|
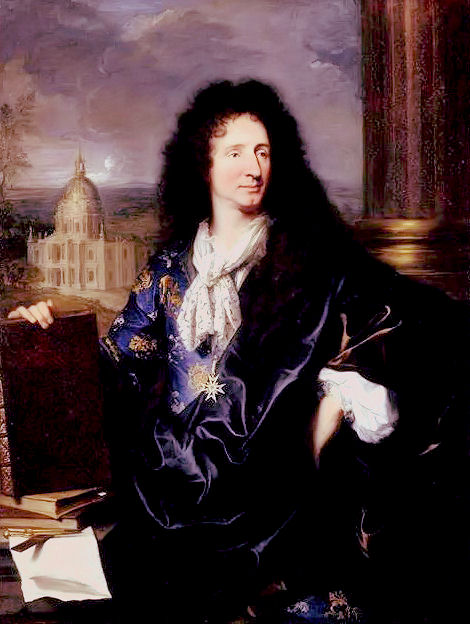
Pierre Cailleteau
Pierre Cailleteau (1655–1724), called Lassurance, was a French architect.Neuman 1996. He is not to be confused with his son Jean Cailleteau, also known as Lassurance, or Lassurance le Jeune to distinguish him from his father. Biography: He was noticed by Jules Hardouin-Mansartin 1679 on the work-site of the Château de Clagny. In 1684, he started as a designer in the administration of the Bâtiments du Roi and played a major role in the new decoration of the royal residences. On the testimony of Saint-Simon, Hardouin-Mansart "was ignorant in his trade, and of Robert De Cotte his brother-in-law, it was hardly less. They both took an artist that they held close and secret to themselves, that was Lassurance, without which they could do nothing." Lassurance is attributed to most of the decorative sketches commissioned for the Château de Versailles and the Trianon de Marbre around 1690: the King's apartments in the left wing of Trianon (round parlor, chapel parlor) and the apartme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Cailleteau
Jean Cailleteau (1690–1755), known as "Lassurance" (or as "Lassurance le jeune" to distinguish him from his architect father Pierre Cailleteau), was a French architect. He was admitted to the Académie royale d'architecture in 1723 and became controller of the château de Marly. 1690 births 1755 deaths 18th-century French architects Members of the Académie royale d'architecture {{France-architect-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avant-corps
An ''avant-corps'' ( it, avancorpo or , plural , german: Risalit, pl, ryzalit), a French term literally meaning "fore-body", is a part of a building, such as a porch or pavilion, that juts out from the ''corps de logis'', often taller than other parts of the building. It is common in façades in French Baroque architecture. Particularly in German architecture, a corner ''Risalit'' is where two wings meet at right-angles. Baroque three-winged constructions often incorporate a median ''Risalit'' in a main hall or a stairwell, such as in Weißenstein Palace Weißenstein ( sl, Bilšak) is a town in the district of Villach-Land in the Austrian state of Carinthia. Geography Weißenstein lies in the lower Drau valley northwest of Villach. The highest point in the municipality is the Spitzeck at 1517 ... and the . Terms By position to the building A central avant-corps stands in the middle of the facade. A side projection is positioned off-centre. Two wings (usually) runn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1724 Deaths
Seventeen or 17 may refer to: *17 (number), the natural number following 16 and preceding 18 * one of the years 17 BC, AD 17, 1917, 2017 Literature Magazines * ''Seventeen'' (American magazine), an American magazine * ''Seventeen'' (Japanese magazine), a Japanese magazine Novels * ''Seventeen'' (Tarkington novel), a 1916 novel by Booth Tarkington *''Seventeen'' (''Sebuntiin''), a 1961 novel by Kenzaburō Ōe * ''Seventeen'' (Serafin novel), a 2004 novel by Shan Serafin Stage and screen Film * ''Seventeen'' (1916 film), an American silent comedy film *''Number Seventeen'', a 1932 film directed by Alfred Hitchcock * ''Seventeen'' (1940 film), an American comedy film *''Eric Soya's '17''' (Danish: ''Sytten''), a 1965 Danish comedy film * ''Seventeen'' (1985 film), a documentary film * ''17 Again'' (film), a 2009 film whose working title was ''17'' * ''Seventeen'' (2019 film), a Spanish drama film Television * ''Seventeen'' (TV drama), a 1994 UK dramatic short starring Christ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1655 Births
Events January–March * January 5 – Emperor Go-Sai ascends to the throne of Japan. * January 7 – Pope Innocent X, leader of the Roman Catholic Church and the Papal States, dies after more than 10 years of rule. * February 14 – The Mapuches launch coordinated attacks against the Spanish in Chile, beginning the Mapuche uprising of 1655. * February 16 – Dutch Grand Pensionary advisor Johan de Witt marries Wendela Bicker. * March 8 – John Casor becomes the first legally recognized slave in what will become the United States, as a court in Northampton County in the Colony of Virginia issues its decision in the Casor lawsuit, the first instance of a judicial determination in the Thirteen Colonies holding that a person who had committed no crime could be held in servitude for life. * March 25 – Saturn's largest moon, Titan, is discovered by Christiaan Huygens. April–June * April 4 – Battle of Porto Farina, Tunis: Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Dictionary Of Art
''Grove Art Online'' is the online edition of ''The Dictionary of Art'', often referred to as the ''Grove Dictionary of Art'', and part of Oxford Art Online, an internet gateway to online art reference publications of Oxford University Press, which also includes the online version of the ''Benezit Dictionary of Artists''. It is a large encyclopedia of art, previously a 34-volume printed encyclopedia first published by Grove in 1996 and reprinted with minor corrections in 1998. A new edition was published in 2003 by Oxford University Press. Scope Written by 6,700 experts from around the world, its 32,600 pages cover over 45,000 topics about art, artists, art critics, art collectors, or anything else connected to the world of art. According to ''The New York Times Book Review'' it is the "most ambitious art-publishing venture of the late 20th century". Almost half the content covers non-Western subjects, and contributors hail from 120 countries. Topics range from Julia Margare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Antin
{{Use dmy dates, date=September 2021 The duchy of Antin was a French duchy created in 1711 by the promotion of the marquisate of Antin (held by the Pardaillan de Gondrin family) into a "duché-pairie". It merged the Marquisate of Antin and the baronies, lands and lordships of Bellisle, Mieslan, Tuilerie de Pis, Certias and their dependencies. List of dukes of Antin * 1711–1722 : Louis Antoine de Pardaillan de Gondrin Louis Antoine de Pardaillan (5 September 1664 – 2 November 1736) was a French nobleman, marquis of Antin, Gondrin and Montespan, and first Duke of Antin. Biography The legitimate son of Louis Henri de Pardaillan, ''marquis of Montespan'', a ... (1665–1736), 1st duke of Antin (creation). * 1722–1743 : Louis de Pardaillan de Gondrin (1707–1743), 2nd duke of Antin, grandson of the former * 1743–1757 : Louis de Pardaillan de Gondrin (1727–1757), 3rd duke of Antin, son of the former. House of Pardaillan de Gondrin Dukes of Antin Antin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château De Petit-Bourg
The Château de Petit-Bourg is located in Évry-sur-Seine (Essonne). The first château known on the site of Petit-Bourg, on the Seine, overlooking the Forêt de Sénart, began in the 17th century for André Courtin, Canon of Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Paris and was completed about 1635 for Jean Galland. Around 1650, Monseigneur Louis Barber de La Rivière, Bishop of Langres, had gardens designed by François Mansart. Jules Hardouin-Mansart would have worked there about 1662. Near 1695, Françoise-Athénaïs, marquise de Montespan acquired the Château de Petit-Bourg. There, she realized important alteration work and charged André Le Nôtre with designing the gardens ''à la françaises'', and staged in terraces. She took refuge there after her disgrace. With her death in 1707, her son Louis Antoine de Pardaillan de Gondrin, inherited the château and remade the gardens. Between 1716 and 1722, he undertook to entirely rebuild with the architect Pierre Cailleteau dit Lassuran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Édouard Fournier
Édouard Fournier (15 June 1819, Orléans – 10 May 1880, Paris) was a 19th-century French homme de lettres, playwright, historian, bibliographer and librarian. Biography Born into a locksmiths artist family, he studied at the Collège d'Orléans then devoted entirely to literary work. After a first play in 1841, and some feuilletons published in the newspaper ''Le Loiret'' in 1842, he published a large number of historical, literary, literature and theater studies. He published numerous authors while continuing to write for the stage. He also contributed a great number of articles to the ''Encyclopédie universelle'', the ''Supplément du Dictionnaire de la conversation'', the ''Historie des villes de France'', ''Le Moniteur universel'', ''Le Constitutionnel'', ''L'Illustration'', '' La Revue française'', ''Le Théâtre'', whose chief editor he was from 1853 to 1855, ''La Patrie'', where he held a Parisian theatrical chronicle from 1856, then theatrical, the ''Revue des provin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
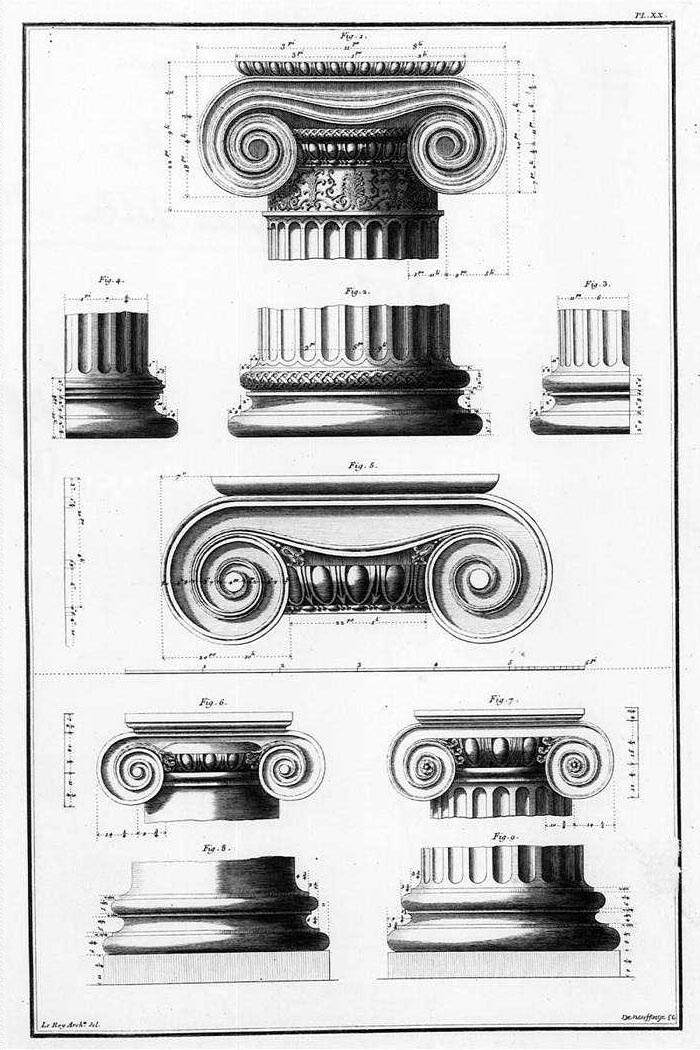
Ionic Columns
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hôtel Particulier
An ''hôtel particulier'' () is a grand townhouse, comparable to the Townhouse (Great Britain), British townhouse or mansion. Whereas an ordinary ''maison'' (house) was built as part of a row, sharing party walls with the houses on either side and directly fronting on a street, an ''hôtel particulier'' was often free-standing and, by the 18th century, would always be located ''entre cour et jardin'' – between the ''cour d'honneur'' (an entrance court) and the garden behind. There are ''hôtels particuliers'' in many large cities in France. Etymology and meaning The word ''hôtel'' represents the Old French "hostel" from the Latin ''hospitālis'' "pertaining to guests", from ''hospes'', a stranger, thus a guest.Cassell's Latin Dictionary The adjective ''particulier'' means "personal" or "private". The English word ''hotel'' developed a more specific meaning as a commercial building accommodating travellers; modern French also uses ''hôtel'' in this sense. For example, the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Hardouin-Mansart
Jules Hardouin-Mansart (; 16 April 1646 – 11 May 1708) was a French Baroque architect and builder whose major work included the Place des Victoires (1684–1690); Place Vendôme (1690); the domed chapel of Les Invalides (1690), and the Grand Trianon of the Palace of Versailles. His monumental work was designed to glorify the reign of Louis XIV of France. Biography Born Jules Hardouin in Paris in 1646, he studied under his renowned great-uncle François Mansart, one of the originators of the classical tradition in French architecture; Hardouin inherited Mansart's collection of plans and drawings and added Mansart's name to his own in 1668. He began his career as an entrepreneur in building construction, in partnership with his brother Michel, but then decided in 1672 to devote himself entirely to architecture. In 1674 he became one of the group of royal architects working for Louis XIV. His first important project was the Château de Clagny, built for the King's consort, Madame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Conseil
The term Grand Conseil () or Great Council refers two different institutions during the Ancien Régime in France. It also is the name of parliaments in several Swiss cantons. Ancien Régime France Part of the King's Council Starting in the 13th century, the "Grand Conseil" was the name given to the largest of the King's Councils, in contrast to the smaller and more elite "Conseil étroit" ("narrow council") or "Conseil secret". Superior Court Under Charles VII, a subcouncil of the King's council appeared to handle particularly contentious affairs. An ordinance by Charles VIII in 1497, and reissued by Louis XII in 1498, removed this section entirely from the King's Council and made it a superior court of justice under the institutional name "Grand Conseil". The "Grand Conseil" was not attended by the king, and it was furnished with its own legal and judicial personnel and with a purview over contentious affairs submitted directly to the king (affairs of "justice retenue", or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |