|
Photoelectrolysis
Photoelectrochemistry is a subfield of study within physical chemistry concerned with the interaction of light with electrochemical systems. It is an active domain of investigation. One of the pioneers of this field of electrochemistry was the German electrochemist Heinz Gerischer. The interest in this domain is high in the context of development of renewable energy conversion and storage technology. Historical approach Photoelectrochemistry has been intensively studied in the 1970-80s because of the first peak oil crisis. Because fossil fuels are non-renewable, it is necessary to develop processes to obtain renewable resources and use clean energy. Artificial photosynthesis, photoelectrochemical water splitting and regenerative solar cells are of special interest in this context. The photovoltaic effect was discovered by Alexandre Edmond Becquerel. Heinz Gerischer, H. Tributsch, AJ. Nozik, AJ. Bard, A. Fujishima, K. Honda, PE. Laibinis, K. Rajeshwar, TJ Meyer, PV. Kamat, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectrochemical Cells
A "photoelectrochemical cell" is one of two distinct classes of device. The first electricity generation, produces electrical energy similarly to a dye-sensitized solar cell, dye-sensitized photovoltaic cell, which meets the standard definition of a solar cell, photovoltaic cell. The second is a photoelectrolytic cell, that is, a device which uses light incident on a photosensitizer, semiconductor, or aqueous Electrical conductor, metal immersed in an electrolytic solution to directly cause a chemical reaction, for example to produce hydrogen via the electrolysis of water. Both types of device are varieties of solar cells, solar cell, in that a photoelectrochemical cell's function is to use the photoelectric effect (or, very similarly, the photovoltaic effect) to convert electromagnetic radiation (typically sunlight) either directly into electrical power, or into something which can itself be easily used to produce electrical power (hydrogen, for example, can be burned to Hydrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectrolysis
Photoelectrochemistry is a subfield of study within physical chemistry concerned with the interaction of light with electrochemical systems. It is an active domain of investigation. One of the pioneers of this field of electrochemistry was the German electrochemist Heinz Gerischer. The interest in this domain is high in the context of development of renewable energy conversion and storage technology. Historical approach Photoelectrochemistry has been intensively studied in the 1970-80s because of the first peak oil crisis. Because fossil fuels are non-renewable, it is necessary to develop processes to obtain renewable resources and use clean energy. Artificial photosynthesis, photoelectrochemical water splitting and regenerative solar cells are of special interest in this context. The photovoltaic effect was discovered by Alexandre Edmond Becquerel. Heinz Gerischer, H. Tributsch, AJ. Nozik, AJ. Bard, A. Fujishima, K. Honda, PE. Laibinis, K. Rajeshwar, TJ Meyer, PV. Kamat, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
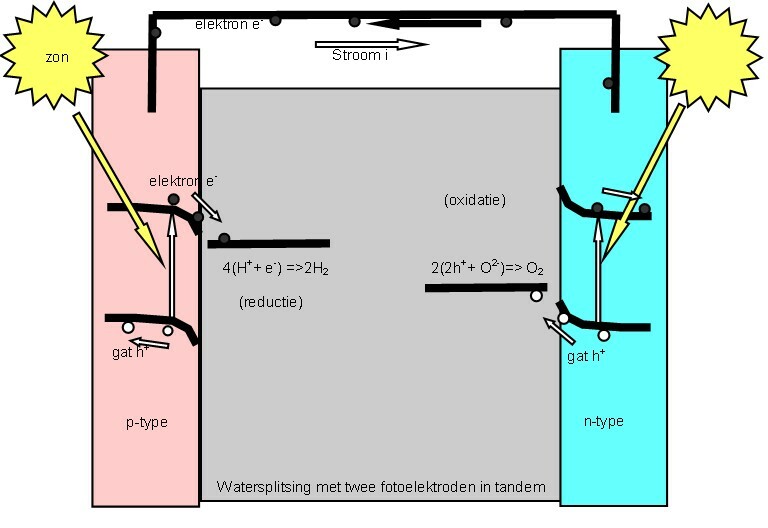
Water Splitting
Water splitting is the chemical reaction in which water is broken down into oxygen and hydrogen: :2 H2O → 2 H2 + O2 Efficient and economical water splitting would be a technological breakthrough that could underpin a hydrogen economy, based on green hydrogen. A version of water splitting occurs in photosynthesis, but hydrogen is not produced. The reverse of water splitting is the basis of the hydrogen fuel cell. Electrolysis Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen (H2) due to an electric current being passed through the water. : * Vion, , "Improved method of using atmospheric electricity", June 1860. In power-to-gas production schemes, the excess power or off peak power created by wind generators or solar arrays is used for load balancing of the energy grid by storing and later injecting the hydrogen into the natural gas grid. Production of hydrogen from water is energy intensive. Potential electrical energy supplies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Gap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference (in electron volts) between the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band in insulators and semiconductors. It is the energy required to promote a valence electron bound to an atom to become a conduction electron, which is free to move within the crystal lattice and serve as a charge carrier to conduct electric current. It is closely related to the HOMO/LUMO gap in chemistry. If the valence band is completely full and the conduction band is completely empty, then electrons cannot move within the solid because there are no available states. If the electrons are not free to move within the crystal lattice, then there is no generated current due to no net charge carrier mobility. However, if some electrons transfer from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "How Batteries Store and Release Energy: Explaining Basic Electrochemistry", ''J. Chem. Educ.'' 95: 1801-1810. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.8b00479 food, and gasoline (as well as oxygen gas, which is of high chemical energy due to its relatively weak double bond and indispensable for chemical-energy release in gasoline combustion). Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2015). "Why Combustions Are Always Exothermic, Yielding About 418 kJ per Mole of O2", ''J. Chem. Educ.'' 92: 2094-2099. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.5b00333 Breaking and re-making of chemical bonds involves energy, which may be either absorbed by or evolved from a chemical system. If reactants with relatively weak electron-pair bonds convert to more strongly bonded products, energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P–n Junction
A p–n junction is a boundary or interface between two types of semiconductor materials, p-type and n-type, inside a single crystal of semiconductor. The "p" (positive) side contains an excess of holes, while the "n" (negative) side contains an excess of electrons in the outer shells of the electrically neutral atoms there. This allows electrical current to pass through the junction only in one direction. The p-n junction is created by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy (growing a layer of crystal doped with one type of dopant on top of a layer of crystal doped with another type of dopant). If two separate pieces of material were used, this would introduce a grain boundary between the semiconductors that would severely inhibit its utility by scattering the electrons and holes. p–n junctions are elementary "building blocks" of semiconductor electronic devices such as diodes, transistors, solar cells, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
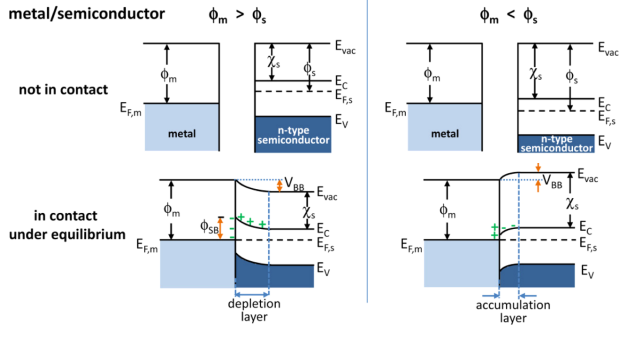
Metal–semiconductor Junction
In solid-state physics, a metal–semiconductor (M–S) junction is a type of electrical junction in which a metal comes in close contact with a semiconductor material. It is the oldest practical semiconductor device. M–S junctions can either be rectifying or non-rectifying. The rectifying metal–semiconductor junction forms a Schottky barrier, making a device known as a Schottky diode, while the non-rectifying junction is called an ohmic contact. (In contrast, a rectifying semiconductor–semiconductor junction, the most common semiconductor device today, is known as a p–n junction.) Metal–semiconductor junctions are crucial to the operation of all semiconductor devices. Usually an ohmic contact is desired, so that electrical charge can be conducted easily between the active region of a transistor and the external circuitry. Occasionally however a Schottky barrier is useful, as in Schottky diodes, Schottky transistors, and metal–semiconductor field effect transist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-type Semiconductor
An extrinsic semiconductor is one that has been '' doped''; during manufacture of the semiconductor crystal a trace element or chemical called a doping agent has been incorporated chemically into the crystal, for the purpose of giving it different electrical properties than the pure semiconductor crystal, which is called an ''intrinsic semiconductor''. In an extrinsic semiconductor it is these foreign dopant atoms in the crystal lattice that mainly provide the charge carriers which carry electric current through the crystal. The doping agents used are of two types, resulting in two types of extrinsic semiconductor. An ''electron donor'' dopant is an atom which, when incorporated in the crystal, releases a mobile conduction electron into the crystal lattice. An extrinsic semiconductor which has been doped with electron donor atoms is called an n-type semiconductor, because the majority of charge carriers in the crystal are negative electrons. An ''electron acceptor'' dopant is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-type Semiconductor
An extrinsic semiconductor is one that has been '' doped''; during manufacture of the semiconductor crystal a trace element or chemical called a doping agent has been incorporated chemically into the crystal, for the purpose of giving it different electrical properties than the pure semiconductor crystal, which is called an ''intrinsic semiconductor''. In an extrinsic semiconductor it is these foreign dopant atoms in the crystal lattice that mainly provide the charge carriers which carry electric current through the crystal. The doping agents used are of two types, resulting in two types of extrinsic semiconductor. An ''electron donor'' dopant is an atom which, when incorporated in the crystal, releases a mobile conduction electron into the crystal lattice. An extrinsic semiconductor which has been doped with electron donor atoms is called an n-type semiconductor, because the majority of charge carriers in the crystal are negative electrons. An ''electron acceptor'' dopant is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Bending
In solid-state physics, band bending refers to the process in which the electronic band structure in a material curves up or down near a junction or interface. It does not involve any physical (spatial) bending. When the electrochemical potential of the free charge carriers around an interface of a semiconductor is dissimilar, charge carriers are transferred between the two materials until an equilibrium state is reached whereby the potential difference vanishes. The band bending concept was first developed in 1938 when Mott, Davidov and Schottky all published theories of the rectifying effect of metal-semiconductor contacts. The use of semiconductor junctions sparked the computer revolution in 1990. Devices such as the diode, the transistor, the photocell and many more still play an important role in technology. Qualitative description Band bending can be induced by several types of contact. In this section metal-semiconductor contact, surface state, applied bias and adsorption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Level
The Fermi level of a solid-state body is the thermodynamic work required to add one electron to the body. It is a thermodynamic quantity usually denoted by ''µ'' or ''E''F for brevity. The Fermi level does not include the work required to remove the electron from wherever it came from. A precise understanding of the Fermi level—how it relates to electronic band structure in determining electronic properties, how it relates to the voltage and flow of charge in an electronic circuit—is essential to an understanding of solid-state physics. In band structure theory, used in solid state physics to analyze the energy levels in a solid, the Fermi level can be considered to be a hypothetical energy level of an electron, such that at thermodynamic equilibrium this energy level would have a ''50% probability of being occupied at any given time''. The position of the Fermi level in relation to the band energy levels is a crucial factor in determining electrical properties. The Fermi le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox Potential
Redox potential (also known as oxidation / reduction potential, ''ORP'', ''pe'', ''E_'', or E_) is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons from or lose electrons to an electrode and thereby be reduced or oxidised respectively. Redox potential is expressed in volts (V). Each species has its own intrinsic redox potential; for example, the more positive the reduction potential (reduction potential is more often used due to general formalism in electrochemistry), the greater the species' affinity for electrons and tendency to be reduced. Measurement and interpretation In aqueous solutions, redox potential is a measure of the tendency of the solution to either gain or lose electrons when it is subjected to change by introduction of a new species. A solution with a higher (more positive) reduction potential than the new species will have a tendency to gain electrons from the new species (i.e. to be reduced by oxidizing the new species) and a solution with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |