|
Piano Trio No. 1 (Mendelssohn)
Felix Mendelssohn's Piano Trio No. 1 in D minor, Op. 49, was completed on 23 September 1839 and published the following year. The work is scored for a standard piano trio consisting of violin, cello and piano. It is one of Mendelssohn's most popular chamber works and is recognized as one of his greatest along with his Octet, Op. 20. During the initial composition of the work, Mendelssohn took the advice of fellow composer Ferdinand Hiller to revise the piano part. Hiller wrote, "with his usual conscientious earnestness when once he had made up his mind, he undertook the length and rewrite the whole pianoforte part''."'' The revised version was in a more romantic, Schumannesque style with the piano given a more important role in the trio. Indeed, the revised piece was reviewed by Schumann, who declared Mendelssohn to be "the Mozart of the nineteenth century, the brightest musician, who most clearly understands the contradictions of the age and is the first to reconcile them." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Mendelssohn
Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy (3 February 18094 November 1847), born and widely known as Felix Mendelssohn, was a German composer, pianist, organist and conductor of the early Romantic period. Mendelssohn's compositions include symphonies, concertos, piano music, organ music and chamber music. His best-known works include the overture and incidental music for '' A Midsummer Night's Dream'' (which includes his "Wedding March"), the '' Italian Symphony'', the '' Scottish Symphony'', the oratorio ''St. Paul'', the oratorio ''Elijah'', the overture ''The Hebrides'', the mature Violin Concerto and the String Octet. The melody for the Christmas carol "Hark! The Herald Angels Sing" is also his. Mendelssohn's ''Songs Without Words'' are his most famous solo piano compositions. Mendelssohn's grandfather was the renowned Jewish philosopher Moses Mendelssohn, but Felix was initially raised without religion. He was baptised at the age of seven, becoming a Reformed Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua Bell
Joshua David Bell (born December 9, 1967) is an American violinist and conductor. He plays the Gibson Stradivarius. Early life and education Bell was born in Bloomington, Indiana, to Shirley Bell, a therapist, and Alan P. Bell, a psychologist, professor emeritus at Indiana University (IU), and former Kinsey researcher. His father is of Scottish descent and his mother is Jewish (her father was born in Mandatory Palestine and her mother was from Minsk). Bell began playing the violin at age four after his mother discovered that he had taken rubber bands from around the house and stretched them across the handles of his nine dresser drawers to pluck out music he had heard her play on the piano. His parents got a scaled-to-size violin for him when he was five and started giving him lessons. Bell took to the instrument but had an otherwise normal Indiana childhood, playing video games and excelling at sports, especially tennis and bowling. He placed in a national tennis tournament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scherzo
A scherzo (, , ; plural scherzos or scherzi), in western classical music, is a short composition – sometimes a movement from a larger work such as a symphony or a sonata. The precise definition has varied over the years, but scherzo often refers to a movement that replaces the minuet as the third movement in a four-movement work, such as a symphony, sonata, or string quartet. The term can also refer to a fast-moving humorous composition that may or may not be part of a larger work. Origins The Italian word ''scherzo'' means 'joke' or 'jest'. More rarely the similar-meaning word ''badinerie'' (also spelled ''battinerie''; from French, 'jesting') has been used. Sometimes the word ''scherzando'' ('joking') is used in musical notation to indicate that a passage should be executed in a playful manner. An early use of the word ''scherzo'' in music is in light-hearted madrigals of the early baroque period, which were often called ''scherzi musicali'', for example: * Claudio Monte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterpoint
In music, counterpoint is the relationship between two or more musical lines (or voices) which are harmonically interdependent yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. It has been most commonly identified in the European classical tradition, strongly developing during the Renaissance and in much of the common practice period, especially in the Baroque period. The term originates from the Latin ''punctus contra punctum'' meaning "point against point", i.e. "note against note". In Western pedagogy, counterpoint is taught through a system of species (see below). There are several different forms of counterpoint, including imitative counterpoint and free counterpoint. Imitative counterpoint involves the repetition of a main melodic idea across different vocal parts, with or without variation. Compositions written in free counterpoint often incorporate non-traditional harmonies and chords, chromaticism and dissonance. General principles The term "counterpoint" has been us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Songs Without Words
''Songs Without Words'' (') is a series of short lyrical piano works by the Romantic composer Felix Mendelssohn written between 1829 and 1845. His sister, Fanny Mendelssohn, and other composers also wrote pieces in the same genre. Music The eight volumes of ''Songs Without Words'', each consisting of six songs (), were written at various points throughout Mendelssohn's life and published separately. The piano became increasingly popular in Europe during the early nineteenth century, when it became a standard item in many middle-class households. The pieces are within the grasp of pianists of various abilities and this undoubtedly contributed to their popularity. This great popularity has caused many critics to under-rate their musical value. The first volume was published by Novello in London (1832) as ''Original Melodies for the Pianoforte'', but the later volumes used the title ''Songs Without Words''. The works were part of the Romantic tradition of writing short lyric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recapitulation (music)
In music theory, the recapitulation is one of the sections of a movement written in sonata form. The recapitulation occurs after the movement's development section, and typically presents once more the musical themes from the movement's exposition. This material is most often recapitulated in the tonic key of the movement, in such a way that it reaffirms that key as the movement's home key. In some sonata form movements, the recapitulation presents a straightforward image of the movement's exposition. However, many sonata form movements, even early examples, depart from this simple procedure. Devices used by composers include incorporating a secondary development section, or varying the character of the original material, or rearranging its order, or adding new material, or omitting material altogether, or overlaying material that was kept separate in the exposition. The composer of a sonata form movement may disguise the start of the recapitulation as an extension of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Development (music)
In music, development is a process by which a musical idea is communicated in the course of a composition. It refers to the transformation and restatement of initial material. Development is often contrasted with musical variation, which is a slightly different means to the same end. ''Development'' is carried out upon portions of material treated in many ''different'' presentations and combinations at a time, while ''variation'' depends upon ''one'' type of presentation at a time. In this process, certain central ideas are repeated in different contexts or in altered form so that the mind of the listener consciously or unconsciously compares the various incarnations of these ideas. Listeners may apprehend a "tension between expected and real results" (see irony), which is one "element of surprise" in music. This practice has its roots in counterpoint, where a theme or subject might create an impression of a pleasing or affective sort, but delight the mind further as its contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncopated
In music, syncopation is a variety of rhythms played together to make a piece of music, making part or all of a tune or piece of music off-beat. More simply, syncopation is "a disturbance or interruption of the regular flow of rhythm": a "placement of rhythmic stresses or accents where they wouldn't normally occur". It is the correlation of at least two sets of time intervals. Syncopation is used in many musical styles, especially dance music. According to music producer Rick Snoman, "All dance music makes use of syncopation, and it's often a vital element that helps tie the whole track together". Syncopation can also occur when a strong harmony is simultaneous with a weak beat, for instance, when a 7th-chord is played on the second beat of measure or a dominant chord is played at the fourth beat of a measure. The latter occurs frequently in tonal cadences for 18th- and early-19th-century music and is the usual conclusion of any section. A hemiola (the equivalent Latin term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantabile
In music, ''cantabile'' , an Italian word, means literally "singable" or "songlike". In instrumental music, it is a particular style of playing designed to imitate the human voice. For 18th-century composers, ''cantabile'' is often synonymous with "cantando" (singing) and indicates a measured tempo and flexible, legato playing. For later composers, particularly in piano music, ''cantabile'' is the drawing out of one particular musical line against the accompaniment (compare counterpoint). Felix Mendelssohn's six books of '' Songs Without Words'' are short lyrical piano pieces with song-like melodies written between 1829 and 1845. A modern example is an instrumental by Harry James & His Orchestra, called "Trumpet Blues and Cantabile". A cantabile movement, or simply a "cantabile", is the first half of a double aria, followed by a cabaletta. The cantabile movement would be slower and more free-form to contrast with the structured and generally faster cabaletta. Louis Spohr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exposition (music)
In musical form and analysis, exposition is the initial presentation of the thematic material of a musical composition, movement, or section. The use of the term generally implies that the material will be developed or varied. *In sonata form, the exposition is "the first major section, incorporating at least one important modulation to the dominant or other secondary key and presenting the principal thematic material." *In a fugue, the exposition is "the statement of the subject in imitation by the several voices; especially the first such statement, with which the fugue begins." In sonata form The term is most widely used as an analytical convenience to denote a portion of a movement identified as an example of classical tonal sonata form. The exposition typically establishes the music's tonic key, and then modulates to, and ends in, the dominant. If the exposition starts in a minor key, it typically modulates to the relative major key. There are many exceptions, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
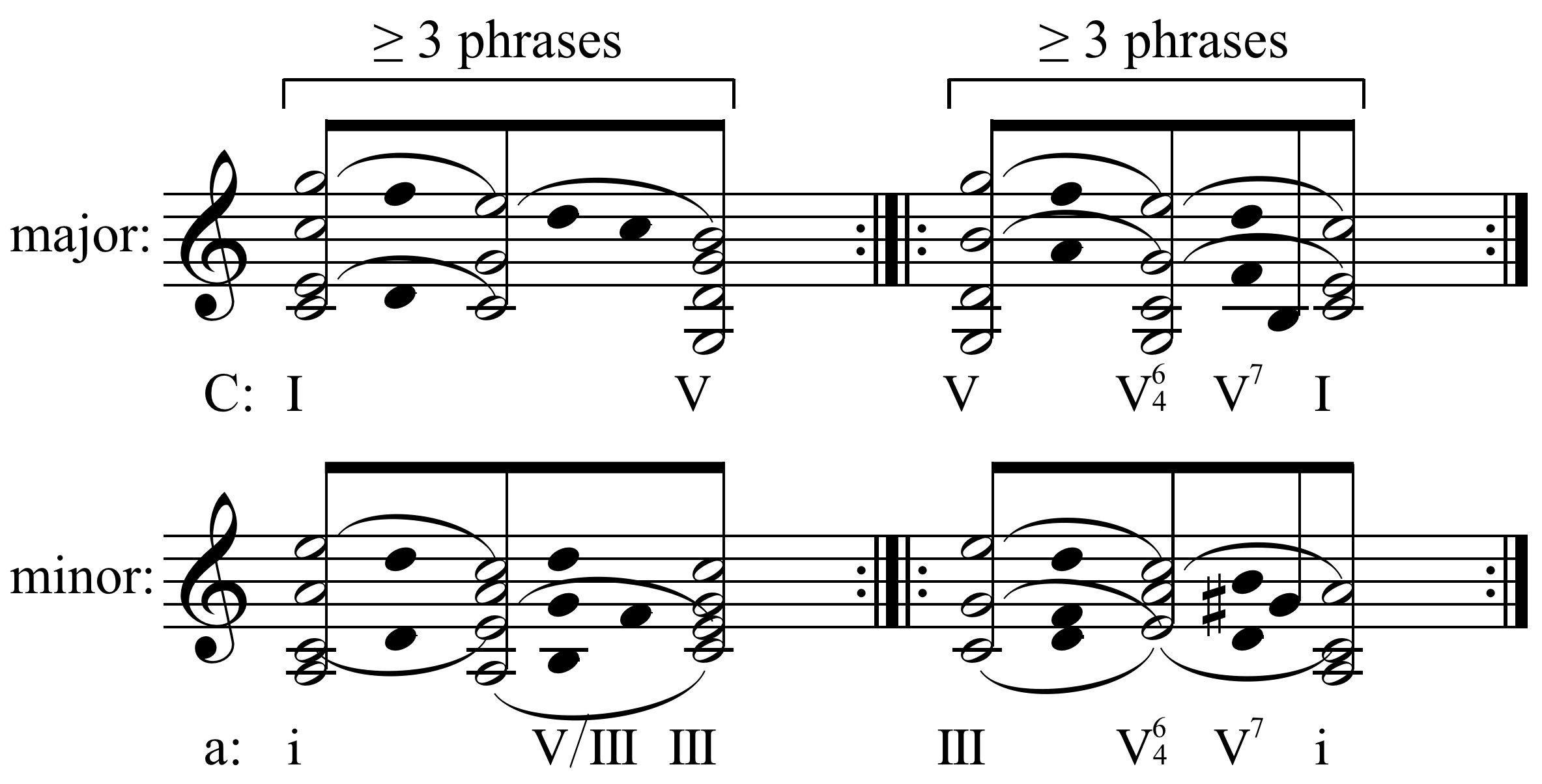
Sonata Form
Sonata form (also ''sonata-allegro form'' or ''first movement form'') is a musical form, musical structure generally consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century (the early Classical music era, Classical period). While it is typically used in the first Movement (music), movement of multi-movement pieces, it is sometimes used in subsequent movements as well—particularly the final movement. The teaching of sonata form in music theory rests on a standard definition and a series of hypotheses about the underlying reasons for the durability and variety of the form—a definition that arose in the second quarter of the 19th century. There is little disagreement that on the largest level, the form consists of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation; however, beneath this general structure, sonata form is difficult to pin down to a single model. The st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonata Form
Sonata form (also ''sonata-allegro form'' or ''first movement form'') is a musical form, musical structure generally consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century (the early Classical music era, Classical period). While it is typically used in the first Movement (music), movement of multi-movement pieces, it is sometimes used in subsequent movements as well—particularly the final movement. The teaching of sonata form in music theory rests on a standard definition and a series of hypotheses about the underlying reasons for the durability and variety of the form—a definition that arose in the second quarter of the 19th century. There is little disagreement that on the largest level, the form consists of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation; however, beneath this general structure, sonata form is difficult to pin down to a single model. The st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |