|
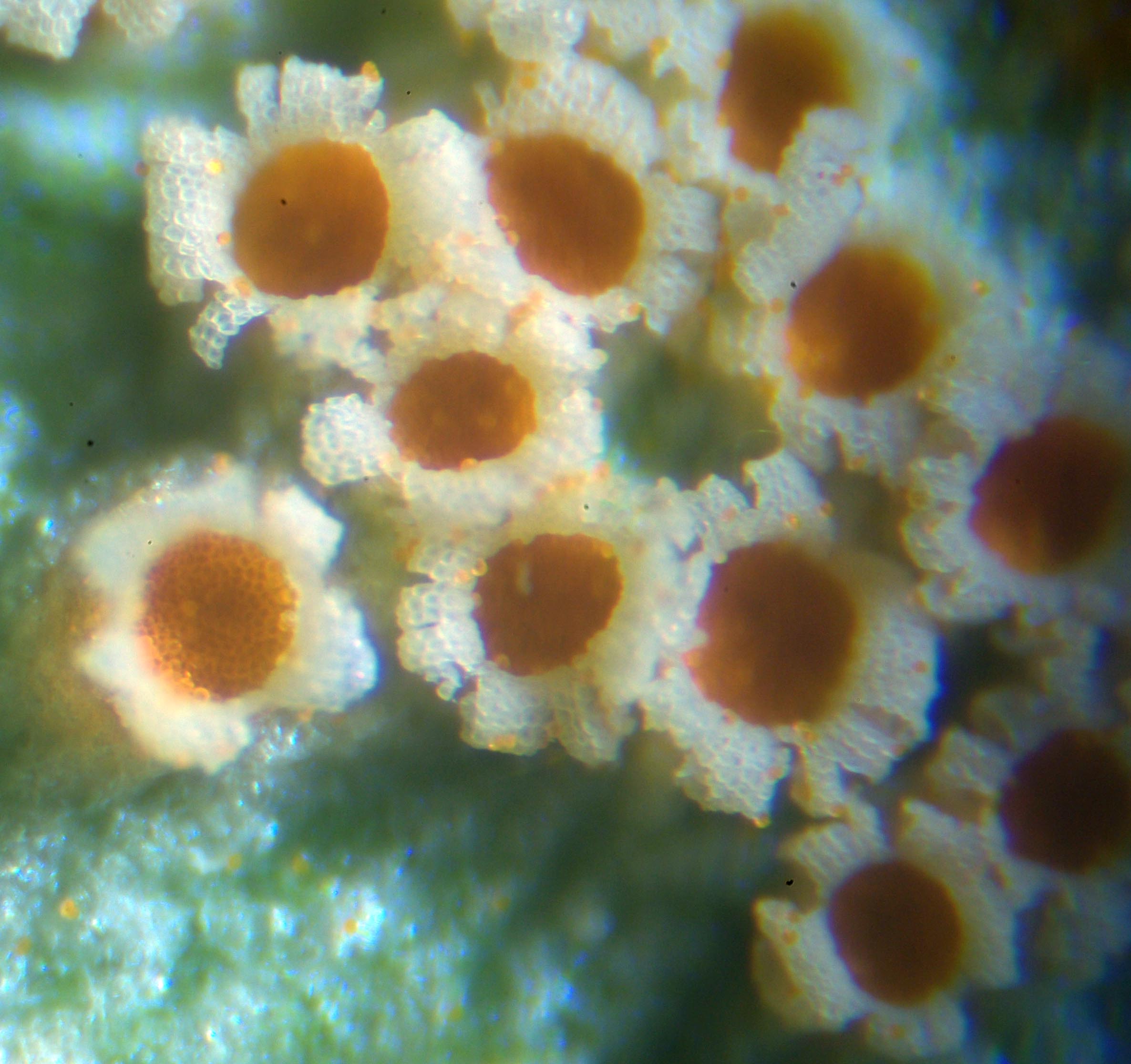
Phragmidium
''Phragmidium '' is a genus of rust fungus that typically infects plant species in the family Rosaceae. It is characterised by having stalked teliospores borne on telia each having a row of four or more cells. All species have a caeoma which is a diffuse aecidium lacking a peridium. There are a number of species of ''Phragmidium'', most of which are restricted to one or a few host species. Examples include: *'' Phragmidium acuminatum'' on '' Rubus saxatile'' *'' Phragmidium bulbosum'' on ''Rubus fruticosus'' and '' Rubeus caesius'' *'' Phragmidium mucronatum'' *'' Phragmidium sterilis'' on ''Potentilla sterilis'' *''Phragmidium potentillae'' on ''Potentilla anglica'' *''Phragmidium rosae-pimpinellifoliae'' *''Phragmidium rubi-idaei'' on raspberry *''Phragmidium tuberculatum'' on some rose cultivars *''Phragmidium violaceum'' on cultivated blackberry and loganberry Possibly the most commonly encountered is ''P. mucronatum'', found on most species of wild roses including ''Rosa c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmidium Bulbosum
''Phragmidium '' is a genus of rust fungus that typically infects plant species in the family Rosaceae. It is characterised by having stalked teliospores borne on telia each having a row of four or more cells. All species have a caeoma which is a diffuse aecidium lacking a peridium. There are a number of species of ''Phragmidium'', most of which are restricted to one or a few host species. Examples include: *'' Phragmidium acuminatum'' on '' Rubus saxatile'' *'' Phragmidium bulbosum'' on ''Rubus fruticosus'' and '' Rubeus caesius'' *'' Phragmidium mucronatum'' *'' Phragmidium sterilis'' on ''Potentilla sterilis'' *''Phragmidium potentillae'' on ''Potentilla anglica'' *''Phragmidium rosae-pimpinellifoliae'' *''Phragmidium rubi-idaei'' on raspberry *''Phragmidium tuberculatum'' on some rose cultivars *''Phragmidium violaceum'' on cultivated blackberry and loganberry Possibly the most commonly encountered is ''P. mucronatum'', found on most species of wild roses including ''Rosa c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmidium Tuberculatum
''Phragmidium '' is a genus of Rust (fungus), rust fungus that typically infects plant species in the family Rosaceae. It is characterised by having stalked teliospores borne on telium, telia each having a row of four or more cells. All species have a caeoma (fungal anatomy), caeoma which is a diffuse aecidium lacking a peridium. There are a number of species of ''Phragmidium'', most of which are restricted to one or a few host species. Examples include: *''Phragmidium acuminatum'' on ''Rubus saxatile'' *''Phragmidium bulbosum'' on ''Rubus fruticosus'' and ''Rubeus caesius'' *''Phragmidium mucronatum'' *''Phragmidium sterilis'' on ''Potentilla sterilis'' *''Phragmidium potentillae'' on ''Potentilla anglica'' *''Phragmidium rosae-pimpinellifoliae'' *''Phragmidium rubi-idaei'' on raspberry *''Phragmidium tuberculatum'' on some rose cultivars *''Phragmidium violaceum'' on cultivated blackberry and loganberry Possibly the most commonly encountered is ''P. mucronatum'', found on most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmidium Sterilis
''Phragmidium '' is a genus of rust fungus that typically infects plant species in the family Rosaceae. It is characterised by having stalked teliospores borne on telia each having a row of four or more cells. All species have a caeoma which is a diffuse aecidium lacking a peridium. There are a number of species of ''Phragmidium'', most of which are restricted to one or a few host species. Examples include: *'' Phragmidium acuminatum'' on '' Rubus saxatile'' *''Phragmidium bulbosum'' on ''Rubus fruticosus'' and '' Rubeus caesius'' *'' Phragmidium mucronatum'' *'' Phragmidium sterilis'' on ''Potentilla sterilis'' *''Phragmidium potentillae'' on ''Potentilla anglica'' *''Phragmidium rosae-pimpinellifoliae'' *''Phragmidium rubi-idaei'' on raspberry *''Phragmidium tuberculatum'' on some rose cultivars *''Phragmidium violaceum'' on cultivated blackberry and loganberry Possibly the most commonly encountered is ''P. mucronatum'', found on most species of wild roses including ''Rosa ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmidium Acuminatum
''Phragmidium '' is a genus of rust fungus that typically infects plant species in the family Rosaceae. It is characterised by having stalked teliospores borne on telia each having a row of four or more cells. All species have a caeoma which is a diffuse aecidium lacking a peridium. There are a number of species of ''Phragmidium'', most of which are restricted to one or a few host species. Examples include: *'' Phragmidium acuminatum'' on '' Rubus saxatile'' *''Phragmidium bulbosum'' on ''Rubus fruticosus'' and '' Rubeus caesius'' *'' Phragmidium mucronatum'' *''Phragmidium sterilis'' on ''Potentilla sterilis'' *''Phragmidium potentillae'' on ''Potentilla anglica'' *''Phragmidium rosae-pimpinellifoliae'' *''Phragmidium rubi-idaei'' on raspberry *''Phragmidium tuberculatum'' on some rose cultivars *''Phragmidium violaceum'' on cultivated blackberry and loganberry Possibly the most commonly encountered is ''P. mucronatum'', found on most species of wild roses including ''Rosa can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmidium Mucronatum
''Phragmidium mucronatum'' is a plant pathogen that causes rose rust Rust is an iron oxide, a usually reddish-brown oxide formed by the reaction of iron and oxygen in the catalytic presence of water or air moisture. Rust consists of hydrous iron(III) oxides (Fe2O3·nH2O) and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO( .... References Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Rose diseases Pucciniales Fungi described in 1790 Taxa named by Christiaan Hendrik Persoon {{plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmidium Rubi-idaei
''Phragmidium rubi-idaei'' is a plant pathogen infecting caneberries, ''Rubus ''Rubus'' is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants in the rose family, Rosaceae, subfamily Rosoideae, with over 1,350 species. Raspberries, blackberries, and dewberries are common, widely distributed members of the genus. Most of the ...'' spp. References External links {{Taxonbar, from=Q7188039 Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Small fruit diseases Pucciniales Taxa named by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle Fungi described in 1815 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmidium Rosae-pimpinellifoliae
''Phragmidium rosae-pimpinellifoliae'' is a species of fungus in the family Phragmidiaceae The Phragmidiaceae are a family of rust fungi in the order Pucciniales. The family contains 14 genera and 164 species. Genera *'' Arthuriomyces'' *'' Frommeella'' *'' Gerwasia'' *'' Gymnoconia'' *'' Hamaspora'' *'' Joerstadia'' *'' Kuehneola'' .... A plant pathogen, it causes a rust on the stem, leaves, petioles and fruits of burnet rose and related hybrids. The fungus is found in Europe and North America. References Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Rose diseases Fungi described in 1873 Fungi of Europe Fungi of North America {{Basidiomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmidium Violaceum
''Phragmidium violaceum'' is a plant pathogen native to Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. It primarily infects ''Rubus'' species. It has been used in the biological control of invasive blackberry species in Chile, Australia, and New Zealand. In 2005, it was discovered growing on Himalayan blackberry plants in Oregon. This accidental introduction does not appear to be infecting native vegetation, so it offers hope for reducing the impact of invasive blackberries in the Pacific Northwest. Symptoms The foliar symptoms that can be found include purple leaf spots along with yellow and tan centers. These can be found on the upper surface of the leaf and can resemble ''Septoria'' leaf spot. On the lower surface of the leaf yellow to orange pustules will be surrounded by a purple tinge. These can resemble cane and leaf rust. The leaves that are severely infected can start to dehydrate as well as start to curl. The leaves that are older and closer to the cane will get infected first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmidium Potentillae
''Frommeella tormentillae'' is a species of rust fungus in the family Phragmidiaceae. It is a plant pathogen affecting the strawberry. See also * List of strawberry diseases This article is a list of diseases of strawberry (''Fragaria × ananassa''). Bacterial diseases Oomycete diseases Fungal diseases Miscellaneous diseases and disorders Nematodes, parasitic Phytoplasma, Virus and virus-like diseases ... References Fungal strawberry diseases Pucciniales Fungi described in 1870 {{fungus-fruit-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caeoma (fungal Anatomy)
An aecium (plural aecia) is a specialised reproductive structure found in some plant pathogenic rust fungi that produce aeciospores. Aecia may also be referred to as "cluster cups". The term aecidium (plural aecidia) is used interchangeably but is not preferred. In some rust fungi such as ''Phragmidium'', aecia lack an outer wall structure (a peridium The peridium is the protective layer that encloses a mass of spores in fungi. This outer covering is a distinctive feature of gasteroid fungi. Description Depending on the species, the peridium may vary from being paper-thin to thick and rubber ...) but instead produce a diffuse aecium called a caeoma.''Fungi''. Lilian E Hawker, 1966, Hutchinson University Library In some species of rust fungi with a life cycle including two different host plants, the binucleate spores produced in the aecia cannot infect the current plant host, but must infect a different plant species. References Fungal morphology and anatomy Reproduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link
Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link (2 February 1767 – 1 January 1851) was a German naturalist and botanist. Biography Link was born at Hildesheim as a son of the minister August Heinrich Link (1738–1783), who taught him love of nature through collection of 'natural objects'. He studied medicine and natural sciences at the Hannoverschen Landesuniversität of Göttingen, and graduated as MD in 1789, promoting on his thesis ''"Flora der Felsgesteine rund um Göttingen"'' (Flora of the rocky beds around Göttingen). One of his teachers was the famous natural scientist Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (1752–1840). He became a private tutor (''Privatdozent'') in Göttingen. In 1792 he became the first professor of the new department of chemistry, zoology and botany at the University of Rostock. During his stay at Rostock, he became an early follower of the antiphlogistic theory of Lavoisier, teaching about the existence of oxygen instead of phlogiston. He was also a proponent of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teliospore
Teliospore (sometimes called teleutospore) is the thick-walled resting spore of some fungi ( rusts and smuts), from which the basidium arises. Development They develop in '' telia'' (sing. ''telium'' or ''teliosorus''). The telial host is the primary host in heteroecious rusts. The aecial host is the alternate host (look for pycnia and aecia). These terms apply when two hosts are required by a heteroecious rust fungus to complete its life cycle. Morphology Teliospores consist of one, two or more dikaryote cells. Teliospores are often dark-coloured and thick-walled, especially in species where they overwinter (acting as chlamydospores). Two-celled teliospores formerly defined the genus ''Puccinia''. Here the wall is particularly thick at the tip of the terminal cell which extends into a beak in some species. Teliospores consist of dikaryote cells. As the teliospore cells germinate, the nuclei undergo karyogamy and thereafter meiosis, giving rise to a four-celled basidiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |