell (biology), cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment. Because individuals with certain variants of the trait tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogenesis
Orthogenesis, also known as orthogenetic evolution, progressive evolution, evolutionary progress, or progressionism, is an obsolete biological hypothesis that organisms have an innate tendency to evolve in a definite direction towards some goal (teleology) due to some internal mechanism or "driving force". According to the theory, the largest-scale trends in evolution have an absolute goal such as increasing biological complexity. Prominent historical figures who have championed some form of evolutionary progress include Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, Pierre Teilhard de Chardin, and Henri Bergson. The term ''orthogenesis'' was introduced by Wilhelm Haacke in 1893 and popularized by Theodor Eimer five years later. Proponents of orthogenesis had rejected the theory of natural selection as the organizing mechanism in evolution for a rectilinear model of directed evolution. With the emergence of the modern synthesis, in which genetics was integrated with evolution, orthogenesis and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |