|
Phosphinite
In organic chemistry, phosphinites are organophosphorus compounds with the formula . They are used as ligands in homogeneous catalysis and coordination chemistry. Preparation Phosphinites are prepared by alcoholysis of organophosphinous chlorides. For example, treatment of chlorodiphenylphosphine with methanol and base gives methyl diphenylphosphinite: :ClPPh2 + CH3OH → CH3OPPh2 + HCl Although they are esters of phosphinous acids (R2POH), phosphinites are not made via such intermediates. Reactions Oxidation of phosphinites gives phosphinates: :2 P(OR)R2 + O2 → 2 OP(OR)R2 Phosphinites are ligands, giving derivatives similar to metal phosphine complexes. They are stronger pi-acceptors than typical phosphine ligands. References See also *Phosphine - PR3 *Phosphine oxide - OPR3 *Phosphonite - P(OR)2R *Phosphite - P(OR)3 *Phosphinate - OP(OR)R2 *Phosphonate - OP(OR)2R *Phosphate - OP(OR)3 {{Organophosphorus Functional groups Phosphinites, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphorus
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents. Organophosphorus chemistry is the corresponding science of the properties and reactivity of organophosphorus compounds. Phosphorus, like nitrogen, is in group 15 of the periodic table, and thus phosphorus compounds and nitrogen compounds have many similar properties. The definition of organophosphorus compounds is variable, which can lead to confusion. In industrial and environmental chemistry, an organophosphorus compound need contain only an organic substituent, but need not have a direct phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bond. Thus a large proportion of pesticides (e.g., malathion), are often included in this class of compounds. Phosphorus can adopt a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
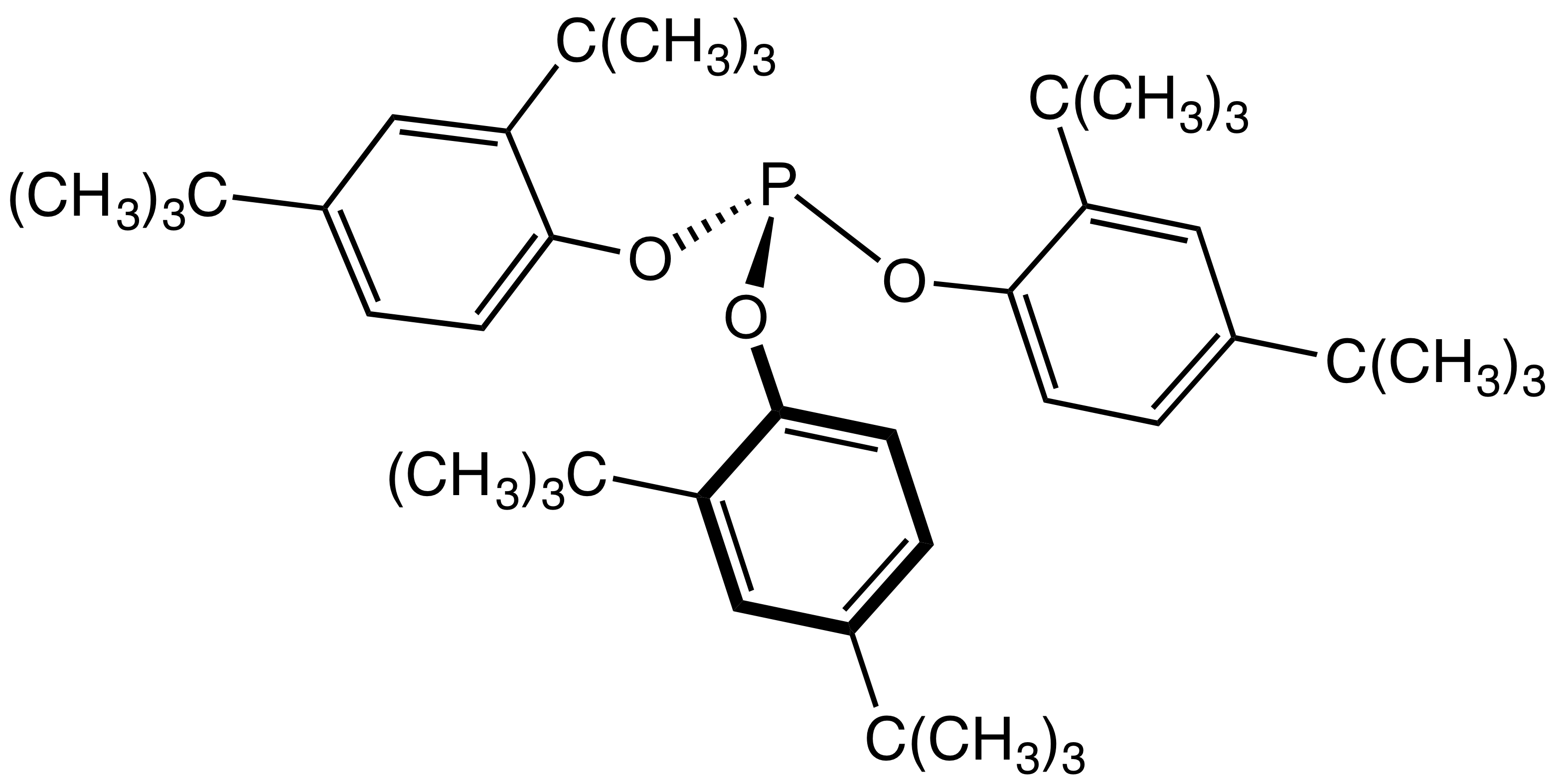
Phosphonite
In organic chemistry, phosphonites are organophosphorus compounds with the formula P(OR)2R. They are found in some pesticides and are used as ligands. Preparation Although they are derivatives of phosphonous acid (RP(OH)2), they are not prepared from such precursors. Phosphonites are prepared by alcoholysis of organophosphinous chlorides. For example, treatment of dichlorophenylphosphine with methanol and base gives dimethyl phenylphosphonite: :Cl2PPh + 2 CH3OH → (CH3O)2PPh + 2 HCl Reactions Oxidation of phosphonites gives phosphonates: :2 P(OR)2R + O2 → 2 OP(OR)2R Phosphonites can function as ligands in homogeneous catalysis In chemistry, homogeneous catalysis is catalysis by a soluble catalyst in a solution. Homogeneous catalysis refers to reactions where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants, principally in solution. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysis ....T. V. (Babu) Rajanbabu “Phosphinite and Phosphonite Ligands” in Phosphorus(III) Ligands in Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphonite
In organic chemistry, phosphonites are organophosphorus compounds with the formula P(OR)2R. They are found in some pesticides and are used as ligands. Preparation Although they are derivatives of phosphonous acid (RP(OH)2), they are not prepared from such precursors. Phosphonites are prepared by alcoholysis of organophosphinous chlorides. For example, treatment of dichlorophenylphosphine with methanol and base gives dimethyl phenylphosphonite: :Cl2PPh + 2 CH3OH → (CH3O)2PPh + 2 HCl Reactions Oxidation of phosphonites gives phosphonates: :2 P(OR)2R + O2 → 2 OP(OR)2R Phosphonites can function as ligands in homogeneous catalysis In chemistry, homogeneous catalysis is catalysis by a soluble catalyst in a solution. Homogeneous catalysis refers to reactions where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants, principally in solution. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysis ....T. V. (Babu) Rajanbabu “Phosphinite and Phosphonite Ligands” in Phosphorus(III) Ligands in Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Phosphine Complex
A metal-phosphine complex is a In coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0). Preparation Many metal phosphine complexes are prepared by reactions of metal halides with preformed phosphines. For example, treatment of a suspension of palladium chloride in ethanol with triphenylphosphine yields monomeric bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) chloride units. :[PdCl2]n + 2PPh3 → PdCl2(PPh3)2 The first reported phosphine complexes were ''cis''- and ''trans''-PtCl2(PEt3)2 reported by Cahours and Gal in 1870. Often the phosphine serves both as a ligand and as a reductant. This property is illustrated by the synthesis of many platinum-metal complexes of triphenylphos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphinate
Phosphinates or hypophosphites are a class of phosphorus compounds conceptually based on the structure of hypophosphorous acid. IUPAC prefers the term phosphinate in all cases, however in practice hypophosphite is usually used to describe inorganic species (e.g. sodium hypophosphite), while phosphinate typically refers to organophosphorus species. Hypophosphites The hypophosphite ion is . The salts are prepared by heating white phosphorus in warm aqueous alkali e.g. Ca(OH)2: :P4 + 2 Ca(OH)2 + 4 H2O → 2 Ca(H2PO2)2 + 2 H2 Hypophosphites are reducing agents: : + 3 OH− → + 2 H2O + 2 e− Hypophosphites are used in electroless nickel plating as the reducing agent to deposit for example Ni metal from Ni salts. The hypophosphite ion is thermodynamically unstable, and disproportionates on heating to phosphine and phosphate salts: : 2 → PH3 + See also *Organophosphinic acid *Phosphine - PR3 * Phosphine oxide - OPR3 *Phosphite - P(OR)3 *Phosphonate - OP(OR)2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one or two protons gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion ion, respectively. These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the triv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphonate
In organic chemistry, phosphonates or phosphonic acids are organophosphorus compounds containing groups (where R = alkyl, aryl, or just hydrogen). Phosphonic acids, typically handled as salts, are generally nonvolatile solids that are poorly soluble in organic solvents, but soluble in water and common alcohols. Many commercially important compounds are phosphonates, including glyphosate (the active molecule of the herbicide Roundup), and ethephon, a widely used plant growth regulator. Bisphosphonates are popular drugs for treatment of osteoporosis.Svara, J.; Weferling, N.; Hofmann, T. "Phosphorus Compounds, Organic," in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2008. . In biochemistry and medicinal chemistry, phosphonate groups are used as stable bioisoteres for phosphate, such as in the antiviral nucleotide analog, Tenofovir, one of the cornerstones of anti-HIV therapy. And there is an indication that phosphonate derivatives are "promising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphinate
Phosphinates or hypophosphites are a class of phosphorus compounds conceptually based on the structure of hypophosphorous acid. IUPAC prefers the term phosphinate in all cases, however in practice hypophosphite is usually used to describe inorganic species (e.g. sodium hypophosphite), while phosphinate typically refers to organophosphorus species. Hypophosphites The hypophosphite ion is . The salts are prepared by heating white phosphorus in warm aqueous alkali e.g. Ca(OH)2: :P4 + 2 Ca(OH)2 + 4 H2O → 2 Ca(H2PO2)2 + 2 H2 Hypophosphites are reducing agents: : + 3 OH− → + 2 H2O + 2 e− Hypophosphites are used in electroless nickel plating as the reducing agent to deposit for example Ni metal from Ni salts. The hypophosphite ion is thermodynamically unstable, and disproportionates on heating to phosphine and phosphate salts: : 2 → PH3 + See also *Organophosphinic acid *Phosphine - PR3 * Phosphine oxide - OPR3 *Phosphite - P(OR)3 *Phosphonate - OP(OR)2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphite
The general structure of a phosphite ester showing the lone pairs on the P In organic chemistry, a phosphite ester or organophosphite usually refers to an organophosphorous compound with the formula P(OR)3. They can be considered as esters of an unobserved tautomer phosphorous acid, H3PO3, with the simplest example being trimethylphosphite, P(OCH3)3. Some phosphites can be considered esters of the dominant tautomer of phosphorous acid (HP(O)(OH)2). The simplest representative is dimethylphosphite with the formula HP(O)(OCH3)2. Both classes of phosphites are usually colorless liquids. Synthesis ;From PCl3 Phosphite esters are typically prepared by treating phosphorus trichloride with an alcohol. Depending on the synthetic details, this alcoholysis can give the diorganophosphites: :PCl3 + 3 C2H5OH → (C2H5O)2P(O)H + 2 HCl + C2H5Cl Alternatively, when the alcoholysis is conducted in the presence of proton acceptors, one obtains the C3-symmetric trialkoxy derivatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine Oxide
Phosphine oxides are phosphorus compounds with the formula OPX3. When X = alkyl or aryl, these are organophosphine oxides. Triphenylphosphine oxide is an example. An inorganic phosphine oxide is phosphoryl chloride (POCl3). Structure and bonding Tertiary phosphine oxides Tertiary phosphine oxides are the most commonly encountered phosphine oxides. With the formula R3PO, they are tetrahedral compounds. They are usually prepared by oxidation of tertiary phosphines. The P-O bond is short and polar. According to molecular orbital theory, the short P–O bond is attributed to the donation of the lone pair electrons from oxygen p-orbitals to the antibonding phosphorus-carbon bonds. The nature of the P–O bond was once hotly debated. Some discussions invoked a role for phosphorus-centered d-orbitals in bonding, but this analysis is not supported by computational analyses. In terms of simple Lewis structure, the bond is more accurately represented as a dative bond, as is currently us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine
Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula , classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (). With traces of present, is spontaneously flammable in air ( pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphine is a highly toxic respiratory poison, and is immediately dangerous to life or health at 50 ppm. Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure. Phosphines are compounds that include and the organophosphines, which are derived from by substituting one or more hydrogen atoms with organic groups. They have the general formula . Phosphanes are saturated phosphorus hydrides of the form , such as triphosphane. Phosphine, PH3, is the smallest of the phosphines and the smallest of the phosphanes. History Philippe Gengembre (1764–1838), a student of Lavois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphinous Acids
Phosphinous acids are usually organophosphorus compounds with the formula R2POH. They are pyramidal in structure. Phosphorus is in the oxidation state III. Most phosphinous acids rapidly convert to the corresponding phosphine oxide, which are tetrahedral and are assigned oxidation state V. Synthesis Only one example is known, bis(trifluoromethyl)phosphinous acid, (CF3)2POH. It is prepared in several steps from phosphorus trichloride (Et = ethyl): :PCl3 + 2 Et2NH → PCl2NEt2 + Et2NH2Cl :2 P(NEt2)3 + PCl2NEt2 + 2 CF3Br → P(CF3)2NEt2 + 2 BrClP(NEt2)3 :P(CF3)2NEt2 + H2O → P(CF3)2OH + HNEt2 Reactions With the lone exception of the bis(trifluoromethyl) derivative, the dominant reaction of phosphinous acids is tautomerization: :PR2OH → OPR2H Even the pentafluorophenyl compound P(C6F5)2OH is unstable with respect to the phosphine oxide. Although phosphinous acids are rare, their P-bonded coordination complexes are well established, e.g. Mo(CO)5P(OH)3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |