|
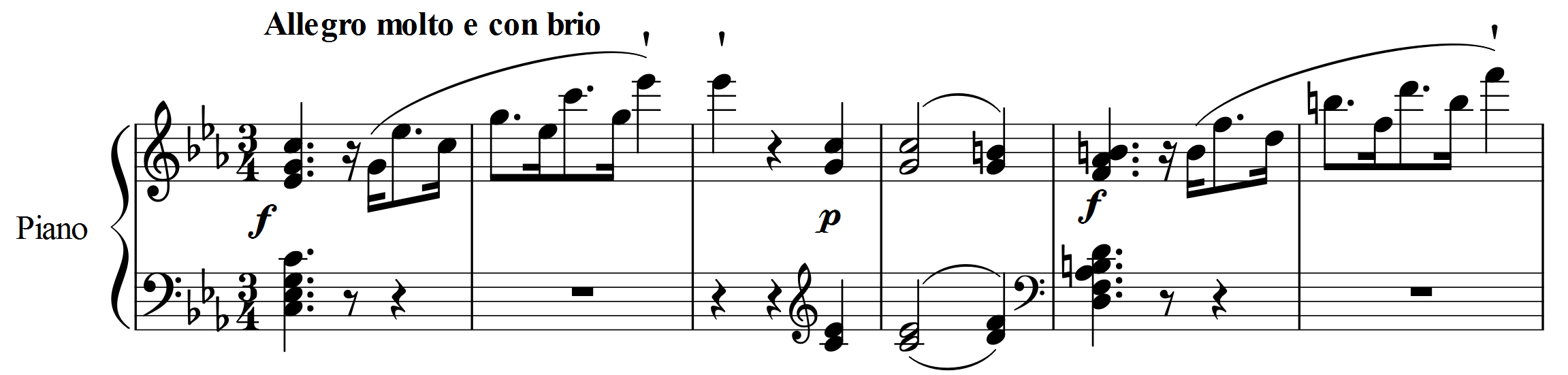
Piano Sonata No. 5 (Beethoven)
Ludwig van Beethoven's Piano Sonata No. 5 in C minor, Op. 10, No. 1 was composed some time during 1796–98. The first movement of the sonata has a meter, the second movement , and the final movement . Beethoven's Piano Sonata No. 5 is a first-period composition, anticipating Beethoven and C minor, more notable C minor works such as the Piano Sonata No. 8 (Beethoven), Pathétique Sonata and the Symphony No. 5 (Beethoven), Fifth Symphony in its nervous energy. Like all three sonatas of his Op. 10, it is dedicated to Anna Margarete von Browne, the wife of one of Beethoven's patrons, a Russian diplomat in Vienna. Form The sonata is divided into three movement (music), movements: First movement The first movement, in sonata form, opens energetically with contrasting loud and soft phrases. The theme is angular in shape, both in its rising arpeggios and its dotted rhythm. The exposition lasts from mm. 1–105. The primary theme, a modified sentence structure, lasts from mm. 1–3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. Beethoven remains one of the most admired composers in the history of Western music; his works rank amongst the most performed of the classical music repertoire and span the transition from the Classical period to the Romantic era in classical music. His career has conventionally been divided into early, middle, and late periods. His early period, during which he forged his craft, is typically considered to have lasted until 1802. From 1802 to around 1812, his middle period showed an individual development from the styles of Joseph Haydn and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and is sometimes characterized as heroic. During this time, he began to grow increasingly deaf. In his late period, from 1812 to 1827, he extended his innovations in musical form and expression. Beethoven was born in Bonn. His musical talent was obvious at an early age. He was initially harshly and intensively t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Caplin
William E. Caplin (born 1948) is an American music theorist who lives and works in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, where he is a James McGill Professor at the Schulich School of Music of McGill University. Caplin served as president of the Society for Music Theory from 2005 to 2007 and was its vice-president from 2001 to 2003. His earlier work concentrated on the history of music theory,William E. Caplin. (1981). ''Theories of Harmonic-Metric Relationships from Rameau to Riemann''. PhD diss. University of Chicago. but he is best known for a series of articles and two books on musical form in European music around 1800. The first of those books, ''Classical Form: A Theory of Formal Functions for the Music of Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven'' has been widely influential and was a major factor in the revival of interest in musical form in North-American music theory. Theory of Formal Functions ''Classical Form'', along with a more recently published, lengthy textbook intended for both undergra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1798 Compositions
Events January–June * January – Eli Whitney contracts with the U.S. federal government for 10,000 muskets, which he produces with interchangeable parts. * January 4 – Constantine Hangerli enters Bucharest, as Prince of Wallachia. * January 22 – A coup d'état is staged in the Netherlands (Batavian Republic). Unitarian Democrat Pieter Vreede ends the power of the parliament (with a conservative-moderate majority). * February 10 – The Pope is taken captive, and the Papacy is removed from power, by French General Louis-Alexandre Berthier. * February 15 – U.S. Representative Roger Griswold (Fed-CT) beats Congressman Matthew Lyon (Dem-Rep-VT) with a cane after the House declines to censure Lyon earlier spitting in Griswold's face; the House declines to discipline either man.''Harper's Encyclopaedia of United States History from 458 A. D. to 1909'', ed. by Benson John Lossing and, Woodrow Wilson (Harper & Brothers, 1910) p171 * March & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piano Sonatas By Ludwig Van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven wrote 32 mature piano sonatas between 1795 and 1822. (He also wrote 3 juvenile sonatas at the age of 13 and one unfinished sonata, WoO. 51.) Although originally not intended to be a meaningful whole, as a set they comprise one of the most important collections of works in the history of music.Rosen (2002), accompanying note Hans von Bülow called them "The New Testament" of piano literature (Johann Sebastian Bach's ''The Well-Tempered Clavier'' being "The Old Testament"). Beethoven's piano sonatas came to be seen as the first cycle of major piano pieces suited to both private and public performance. They form "a bridge between the worlds of the salon and the concert hall". The first person to play them all in a single concert cycle was Hans von Bülow; the first complete recording is Artur Schnabel's for the label His Master's Voice. List of sonatas Juvenilia The first three sonatas, written in 1782–1783, are usually not acknowledged as part of the compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum
The Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum is an art museum in Boston, Massachusetts, which houses significant examples of European, Asian, and American art. Its collection includes paintings, sculpture, tapestries, and decorative arts. It was founded by Isabella Stewart Gardner, whose will called for her art collection to be permanently exhibited "for the education and enjoyment of the public forever." An auxiliary wing designed by Italian architect Renzo Piano, adjacent to the original structure near the Back Bay Fens, was completed in 2012. In 1990, thirteen of the museum's works were stolen; the crime remains unsolved, and the works, valued at an estimated $500 million, have not been recovered. A $10 million reward for information leading to the art's recovery remains in place. History The museum was built in 1898–1901 by Isabella Stewart Gardner (1840–1924), an American art collector, philanthropist, and patron of the arts in the style of a 15th-century Venetian palac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
András Schiff
Sir András Schiff (; born 21 December 1953) is a Hungarian-born British classical pianist and conductor, who has received numerous major awards and honours, including the Grammy Award, Gramophone Award, Mozart Medal, and Royal Academy of Music Bach Prize, and was appointed Knight Bachelor in the 2014 Queen's Birthday Honours for services to music. He is also known for his public criticism of political movements in Hungary and Austria. Schiff is distinguished visiting professor of piano at the Barenboim–Said Akademie in Berlin, and the first artist-in-residence of the Israel Philharmonic Orchestra. Biography Schiff was born in Budapest to a Jewish family, the only child of two Holocaust survivors. He began piano lessons at age five, studying at the Franz Liszt Academy of Music in Budapest with Elisabeth Vadász, then with Pál Kadosa and Ferenc Rados. Of Rados, Schiff said, "There was never a positive word from him. Everything was bad, horrible. But it instilled a he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picardy Third
A Picardy third, (; french: tierce picarde) also known as a Picardy cadence or Tierce de Picardie, is a major chord of the tonic at the end of a musical section that is either modal or in a minor key. This is achieved by raising the third of the expected minor triad by a semitone to create a major triad, as a form of resolution. For example, instead of a cadence ending on an A minor chord containing the notes A, C, and E, a Picardy third ending would consist of an A major chord containing the notes A, C, and E. The minor third between the A and C of the A minor chord has become a major third in the Picardy third chord. Philosopher Peter Kivy writes: According to Deryck Cooke, "Western composers, expressing the 'rightness' of happiness by means of a major third, expressed the 'wrongness' of grief by means of the minor third, and for centuries, pieces in a minor key had to have a 'happy ending' – a final major chord (the 'tierce de Picardie') or a bare fifth." As a harmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Cadence
In Western musical theory, a cadence (Latin ''cadentia'', "a falling") is the end of a phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards.Don Michael Randel (1999). ''The Harvard Concise Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', pp. 105-106. . A harmonic cadence is a progression of two or more chords that concludes a phrase, section, or piece of music. A rhythmic cadence is a characteristic rhythmic pattern that indicates the end of a phrase. A cadence can be labeled "weak" or "strong" depending on the impression of finality it gives. While cadences are usually classified by specific chord or melodic progressions, the use of such progressions does not necessarily constitute a cadence—there must be a sense of closure, as at the end of a phrase. Harmonic rhythm plays an important part in determining where a cadence occurs. Cadences are strong indicators of the tonic or central pitch of a passage or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonatina Form
A sonatina is a small sonata. As a musical term, sonatina has no single strict definition; it is rather a title applied by the composer to a piece that is in basic sonata form, but is shorter and lighter in character, or technically more elementary, than a typical sonata. The term has been in use at least since the late baroque; there is a one-page, one-movement harpsichord piece by Handel called "Sonatina". It is most often applied to solo keyboard works, but a number of composers have written sonatinas for violin and piano (see list under Violin sonata), for example the Sonatina in G major for Violin and Piano by Antonín Dvořák, and occasionally for other instruments, for example the Clarinet Sonatina by Malcolm Arnold. Term The title "Sonatina" was used occasionally by J.S. Bach for short orchestral introductions to large vocal works, as in his cantata ''Gottes Zeit ist die allerbeste Zeit'', BWV 106, a practice with precedent in the work of the earlier German comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonata Theory
Sonata Theory is an approach to the description of sonata form in terms of individual works' treatment of generic expectations. For example, it is normative for the secondary theme of a minor-mode sonata to be in either the key of III or v. If a composer chooses to break this norm in a given piece, that is a deviation that requires analytical and interpretive explanation. The essentials of the theory are presented by its developers, James Hepokoski and Warren Darcy, in the book ''Elements of Sonata Theory'', which won the Society for Music Theory's Wallace Berry Award in 2008. Although the theory is particularly designed to treat late-eighteenth-century works such as those by Mozart, Haydn, and Beethoven, many of its principles are applicable to works in sonata form from later centuries. Methodology Rather than attempt to prescribe a set of rules to which all pieces in sonata form must adhere, sonata theory seeks to demonstrate that sonata form is "a constellation of normative a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beethoven And C Minor
The compositions of Ludwig van Beethoven in the key of C minor carry special significance for many listeners. His works in this key have been said to be powerful and emotive, evoking dark and stormy sentiments. Background During the Classical era, C minor was used infrequently and always for works of a particularly turbulent cast. Mozart, for instance, wrote only very few works in this key, but they are among his most dramatic ones (the twenty-fourth piano concerto, the fourteenth piano sonata, the Masonic Funeral Music, the Adagio and Fugue in C minor and the Great Mass in C minor, for instance). Beethoven chose to write a much larger proportion of his works in this key, especially traditionally "salon" (i.e. light and diverting) genres such as sonatas and trios, were a sort of conscious rejection of older aesthetics, valuing the "sublime" and "difficult" above music that is "merely" pleasing to the ear. The key is said to represent for Beethoven a "stormy, heroic tonalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberti Bass
Alberti bass is a particular kind of accompaniment figure in music, often used in the Classical era, and sometimes the Romantic era. It was named after Domenico Alberti (1710–1740/46), who used it extensively, although he was not the first to use it."Alberti Bass." ''Baker's Student Encyclopedia of Music''. Ed. Laura Kuhn. Schirmer-Thomson Gale, 1999. . Alberti bass is a kind of broken chord or arpeggiated accompaniment, where the notes of the chord are presented in the order lowest, highest, middle, highest. This pattern is then repeated several times throughout the music. The broken chord pattern helps to create a smooth, sustained, flowing sound on the piano. "Chords of harmony broken up into short patterns. Steady bass patterns in orchestral music which give the rhythmic drive to Classical music, compensating for the energetic drive of the Baroque basso continuo line." Alberti bass is usually found in the left hand of pieces for keyboard instruments, especially for M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |