|
Phonetician
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds, or in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians. The field of phonetics is traditionally divided into three sub-disciplines based on the research questions involved such as how humans plan and execute movements to produce speech (articulatory phonetics), how various movements affect the properties of the resulting sound (acoustic phonetics), or how humans convert sound waves to linguistic information (auditory phonetics). Traditionally, the minimal linguistic unit of phonetics is the phone—a speech sound in a language which differs from the phonological unit of phoneme; the phoneme is an abstract categorization of phones. Phonetics deals with two aspects of human speech: production—the ways humans make sounds—and perception—the way speech is understood. The communicative modalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Melville Bell
Alexander Melville Bell (1 March 18197 August 1905) was a teacher and researcher of physiological phonetics and was the author of numerous works on orthoepy and elocution. Additionally he was also the creator of Visible Speech which was used to help the deaf learn to talk, and was the father of Alexander Graham Bell. Biography Alexander Melville Bell was born in Edinburgh, Scotland, and studied under and became the principal assistant of his father, Alexander Bell (b. 3 March 1790, Fife, Scotland d. 23 April 1865, St. Pancras, North London),Ancestry.com Historical Person Overview: Alexander Melville Bell Retrieved May 2017 an authority on |
Peter Ladefoged
Peter Nielsen Ladefoged ( , ; 17 September 1925 – 24 January 2006) was a British linguist and phonetician. He was Professor of Phonetics at University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), where he taught from 1962 to 1991. His book ''A Course in Phonetics'' is a common introductory text in phonetics, and ''The Sounds of the World's Languages'' (co-authored with Ian Maddieson) is widely regarded as a standard phonetics reference. Ladefoged also wrote several books on the phonetics of African languages. Prior to UCLA, he was a lecturer at the universities of Edinburgh, Scotland (1953–59, 1960–1) and Ibadan, Nigeria (1959–60). Early life Peter Ladefoged was born on 17 September 1925, in Sutton (then in Surrey, now in Greater London), England. He attended Haileybury College from 1938 to 1943, and Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge, Cambridge University from 1943 to 1944. He received an MA (1951) and a PhD (1959) in Phonetics from the University of Edinburgh in 1959. Care ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
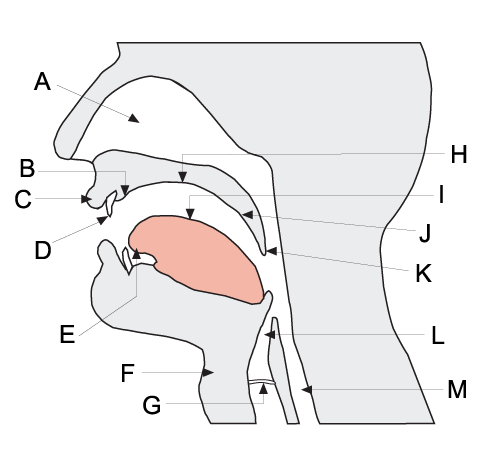
Articulatory Phonetics
The field of articulatory phonetics is a subfield of phonetics that studies articulation and ways that humans produce speech. Articulatory phoneticians explain how humans produce speech sounds via the interaction of different physiological structures. Generally, articulatory phonetics is concerned with the transformation of aerodynamic energy into acoustic energy. Aerodynamic energy refers to the airflow through the vocal tract. Its potential form is air pressure; its kinetic form is the actual dynamic airflow. Acoustic energy is variation in the air pressure that can be represented as sound waves, which are then perceived by the human auditory system as sound. Respiratory sounds can be produced by expelling air from the lungs. However, to vary the sound quality in a way useful for speaking, two speech organs normally move towards each other to contact each other to create an obstruction that shapes the air in a particular fashion. The point of maximum obstruction is called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Places Of Articulation
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation (also point of articulation) of a consonant is a location along the vocal tract where its production occurs. It is a point where a constriction is made between an active and a passive articulator. Active articulators are organs capable of voluntary movement which create the constriction, while passive articulators are so called because they are normally fixed and are the parts with which an active articulator makes contact. Along with the manner of articulation and phonation, the place of articulation gives the consonant its distinctive sound. Since vowels are produced with an open vocal tract, the point where their production occurs cannot be easily determined. Therefore, they are not described in terms of a place of articulation but by the relative positions in vowel space. This is mostly dependent on their formant frequencies and less on the specific tongue position and lip rounding. The terminology used in describing place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal Vowel
Cardinal vowels are a set of reference vowels used by phoneticians in describing the sounds of languages. They are classified depending on the position of the tongue relative to the roof of the mouth, how far forward or back is the highest point of the tongue, and the position of the lips (rounded or unrounded). A cardinal vowel is a vowel sound produced when the tongue is in an extreme position, either front or back, high or low. The current system was systematised by Daniel Jones in the early 20th century, though the idea goes back to earlier phoneticians, notably Ellis and Bell. Table of cardinal vowels Three of the cardinal vowels—, and —have articulatory definitions. The vowel is produced with the tongue as far forward and as high in the mouth as is possible (without producing friction), with spread lips. The vowel is produced with the tongue as far back and as high in the mouth as is possible, with protruded lips. This sound can be approximated by adopting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic transcription, phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standardized representation of speech sounds in written form.International Phonetic Association (IPA), ''Handbook''. The IPA is used by lexicography, lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, linguistics, linguists, speech–language pathology, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators. The IPA is designed to represent those qualities of speech that are part of wiktionary:lexical, lexical (and, to a limited extent, prosodic) sounds in oral language: phone (phonetics), phones, phonemes, Intonation (linguistics), intonation, and the separation of words and syllables. To represent additional qualities of speech—such as tooth wiktionary:gnash, gnashing, lisping, and sounds made wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oralism
Oralism is the education of deaf students through oral language by using lip reading, speech, and mimicking the mouth shapes and breathing patterns of speech.Through Deaf Eyes. Diane Garey, Lawrence R. Hott. DVD, PBS (Direct), 2007. Oralism came into popular use in the United States around the late 1860s. In 1867, the Clarke School for the Deaf in Northampton, Massachusetts, was the first school to start teaching in this manner. Oralism and its contrast, manualism, manifest differently in deaf education and are a source of controversy for involved communities. Oralism should not be confused with Listening and Spoken Language, a technique for teaching deaf children that emphasizes the child's perception of auditory signals from hearing aids or cochlear implants. History Early 18th century Since the beginning of formal deaf education in the 18th century in the United States, manualism and oralism have been on opposing sides of a heated debate that continues to this day.Winefield, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taittiriya Upanishad
The Taittirīya Upanishad (Devanagari: तैत्तिरीय उपनिषद्) is a Vedic era Sanskrit text, embedded as three chapters (''adhyāya'') of the Yajurveda. It is a ''mukhya'' (primary, principal) Upanishad, and likely composed about 6th century BC. The Taittirīya Upanishad is associated with the Taittirīya school of the Yajurveda, attributed to the pupils of sage Vaishampayana. It lists as number 7 in the Muktika canon of 108 Upanishads. The Taittirīya Upanishad is the seventh, eighth and ninth chapters of ''Taittirīya Āraṇyaka'', which are also called, respectively, the ''Śikṣāvallī'', the ''Ānandavallī'' and the ''Bhṛguvallī''. This Upanishad is classified as part of the "black" Yajurveda, with the term "black" implying "the un-arranged, motley collection" of verses in Yajurveda, in contrast to the "white" (well arranged) Yajurveda where ''Brihadaranyaka Upanishad'' and ''Isha Upanishad'' are embedded. Paul Deussen, Sixty Upanishads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiksha
''Shiksha'' ( sa, शिक्षा IAST: ISO: Śikṣā) is a Sanskrit word, which means "instruction, lesson, learning, study of skill".Sir Monier Monier-WilliamsSiksha A DkSanskrit-English Dictionary: Etymologically and Philologically Arranged with Special Reference to Cognate Indo-European Languages, Oxford University Press (Reprinted: Motilal Banarsidass), , page 1070 It also refers to one of the six Vedangas, or limbs of Vedic studies, on phonetics and phonology in Sanskrit. ''Shiksha'' is the field of Vedic study of sound, focussing on the letters of the Sanskrit alphabet, accent, quantity, stress, melody and rules of euphonic combination of words during a Vedic recitation. Each ancient Vedic school developed this field of ''Vedanga'', and the oldest surviving phonetic textbooks are the ''Pratishakyas''. The ''Paniniya-Shiksha'' and ''Naradiya-Shiksha'' are examples of extant ancient manuscripts of this field of Vedic studies. ''Shiksha'' is the oldest and the first a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pāṇini
, era = ;;6th–5th century BCE , region = Indian philosophy , main_interests = Grammar, linguistics , notable_works = ' (Sanskrit#Classical Sanskrit, Classical Sanskrit) , influenced= , notable_ideas=Descriptive linguistics (Devanagari: पाणिनि, ) was a Sanskrit Philology, philologist, grammarian, and revered scholar in ancient India, variously dated between the 6th and 4th century BCE. Since the discovery and publication of his work by European scholars in the nineteenth century, Pāṇini has been considered the "first Descriptive linguistics, descriptive linguist",#FPencyclo, François & Ponsonnet (2013: 184). and even labelled as “the father of linguistics”. Pāṇini's grammar was influential on such foundational linguists as Ferdinand de Saussure and Leonard Bloomfield. Legacy Pāṇini is known for his text ''Pāṇini#Aṣṭādhyāyī, Aṣṭādhyāyī'', a sutra-style treatise on Sanskrit grammar, 3,996 verses or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |