|
Phrynobatrachus Scapularis
''Phrynobatrachus scapularis'' is a species of frog in the family Phrynobatrachidae. It is endemic to the northern and northeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. The specific name ''scapularis'' refers to shoulder blades (scapulae). Common name Buta river frog has been coined for it. Description The male holotype measures in snout–vent length, though a later measurements was only . Adult males from the Garamba National Park measure and adult females in snout–vent length. The tympanum is present but is usually obscured by the skin, also described as being completely hidden. The toe webbing is extremely reduced. Dorsal skin is very warty, especially in the scapular region. Alcohol-preserved individuals from the Garamba National Park are dorsally brown with black spots that usually coincide with the warts; a few individuals have a light vertebral line. The type series has greyish dorsum with blackish mottling. The chin and, sometimes, throat have small brown spots. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaston-François De Witte
Content in this edit is translated from the existing French Wikipedia article at :fr:Gaston-François de Witte; see its history for attribution. Gaston-François de Witte (12 June 1897, Antwerp – 1 June 1980, Brussels) was a Belgian herpetologist who discovered and described at least 24 different species of reptiles. During his career, he was associated with the Royal Museum for Central Africa in Tervuren (from 1920) and the Museum of Natural Sciences in Brussels (from 1937). He is best known for his research of amphibians and reptiles found in the Belgian Congo, from where he collected thousands of specimens. While in central Africa, he also collected botanical specimens. Biography Gaston-François de Witte was the son of Henry de Witte and Jeanne della Faine de Leverghem, and the grand-son of Jean de Witte. As a child, he already liked natural science. During his scholarship at the Bénédictins of the Abbaye de Maredsours, Gaston-François met the british zoologist George Alb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsum (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Gaston-François De Witte
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Fauna Of The Democratic Republic Of The Congo
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Of The Democratic Republic Of The Congo
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frogs Of Africa
The fauna of Africa, in its broader sense, is all the animals living in Africa and its surrounding seas and islands. The more characteristic African fauna is found in the Afrotropical realm. Lying almost entirely within the tropics, and equally to north and south of the equator creates favourable conditions for rich wildlife. Africa is home to many of the world's most famous fauna in human culture such as lions‚ rhinos‚ cheetahs‚ giraffes‚ antelope, hippos, leopards, zebras‚ and African elephants among many others. Origins and history of African fauna Whereas the earliest traces of life in fossil record of Africa date back to the earliest times, the formation of African fauna as we know it today, began with the splitting up of the Gondwana supercontinent in the mid-Mesozoic era. After that, four to six faunal assemblages, the so-called African Faunal Strata (AFSs) can be distinguished. The isolation of Africa was broken intermittently by discontinuous "filter routes" tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrynobatrachus
''Phrynobatrachus'' is a genus of Sub-Saharan frogs that form the monogeneric family Phrynobatrachidae. Their common name is puddle frogs, dwarf puddle frogs, African puddle frogs, or African river frogs. The common name, puddle frog, refers to the fact that many species breed in temporary waterbodies such as puddles. ''Phrynobatrachus'' are among the most common amphibians in Africa. They are typically small (mostly less than ), fast-moving frogs. They occupy a variety of habitats from dry savannas to rainforests. Most species deposit many small eggs as a surface clutch in standing or slowly moving water and have exotrophic tadpoles. Taxonomy Phrynobatrachidae has earlier been considered as a subfamily of Ranidae, but its recognition as a family is now well-established. It is probably most closely related to Petropedetidae and Pyxicephalidae or Ptychadenidae. This large genus may be further divided into three major clades. These clades could be treated as different genera, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of grasses. According to '' Britannica'', there exists four savanna forms; ''savanna woodland'' where trees and shrubs form a light canopy, ''tree savanna'' with scattered trees and shrubs, ''shrub savanna'' with distributed shrubs, and ''grass savanna'' where trees and shrubs are mostly nonexistent.Smith, Jeremy M.B.. "savanna". Encyclopedia Britannica, 5 Sep. 2016, https://www.britannica.com/science/savanna/Environment. Accessed 17 September 2022. Savannas maintain an open canopy despite a high tree density. It is often believed that savannas feature widely spaced, scattered trees. However, in many savannas, tree densities are higher and trees are more regularly spaced than in for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Sac
The vocal sac is the flexible membrane of skin possessed by most male frogs and toads. The purpose of the vocal sac is usually as an amplification of their mating or advertisement call. The presence or development of the vocal sac is one way of externally determining the sex of a frog or toad in many species; taking frogs as an example; The vocal sac is open to the mouth cavity of the frog, with two slits on either side of the tongue. To call, the frog inflates its lungs and shuts its nose and mouth. Air is then expelled from the lungs, through the larynx, and into the vocal sac. The vibrations of the larynx emits a sound, which resonates on the elastic membrane of the vocal sac. The resonance causes the sound to be amplified and allows the call to carry further. Muscles within the body wall force the air back and forth between the lungs and vocal sac. Development The development of the vocal sac is different in most species, however they mostly follow the same process. The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tympanum (anatomy)
The tympanum is an external hearing structure in animals such as mammals, birds, some reptiles, some amphibians and some insects. Using sound, vertebrates and many insects are capable of sensing their prey, identifying and locating their predators, warning other individuals, and locating potential mates and rivals by hearing the intentional or unintentional sounds they make. In general, any animal that reacts to sounds or communicates by means of sound, needs to have an auditory mechanism. This typically consists of a membrane capable of vibration known as the tympanum, an air-filled chamber and sensory organs to detect the auditory stimuli. Anurans In frogs and toads, the tympanum is a large external oval shape membrane made up of nonglandular skin. It is located just behind the eye. It does not process sound waves; it simply transmits them to the inner parts of the amphibian's ear, which is protected from the entry of water and other foreign objects. A frog's ear drum works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
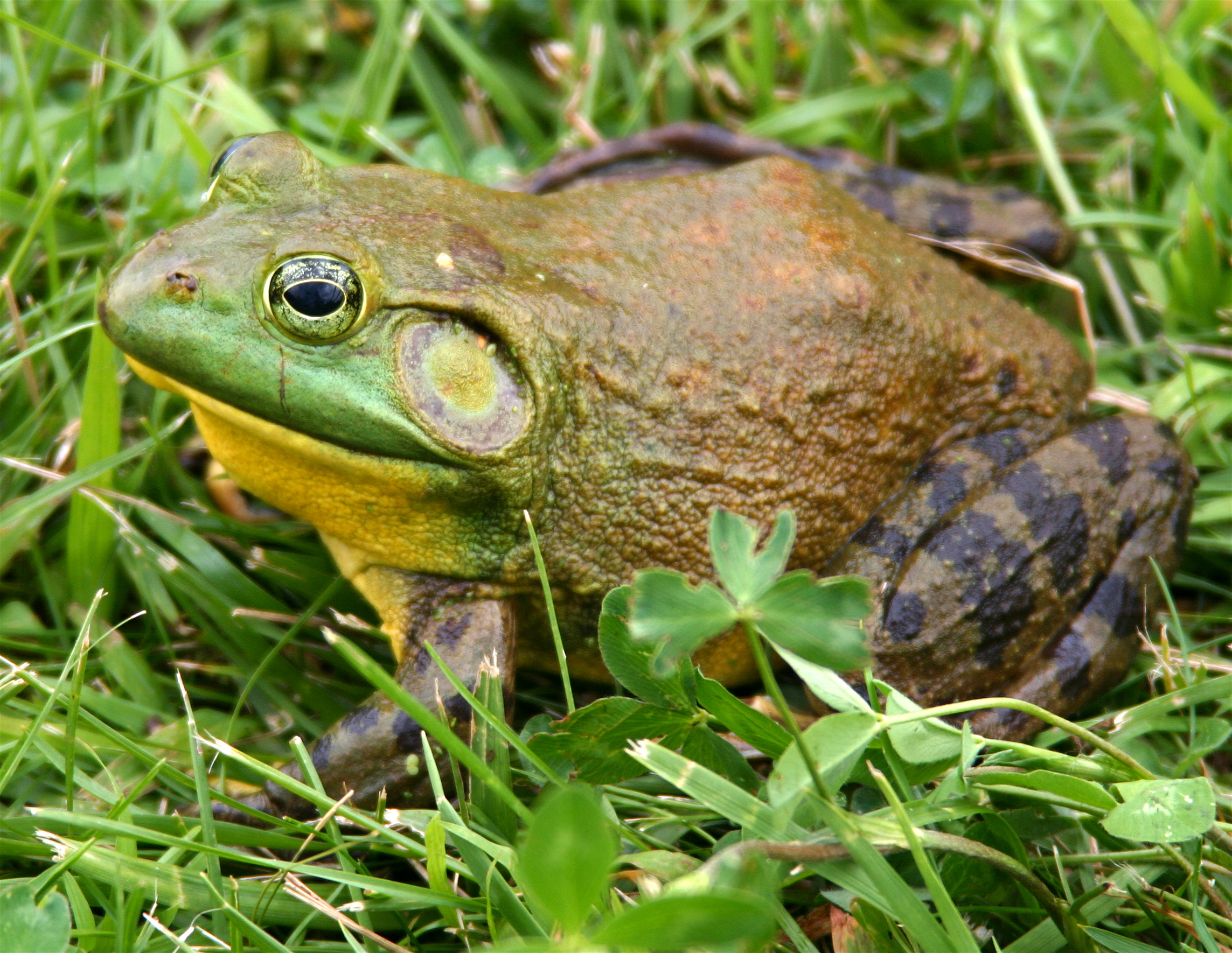
Frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely Carnivore, carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order (biology), order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is known from the Early Triassic of Madagascar, but molecular clock, molecular clock dating suggests their split from other amphibians may extend further back to the Permian, 265 Myr, million years ago. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest. Frogs account for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy or evolutionary history. An adult frog has a stout body, protruding eyes, anteriorly-attached tongue, limb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garamba National Park
Garamba National Park is a nearly national park in north-eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is among Africa's oldest parks, and was designated a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1980 for its protection of critical habitat for northern white rhinoceroses, elephants, hippopotamuses, and giraffes. Garamba has been managed by African Parks in partnership with the Institut Congolais pour la Conservation de la Nature (ICCN), since 2005. Overview Garamba National Park was established in 1938 and covers an area of a in northeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is bounded by Gangala-na-Bodio Hunting Reserve on the west, south, and east, and borders South Sudan on the north and northeast. It is part of the Sudano– Guinean savanna zone. The park is one of Africa's oldest protected areas. It lies in the transition zone between two centres of endemism: Guinea-Congolian and Guinean-Sudanese savanna. These two biogeographic zones support a variety of wildlife, which hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.png)



_Ranomafana.jpg)